Wonbin Kweon
Improving Scientific Document Retrieval with Academic Concept Index
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Adapting general-domain retrievers to scientific domains is challenging due to the scarcity of large-scale domain-specific relevance annotations and the substantial mismatch in vocabulary and information needs. Recent approaches address these issues through two independent directions that leverage large language models (LLMs): (1) generating synthetic queries for fine-tuning, and (2) generating auxiliary contexts to support relevance matching. However, both directions overlook the diverse academic concepts embedded within scientific documents, often producing redundant or conceptually narrow queries and contexts. To address this limitation, we introduce an academic concept index, which extracts key concepts from papers and organizes them guided by an academic taxonomy. This structured index serves as a foundation for improving both directions. First, we enhance the synthetic query generation with concept coverage-based generation (CCQGen), which adaptively conditions LLMs on uncovered concepts to generate complementary queries with broader concept coverage. Second, we strengthen the context augmentation with concept-focused auxiliary contexts (CCExpand), which leverages a set of document snippets that serve as concise responses to the concept-aware CCQGen queries. Extensive experiments show that incorporating the academic concept index into both query generation and context augmentation leads to higher-quality queries, better conceptual alignment, and improved retrieval performance.
Personalized Federated Recommendation With Knowledge Guidance
Nov 18, 2025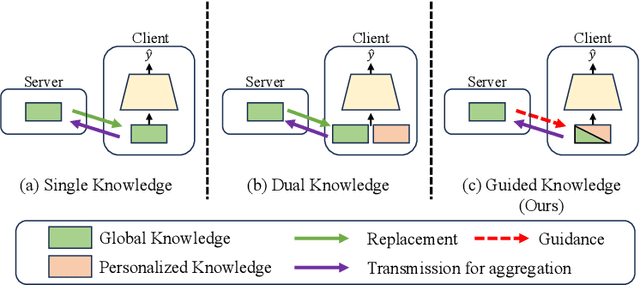
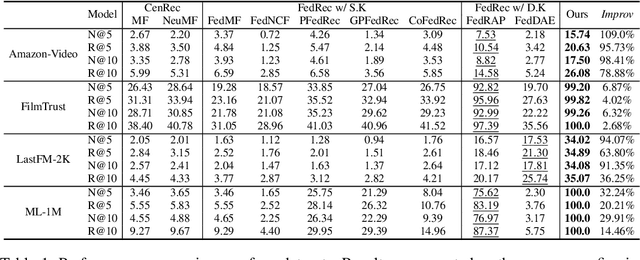
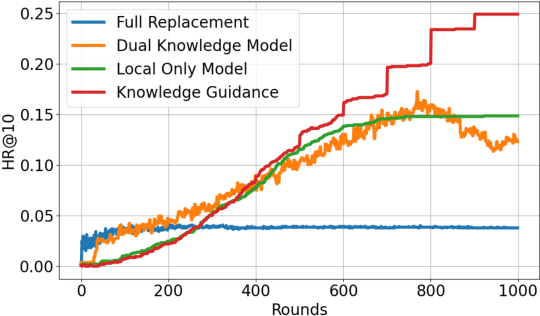
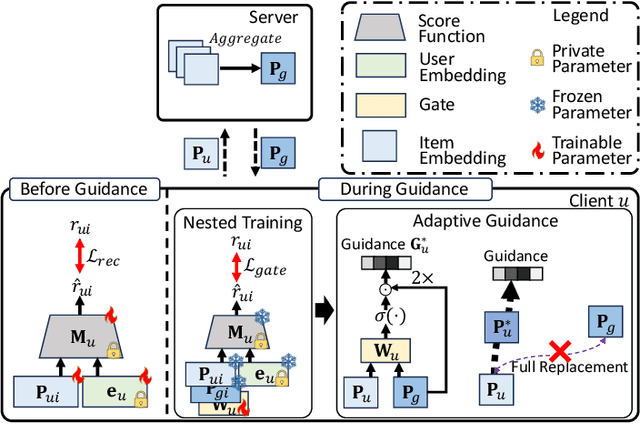
Abstract:Federated Recommendation (FedRec) has emerged as a key paradigm for building privacy-preserving recommender systems. However, existing FedRec models face a critical dilemma: memory-efficient single-knowledge models suffer from a suboptimal knowledge replacement practice that discards valuable personalization, while high-performance dual-knowledge models are often too memory-intensive for practical on-device deployment. We propose Federated Recommendation with Knowledge Guidance (FedRKG), a model-agnostic framework that resolves this dilemma. The core principle, Knowledge Guidance, avoids full replacement and instead fuses global knowledge into preserved local embeddings, attaining the personalization benefits of dual-knowledge within a single-knowledge memory footprint. Furthermore, we introduce Adaptive Guidance, a fine-grained mechanism that dynamically modulates the intensity of this guidance for each user-item interaction, overcoming the limitations of static fusion methods. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that FedRKG significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, validating the effectiveness of our approach. The code is available at https://github.com/Jaehyung-Lim/fedrkg.
Topic Coverage-based Demonstration Retrieval for In-Context Learning
Sep 15, 2025Abstract:The effectiveness of in-context learning relies heavily on selecting demonstrations that provide all the necessary information for a given test input. To achieve this, it is crucial to identify and cover fine-grained knowledge requirements. However, prior methods often retrieve demonstrations based solely on embedding similarity or generation probability, resulting in irrelevant or redundant examples. In this paper, we propose TopicK, a topic coverage-based retrieval framework that selects demonstrations to comprehensively cover topic-level knowledge relevant to both the test input and the model. Specifically, TopicK estimates the topics required by the input and assesses the model's knowledge on those topics. TopicK then iteratively selects demonstrations that introduce previously uncovered required topics, in which the model exhibits low topical knowledge. We validate the effectiveness of TopicK through extensive experiments across various datasets and both open- and closed-source LLMs. Our source code is available at https://github.com/WonbinKweon/TopicK_EMNLP2025.
Federated Continual Recommendation
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:The increasing emphasis on privacy in recommendation systems has led to the adoption of Federated Learning (FL) as a privacy-preserving solution, enabling collaborative training without sharing user data. While Federated Recommendation (FedRec) effectively protects privacy, existing methods struggle with non-stationary data streams, failing to maintain consistent recommendation quality over time. On the other hand, Continual Learning Recommendation (CLRec) methods address evolving user preferences but typically assume centralized data access, making them incompatible with FL constraints. To bridge this gap, we introduce Federated Continual Recommendation (FCRec), a novel task that integrates FedRec and CLRec, requiring models to learn from streaming data while preserving privacy. As a solution, we propose F3CRec, a framework designed to balance knowledge retention and adaptation under the strict constraints of FCRec. F3CRec introduces two key components: Adaptive Replay Memory on the client side, which selectively retains past preferences based on user-specific shifts, and Item-wise Temporal Mean on the server side, which integrates new knowledge while preserving prior information. Extensive experiments demonstrate that F3CRec outperforms existing approaches in maintaining recommendation quality over time in a federated environment.
Uncertainty Quantification and Decomposition for LLM-based Recommendation
Jan 29, 2025Abstract:Despite the widespread adoption of large language models (LLMs) for recommendation, we demonstrate that LLMs often exhibit uncertainty in their recommendations. To ensure the trustworthy use of LLMs in generating recommendations, we emphasize the importance of assessing the reliability of recommendations generated by LLMs. We start by introducing a novel framework for estimating the predictive uncertainty to quantitatively measure the reliability of LLM-based recommendations. We further propose to decompose the predictive uncertainty into recommendation uncertainty and prompt uncertainty, enabling in-depth analyses of the primary source of uncertainty. Through extensive experiments, we (1) demonstrate predictive uncertainty effectively indicates the reliability of LLM-based recommendations, (2) investigate the origins of uncertainty with decomposed uncertainty measures, and (3) propose uncertainty-aware prompting for a lower predictive uncertainty and enhanced recommendation. Our source code and model weights are available at https://github.com/WonbinKweon/UNC_LLM_REC_WWW2025
Verbosity-Aware Rationale Reduction: Effective Reduction of Redundant Rationale via Principled Criteria
Dec 30, 2024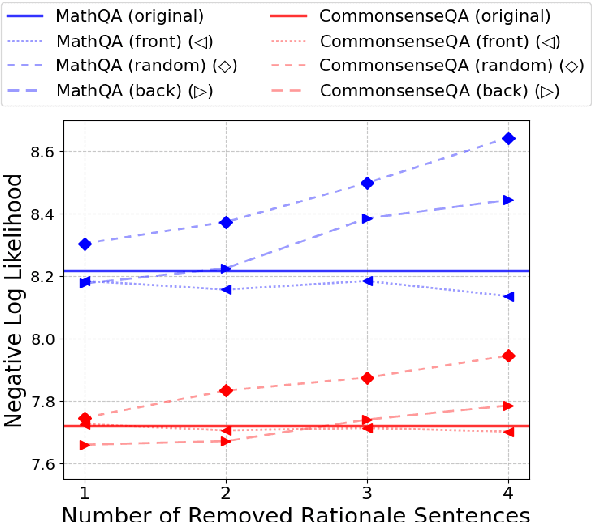
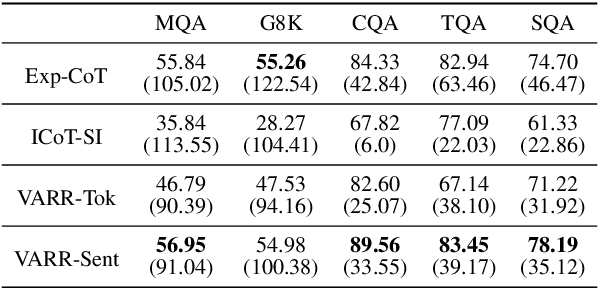
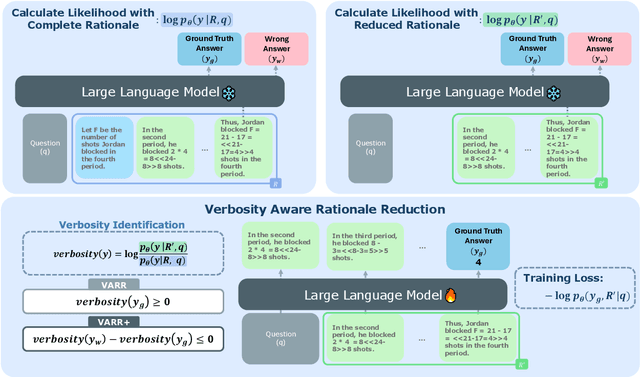
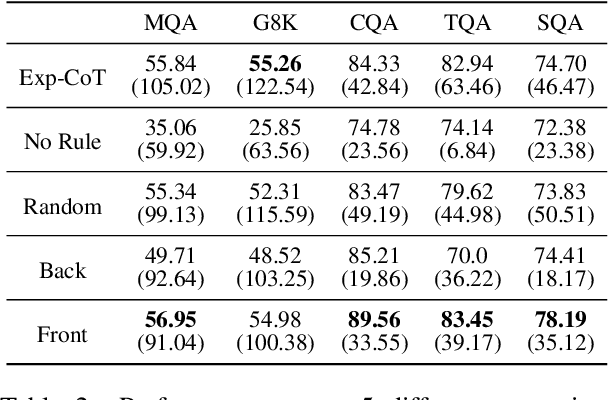
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) rely on generating extensive intermediate reasoning units (e.g., tokens, sentences) to enhance final answer quality across a wide range of complex tasks. While generating multiple reasoning paths or iteratively refining rationales proves effective for improving performance, these approaches inevitably result in significantly higher inference costs. In this work, we propose a novel sentence-level rationale reduction training framework that leverages likelihood-based criteria, verbosity, to identify and remove redundant reasoning sentences. Unlike previous approaches that utilize token-level reduction, our sentence-level reduction framework maintains model performance while reducing generation length. This preserves the original reasoning abilities of LLMs and achieves an average 17.15% reduction in generation costs across various models and tasks.
Controlling Diversity at Inference: Guiding Diffusion Recommender Models with Targeted Category Preferences
Nov 21, 2024Abstract:Diversity control is an important task to alleviate bias amplification and filter bubble problems. The desired degree of diversity may fluctuate based on users' daily moods or business strategies. However, existing methods for controlling diversity often lack flexibility, as diversity is decided during training and cannot be easily modified during inference. We propose \textbf{D3Rec} (\underline{D}isentangled \underline{D}iffusion model for \underline{D}iversified \underline{Rec}ommendation), an end-to-end method that controls the accuracy-diversity trade-off at inference. D3Rec meets our three desiderata by (1) generating recommendations based on category preferences, (2) controlling category preferences during the inference phase, and (3) adapting to arbitrary targeted category preferences. In the forward process, D3Rec removes category preferences lurking in user interactions by adding noises. Then, in the reverse process, D3Rec generates recommendations through denoising steps while reflecting desired category preferences. Extensive experiments on real-world and synthetic datasets validate the effectiveness of D3Rec in controlling diversity at inference.
Continual Collaborative Distillation for Recommender System
May 29, 2024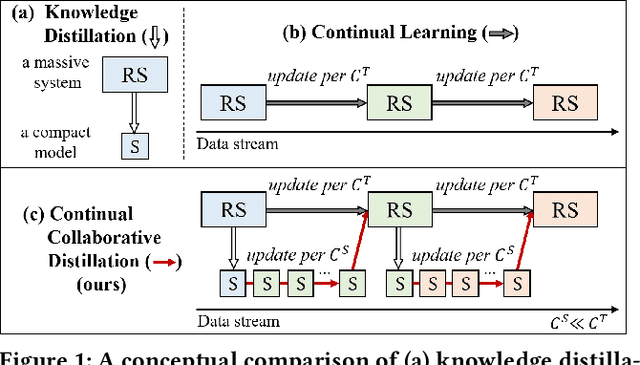
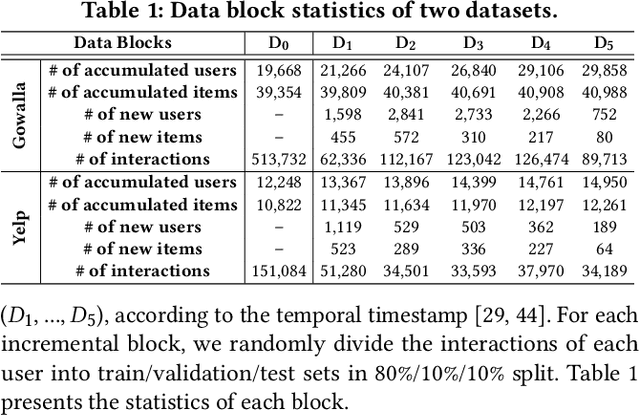
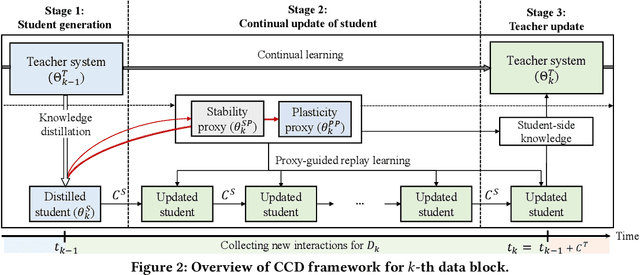
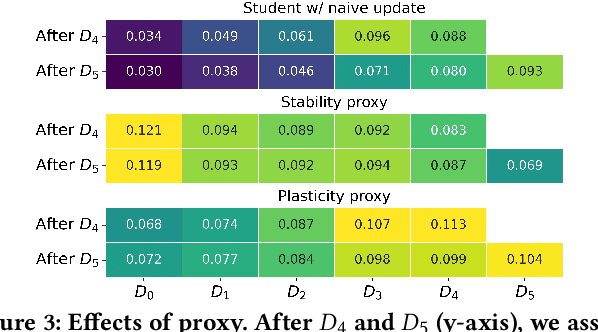
Abstract:Knowledge distillation (KD) has emerged as a promising technique for addressing the computational challenges associated with deploying large-scale recommender systems. KD transfers the knowledge of a massive teacher system to a compact student model, to reduce the huge computational burdens for inference while retaining high accuracy. The existing KD studies primarily focus on one-time distillation in static environments, leaving a substantial gap in their applicability to real-world scenarios dealing with continuously incoming users, items, and their interactions. In this work, we delve into a systematic approach to operating the teacher-student KD in a non-stationary data stream. Our goal is to enable efficient deployment through a compact student, which preserves the high performance of the massive teacher, while effectively adapting to continuously incoming data. We propose Continual Collaborative Distillation (CCD) framework, where both the teacher and the student continually and collaboratively evolve along the data stream. CCD facilitates the student in effectively adapting to new data, while also enabling the teacher to fully leverage accumulated knowledge. We validate the effectiveness of CCD through extensive quantitative, ablative, and exploratory experiments on two real-world datasets. We expect this research direction to contribute to narrowing the gap between existing KD studies and practical applications, thereby enhancing the applicability of KD in real-world systems.
Rectifying Demonstration Shortcut in In-Context Learning
Mar 29, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are able to solve various tasks with only a few demonstrations utilizing their in-context learning (ICL) abilities. However, LLMs often rely on their pre-trained semantic priors of demonstrations rather than on the input-label relationships to proceed with ICL prediction. In this work, we term this phenomenon as the 'Demonstration Shortcut'. While previous works have primarily focused on improving ICL prediction results for predefined tasks, we aim to rectify the Demonstration Shortcut, thereby enabling the LLM to effectively learn new input-label relationships from demonstrations. To achieve this, we introduce In-Context Calibration, a demonstration-aware calibration method. We evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method in two settings: (1) the Original ICL Task using the standard label space and (2) the Task Learning setting, where the label space is replaced with semantically unrelated tokens. In both settings, In-Context Calibration demonstrates substantial improvements, with results generalized across three LLM families (OPT, GPT, and Llama2) under various configurations.
Confidence Calibration for Recommender Systems and Its Applications
Feb 26, 2024Abstract:Despite the importance of having a measure of confidence in recommendation results, it has been surprisingly overlooked in the literature compared to the accuracy of the recommendation. In this dissertation, I propose a model calibration framework for recommender systems for estimating accurate confidence in recommendation results based on the learned ranking scores. Moreover, I subsequently introduce two real-world applications of confidence on recommendations: (1) Training a small student model by treating the confidence of a big teacher model as additional learning guidance, (2) Adjusting the number of presented items based on the expected user utility estimated with calibrated probability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge