A Gradient Accumulation Method for Dense Retriever under Memory Constraint
Paper and Code
Jun 18, 2024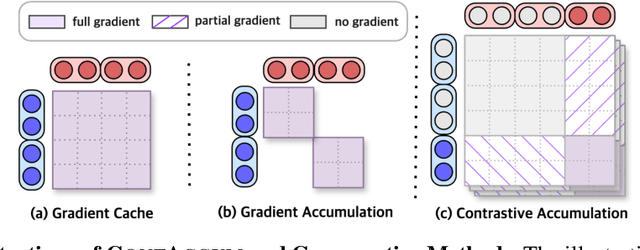
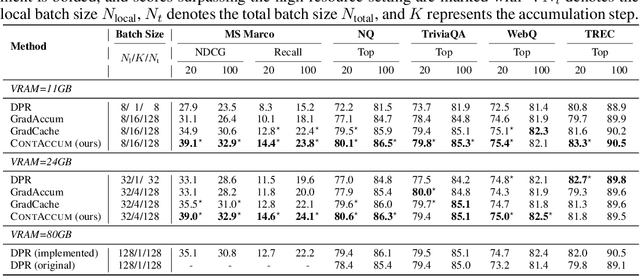
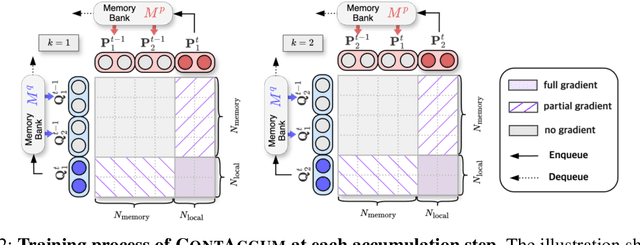
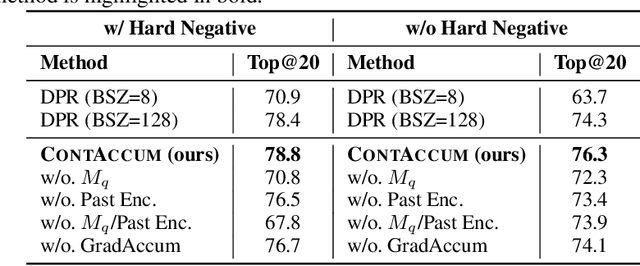
InfoNCE loss is commonly used to train dense retriever in information retrieval tasks. It is well known that a large batch is essential to stable and effective training with InfoNCE loss, which requires significant hardware resources. Due to the dependency of large batch, dense retriever has bottleneck of application and research. Recently, memory reduction methods have been broadly adopted to resolve the hardware bottleneck by decomposing forward and backward or using a memory bank. However, current methods still suffer from slow and unstable training. To address these issues, we propose \longmodelname\ (\modelname), a stable and efficient memory reduction method for dense retriever trains that uses a dual memory bank structure to leverage previously generated query and passage representations. Experiments on widely used five information retrieval datasets indicate that \modelname\ can surpass not only existing memory reduction methods but also high-resource scenario. Moreover, theoretical analysis and experimental results confirm that \modelname\ provides more stable dual-encoder training than current memory bank utilization methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge