Jianqi Gao
GLOW: Graph-Language Co-Reasoning for Agentic Workflow Performance Prediction
Dec 11, 2025



Abstract:Agentic Workflows (AWs) have emerged as a promising paradigm for solving complex tasks. However, the scalability of automating their generation is severely constrained by the high cost and latency of execution-based evaluation. Existing AW performance prediction methods act as surrogates but fail to simultaneously capture the intricate topological dependencies and the deep semantic logic embedded in AWs. To address this limitation, we propose GLOW, a unified framework for AW performance prediction that combines the graph-structure modeling capabilities of GNNs with the reasoning power of LLMs. Specifically, we introduce a graph-oriented LLM, instruction-tuned on graph tasks, to extract topologically aware semantic features, which are fused with GNN-encoded structural representations. A contrastive alignment strategy further refines the latent space to distinguish high-quality AWs. Extensive experiments on FLORA-Bench show that GLOW outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in prediction accuracy and ranking utility.
Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning for Safe Mapless Navigation with Congestion Estimation
Mar 15, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning-based mapless navigation holds significant potential. However, it faces challenges in indoor environments with local minima area. This paper introduces a safe mapless navigation framework utilizing hierarchical reinforcement learning (HRL) to enhance navigation through such areas. The high-level policy creates a sub-goal to direct the navigation process. Notably, we have developed a sub-goal update mechanism that considers environment congestion, efficiently avoiding the entrapment of the robot in local minimum areas. The low-level motion planning policy, trained through safe reinforcement learning, outputs real-time control instructions based on acquired sub-goal. Specifically, to enhance the robot's environmental perception, we introduce a new obstacle encoding method that evaluates the impact of obstacles on the robot's motion planning. To validate the performance of our HRL-based navigation framework, we conduct simulations in office, home, and restaurant environments. The findings demonstrate that our HRL-based navigation framework excels in both static and dynamic scenarios. Finally, we implement the HRL-based navigation framework on a TurtleBot3 robot for physical validation experiments, which exhibits its strong generalization capabilities.
LogLLM: Log-based Anomaly Detection Using Large Language Models
Nov 13, 2024



Abstract:Software systems often record important runtime information in logs to help with troubleshooting. Log-based anomaly detection has become a key research area that aims to identify system issues through log data, ultimately enhancing the reliability of software systems. Traditional deep learning methods often struggle to capture the semantic information embedded in log data, which is typically organized in natural language. In this paper, we propose LogLLM, a log-based anomaly detection framework that leverages large language models (LLMs). LogLLM employs BERT for extracting semantic vectors from log messages, while utilizing Llama, a transformer decoder-based model, for classifying log sequences. Additionally, we introduce a projector to align the vector representation spaces of BERT and Llama, ensuring a cohesive understanding of log semantics. Unlike conventional methods that require log parsers to extract templates, LogLLM preprocesses log messages with regular expressions, streamlining the entire process. Our framework is trained through a novel three-stage procedure designed to enhance performance and adaptability. Experimental results across four public datasets demonstrate that LogLLM outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Even when handling unstable logs, it effectively captures the semantic meaning of log messages and detects anomalies accurately.
Multi-Agent Target Assignment and Path Finding for Intelligent Warehouse: A Cooperative Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning Perspective
Aug 25, 2024



Abstract:Multi-agent target assignment and path planning (TAPF) are two key problems in intelligent warehouse. However, most literature only addresses one of these two problems separately. In this study, we propose a method to simultaneously solve target assignment and path planning from a perspective of cooperative multi-agent deep reinforcement learning (RL). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to model the TAPF problem for intelligent warehouse to cooperative multi-agent deep RL, and the first to simultaneously address TAPF based on multi-agent deep RL. Furthermore, previous literature rarely considers the physical dynamics of agents. In this study, the physical dynamics of the agents is considered. Experimental results show that our method performs well in various task settings, which means that the target assignment is solved reasonably well and the planned path is almost shortest. Moreover, our method is more time-efficient than baselines.
DABL: Detecting Semantic Anomalies in Business Processes Using Large Language Models
Jun 22, 2024Abstract:Detecting anomalies in business processes is crucial for ensuring operational success. While many existing methods rely on statistical frequency to detect anomalies, it's important to note that infrequent behavior doesn't necessarily imply undesirability. To address this challenge, detecting anomalies from a semantic viewpoint proves to be a more effective approach. However, current semantic anomaly detection methods treat a trace (i.e., process instance) as multiple event pairs, disrupting long-distance dependencies. In this paper, we introduce DABL, a novel approach for detecting semantic anomalies in business processes using large language models (LLMs). We collect 143,137 real-world process models from various domains. By generating normal traces through the playout of these process models and simulating both ordering and exclusion anomalies, we fine-tune Llama 2 using the resulting log. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that DABL surpasses existing state-of-the-art semantic anomaly detection methods in terms of both generalization ability and learning of given processes. Users can directly apply DABL to detect semantic anomalies in their own datasets without the need for additional training. Furthermore, DABL offers the capability to interpret the causes of anomalies in natural language, providing valuable insights into the detected anomalies.
RDE: A Hybrid Policy Framework for Multi-Agent Path Finding Problem
Nov 03, 2023


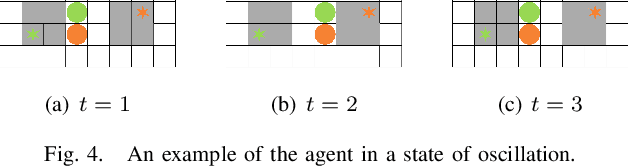
Abstract:Multi-agent path finding (MAPF) is an abstract model for the navigation of multiple robots in warehouse automation, where multiple robots plan collision-free paths from the start to goal positions. Reinforcement learning (RL) has been employed to develop partially observable distributed MAPF policies that can be scaled to any number of agents. However, RL-based MAPF policies often get agents stuck in deadlock due to warehouse automation's dense and structured obstacles. This paper proposes a novel hybrid MAPF policy, RDE, based on switching among the RL-based MAPF policy, the Distance heat map (DHM)-based policy and the Escape policy. The RL-based policy is used for coordination among agents. In contrast, when no other agents are in the agent's field of view, it can get the next action by querying the DHM. The escape policy that randomly selects valid actions can help agents escape the deadlock. We conduct simulations on warehouse-like structured grid maps using state-of-the-art RL-based MAPF policies (DHC and DCC), which show that RDE can significantly improve their performance.
Back to Prior Knowledge: Joint Event Causality Extraction via Convolutional Semantic Infusion
Feb 19, 2021



Abstract:Joint event and causality extraction is a challenging yet essential task in information retrieval and data mining. Recently, pre-trained language models (e.g., BERT) yield state-of-the-art results and dominate in a variety of NLP tasks. However, these models are incapable of imposing external knowledge in domain-specific extraction. Considering the prior knowledge of frequent n-grams that represent cause/effect events may benefit both event and causality extraction, in this paper, we propose convolutional knowledge infusion for frequent n-grams with different windows of length within a joint extraction framework. Knowledge infusion during convolutional filter initialization not only helps the model capture both intra-event (i.e., features in an event cluster) and inter-event (i.e., associations across event clusters) features but also boosts training convergence. Experimental results on the benchmark datasets show that our model significantly outperforms the strong BERT+CSNN baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge