Jianguang Lou
AgentGen: Enhancing Planning Abilities for Large Language Model based Agent via Environment and Task Generation
Aug 01, 2024Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM) based agents have garnered significant attention and are becoming increasingly popular. Furthermore, planning ability is a crucial component of an LLM-based agent, involving interaction with the environment and executing actions to complete a planning task, which generally entails achieving a desired goal from an initial state. This paper investigates enhancing the planning abilities of LLMs through instruction tuning, referred to as agent training. Recent studies have demonstrated that utilizing expert-level trajectory for instruction-tuning LLMs effectively enhances their planning capabilities. However, existing work primarily focuses on synthesizing trajectories from manually designed planning tasks and environments. The labor-intensive nature of creating these environments and tasks impedes the generation of sufficiently varied and extensive trajectories. To address this limitation, this paper explores the automated synthesis of diverse environments and a gradual range of planning tasks, from easy to difficult. We introduce a framework, AgentGen, that leverages LLMs first to generate environments and subsequently generate planning tasks conditioned on these environments. Specifically, to improve environmental diversity, we propose using an inspiration corpus composed of various domain-specific text segments as the context for synthesizing environments. Moreover, to increase the difficulty diversity of generated planning tasks, we propose a bidirectional evolution method, Bi-Evol, that evolves planning tasks from easier and harder directions to synthesize a task set with a smoother difficulty curve. The evaluation results derived from AgentBoard show that AgentGen greatly improves LLMs' planning ability, e.g., the AgentGen instruction-tuned Llama-3 8B surpasses GPT-3.5 in overall performance. Moreover, in certain tasks, it even outperforms GPT-4.
Arena Learning: Build Data Flywheel for LLMs Post-training via Simulated Chatbot Arena
Jul 15, 2024



Abstract:Assessing the effectiveness of large language models (LLMs) presents substantial challenges. The method of conducting human-annotated battles in an online Chatbot Arena is a highly effective evaluative technique. However, this approach is limited by the costs and time required for human annotation. In this paper, we introduce Arena Learning, an innovative offline strategy designed to simulate these arena battles using AI-driven annotations to evaluate battle outcomes, thus facilitating the continuous improvement of the target model through both supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning. Arena Learning comprises two key elements. First, it ensures precise evaluations and maintains consistency between offline simulations and online competitions via WizardArena, a pipeline developed to accurately predict the Elo rankings of various models using a meticulously designed offline test set. Our results demonstrate that WizardArena's predictions closely align with those from the online Arena. Second, it involves the continuous improvement of training data based on the battle results and the refined model. We establish a data flywheel to iteratively update the training data by highlighting the weaknesses of the target model based on its battle results, enabling it to learn from the strengths of multiple different models. We apply Arena Learning to train our target model, WizardLM-$\beta$, and demonstrate significant performance enhancements across various metrics. This fully automated training and evaluation pipeline sets the stage for continuous advancements in various LLMs via post-training. Notably, Arena Learning plays a pivotal role in the success of WizardLM-2, and this paper serves both as an exploration of its efficacy and a foundational study for future discussions related to WizardLM-2 and its derivatives.
WizardMath: Empowering Mathematical Reasoning for Large Language Models via Reinforced Evol-Instruct
Aug 18, 2023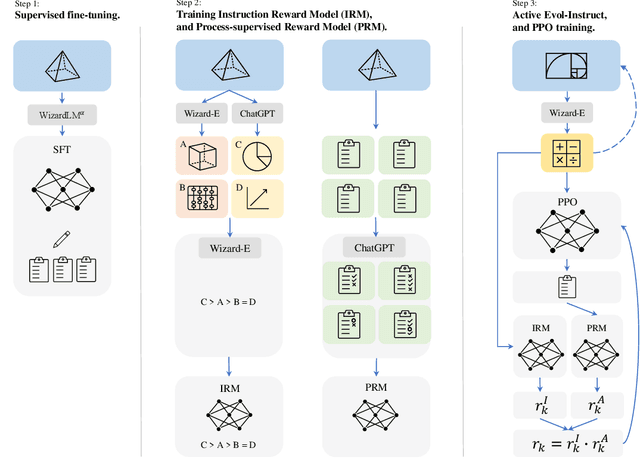
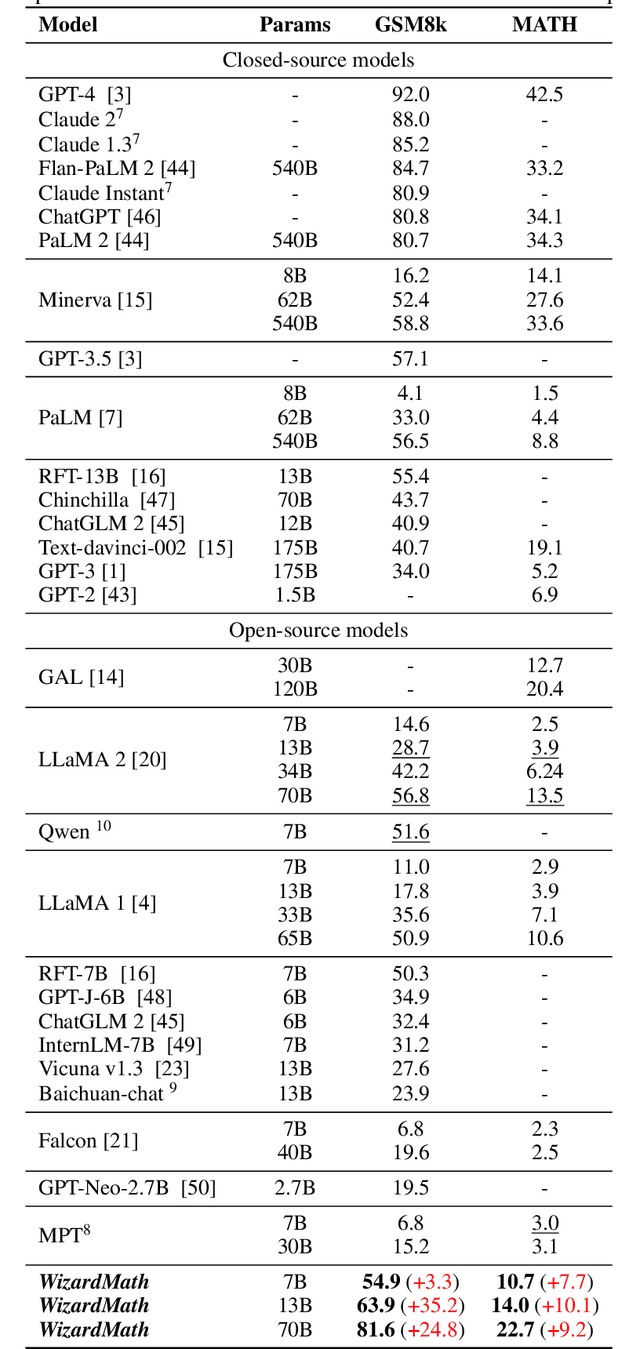
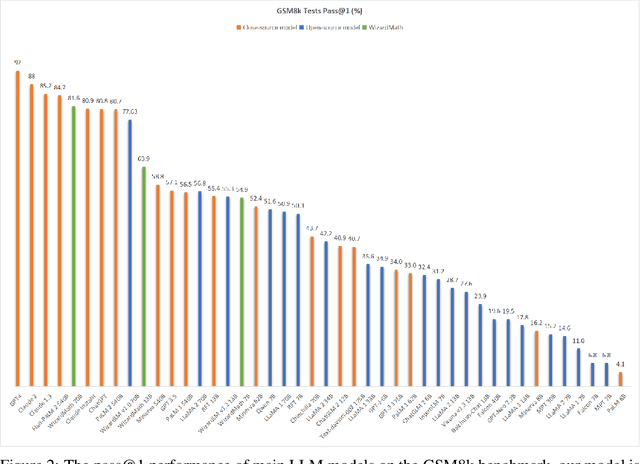

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), such as GPT-4, have shown remarkable performance in natural language processing (NLP) tasks, including challenging mathematical reasoning. However, most existing open-source models are only pre-trained on large-scale internet data and without math-related optimization. In this paper, we present WizardMath, which enhances the mathematical reasoning abilities of Llama-2, by applying our proposed Reinforcement Learning from Evol-Instruct Feedback (RLEIF) method to the domain of math. Through extensive experiments on two mathematical reasoning benchmarks, namely GSM8k and MATH, we reveal the extraordinary capabilities of our model. WizardMath surpasses all other open-source LLMs by a substantial margin. Furthermore, our model even outperforms ChatGPT-3.5, Claude Instant-1, PaLM-2 and Minerva on GSM8k, simultaneously surpasses Text-davinci-002, PaLM-1 and GPT-3 on MATH. More details and model weights are public at https://github.com/nlpxucan/WizardLM and https://huggingface.co/WizardLM.
GRN: Gated Relation Network to Enhance Convolutional Neural Network for Named Entity Recognition
Jul 19, 2019



Abstract:The dominant approaches for named entity recognition (NER) mostly adopt complex recurrent neural networks (RNN), e.g., long-short-term-memory (LSTM). However, RNNs are limited by their recurrent nature in terms of computational efficiency. In contrast, convolutional neural networks (CNN) can fully exploit the GPU parallelism with their feedforward architectures. However, little attention has been paid to performing NER with CNNs, mainly owing to their difficulties in capturing the long-term context information in a sequence. In this paper, we propose a simple but effective CNN-based network for NER, i.e., gated relation network (GRN), which is more capable than common CNNs in capturing long-term context. Specifically, in GRN we firstly employ CNNs to explore the local context features of each word. Then we model the relations between words and use them as gates to fuse local context features into global ones for predicting labels. Without using recurrent layers that process a sentence in a sequential manner, our GRN allows computations to be performed in parallel across the entire sentence. Experiments on two benchmark NER datasets (i.e., CoNLL2003 and Ontonotes 5.0) show that, our proposed GRN can achieve state-of-the-art performance with or without external knowledge. It also enjoys lower time costs to train and test.We have made the code publicly available at https://github.com/HuiChen24/NER-GRN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge