JiaWang Bian
Salient Object Detection via High-to-Low Hierarchical Context Aggregation
Dec 28, 2018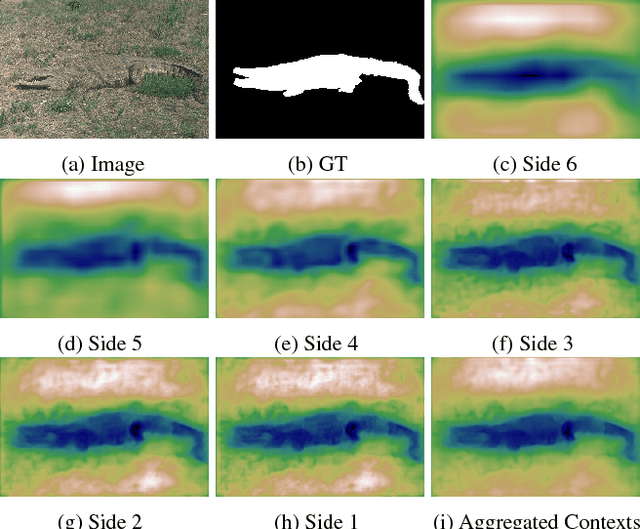
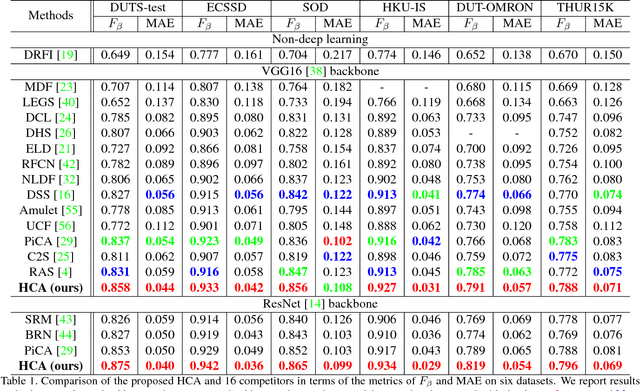


Abstract:Recent progress on salient object detection mainly aims at exploiting how to effectively integrate convolutional side-output features in convolutional neural networks (CNN). Based on this, most of the existing state-of-the-art saliency detectors design complex network structures to fuse the side-output features of the backbone feature extraction networks. However, should the fusion strategies be more and more complex for accurate salient object detection? In this paper, we observe that the contexts of a natural image can be well expressed by a high-to-low self-learning of side-output convolutional features. As we know, the contexts of an image usually refer to the global structures, and the top layers of CNN usually learn to convey global information. On the other hand, it is difficult for the intermediate side-output features to express contextual information. Here, we design an hourglass network with intermediate supervision to learn contextual features in a high-to-low manner. The learned hierarchical contexts are aggregated to generate the hybrid contextual expression for an input image. At last, the hybrid contextual features can be used for accurate saliency estimation. We extensively evaluate our method on six challenging saliency datasets, and our simple method achieves state-of-the-art performance under various evaluation metrics. Code will be released upon paper acceptance.
MatchBench: An Evaluation of Feature Matchers
Aug 07, 2018



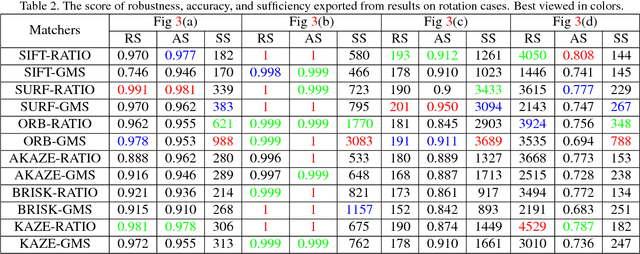
Abstract:Feature matching is one of the most fundamental and active research areas in computer vision. A comprehensive evaluation of feature matchers is necessary, since it would advance both the development of this field and also high-level applications such as Structure-from-Motion or Visual SLAM. However, to the best of our knowledge, no previous work targets the evaluation of feature matchers while they only focus on evaluating feature detectors and descriptors. This leads to a critical absence in this field that there is no standard datasets and evaluation metrics to evaluate different feature matchers fairly. To this end, we present the first uniform feature matching benchmark to facilitate the evaluation of feature matchers. In the proposed benchmark, matchers are evaluated in different aspects, involving matching ability, correspondence sufficiency, and efficiency. Also, their performances are investigated in different scenes and in different matching types. Subsequently, we carry out an extensive evaluation of different state-of-the-art matchers on the benchmark and make in-depth analyses based on the reported results. This can be used to design practical matching systems in real applications and also advocates the potential future research directions in the field of feature matching.
Image Matching: An Application-oriented Benchmark
Aug 07, 2018
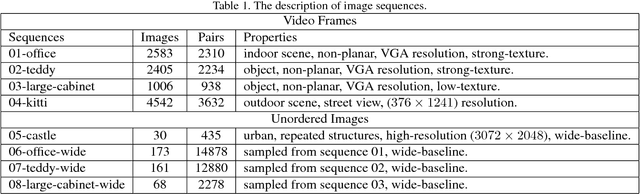
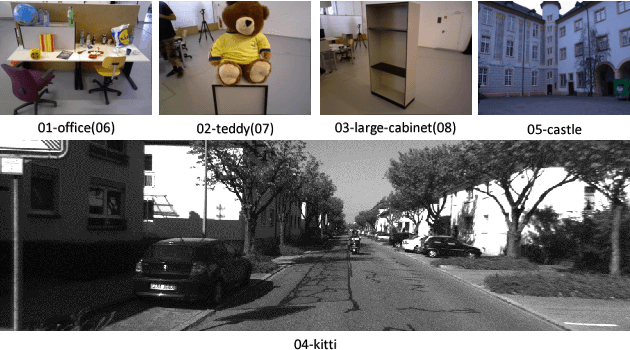
Abstract:Image matching approaches have been widely used in computer vision applications in which the image-level matching performance of matchers is critical. However, it has not been well investigated by previous works which place more emphases on evaluating local features. To this end, we present a uniform benchmark with novel evaluation metrics and a large-scale dataset for evaluating the overall performance of image matching methods. The proposed metrics are application-oriented as they emphasize application requirements for matchers. The dataset contains two portions for benchmarking video frame matching and unordered image matching separately, where each portion consists of real-world image sequences and each sequence has a specific attribute. Subsequently, we carry out a comprehensive performance evaluation of different state-of-the-art methods and conduct in-depth analyses regarding various aspects such as application requirements, matching types, and data diversity. Moreover, we shed light on how to choose appropriate approaches for different applications based on empirical results and analyses. Conclusions in this benchmark can be used as general guidelines to design practical matching systems and also advocate potential future research directions in this field.
Learning Pixel-wise Labeling from the Internet without Human Interaction
May 19, 2018



Abstract:Deep learning stands at the forefront in many computer vision tasks. However, deep neural networks are usually data-hungry and require a huge amount of well-annotated training samples. Collecting sufficient annotated data is very expensive in many applications, especially for pixel-level prediction tasks such as semantic segmentation. To solve this fundamental issue, we consider a new challenging vision task, Internetly supervised semantic segmentation, which only uses Internet data with noisy image-level supervision of corresponding query keywords for segmentation model training. We address this task by proposing the following solution. A class-specific attention model unifying multiscale forward and backward convolutional features is proposed to provide initial segmentation "ground truth". The model trained with such noisy annotations is then improved by an online fine-tuning procedure. It achieves state-of-the-art performance under the weakly-supervised setting on PASCAL VOC2012 dataset. The proposed framework also paves a new way towards learning from the Internet without human interaction and could serve as a strong baseline therein. Code and data will be released upon the paper acceptance.
Semantic Edge Detection with Diverse Deep Supervision
Apr 09, 2018



Abstract:Semantic edge detection (SED), which aims at jointly extracting edges as well as their category information, has far-reaching applications in domains such as semantic segmentation, object proposal generation, and object recognition. SED naturally requires achieving two distinct supervision targets: locating fine detailed edges and identifying high-level semantics. We shed light on how such distracted supervision targets prevent state-of-the-art SED methods from effectively using deep supervision to improve results. In this paper, we propose a novel fully convolutional neural network architecture using diverse deep supervision (DDS) within a multi-task framework where lower layers aim at generating category-agnostic edges, while higher layers are responsible for the detection of category-aware semantic edges. To overcome the distracted supervision challenge, a novel information converter unit is introduced, whose effectiveness has been extensively evaluated in several popular benchmark datasets, including SBD, Cityscapes, and PASCAL VOC2012. Source code will be released upon paper acceptance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge