Jeric Lew
FARE: Fast-Slow Agentic Robotic Exploration
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:This work advances autonomous robot exploration by integrating agent-level semantic reasoning with fast local control. We introduce FARE, a hierarchical autonomous exploration framework that integrates a large language model (LLM) for global reasoning with a reinforcement learning (RL) policy for local decision making. FARE follows a fast-slow thinking paradigm. The slow-thinking LLM module interprets a concise textual description of the unknown environment and synthesizes an agent-level exploration strategy, which is then grounded into a sequence of global waypoints through a topological graph. To further improve reasoning efficiency, this module employs a modularity-based pruning mechanism that reduces redundant graph structures. The fast-thinking RL module executes exploration by reacting to local observations while being guided by the LLM-generated global waypoints. The RL policy is additionally shaped by a reward term that encourages adherence to the global waypoints, enabling coherent and robust closed-loop behavior. This architecture decouples semantic reasoning from geometric decision, allowing each module to operate in its appropriate temporal and spatial scale. In challenging simulated environments, our results show that FARE achieves substantial improvements in exploration efficiency over state-of-the-art baselines. We further deploy FARE on hardware and validate it in complex, large scale $200m\times130m$ building environment.
HELM: Human-Preferred Exploration with Language Models
Mar 10, 2025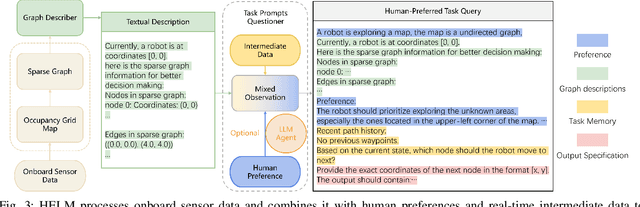
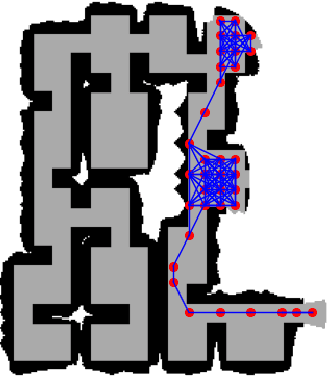
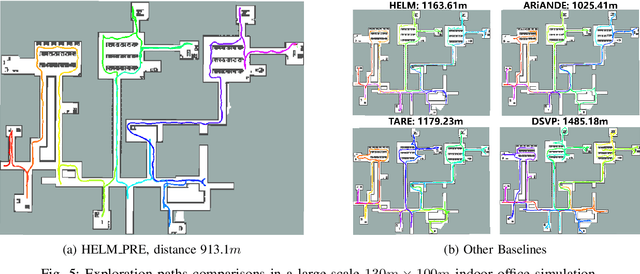
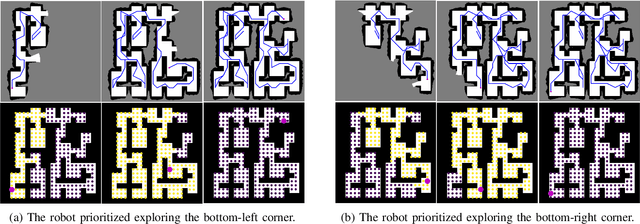
Abstract:In autonomous exploration tasks, robots are required to explore and map unknown environments while efficiently planning in dynamic and uncertain conditions. Given the significant variability of environments, human operators often have specific preference requirements for exploration, such as prioritizing certain areas or optimizing for different aspects of efficiency. However, existing methods struggle to accommodate these human preferences adaptively, often requiring extensive parameter tuning or network retraining. With the recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), which have been widely applied to text-based planning and complex reasoning, their potential for enhancing autonomous exploration is becoming increasingly promising. Motivated by this, we propose an LLM-based human-preferred exploration framework that seamlessly integrates a mobile robot system with LLMs. By leveraging the reasoning and adaptability of LLMs, our approach enables intuitive and flexible preference control through natural language while maintaining a task success rate comparable to state-of-the-art traditional methods. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework effectively bridges the gap between human intent and policy preference in autonomous exploration, offering a more user-friendly and adaptable solution for real-world robotic applications.
SALON: Self-supervised Adaptive Learning for Off-road Navigation
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous robot navigation in off-road environments presents a number of challenges due to its lack of structure, making it difficult to handcraft robust heuristics for diverse scenarios. While learned methods using hand labels or self-supervised data improve generalizability, they often require a tremendous amount of data and can be vulnerable to domain shifts. To improve generalization in novel environments, recent works have incorporated adaptation and self-supervision to develop autonomous systems that can learn from their own experiences online. However, current works often rely on significant prior data, for example minutes of human teleoperation data for each terrain type, which is difficult to scale with more environments and robots. To address these limitations, we propose SALON, a perception-action framework for fast adaptation of traversability estimates with minimal human input. SALON rapidly learns online from experience while avoiding out of distribution terrains to produce adaptive and risk-aware cost and speed maps. Within seconds of collected experience, our results demonstrate comparable navigation performance over kilometer-scale courses in diverse off-road terrain as methods trained on 100-1000x more data. We additionally show promising results on significantly different robots in different environments. Our code is available at https://theairlab.org/SALON.
DARE: Diffusion Policy for Autonomous Robot Exploration
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous robot exploration requires a robot to efficiently explore and map unknown environments. Compared to conventional methods that can only optimize paths based on the current robot belief, learning-based methods show the potential to achieve improved performance by drawing on past experiences to reason about unknown areas. In this paper, we propose DARE, a novel generative approach that leverages diffusion models trained on expert demonstrations, which can explicitly generate an exploration path through one-time inference. We build DARE upon an attention-based encoder and a diffusion policy model, and introduce ground truth optimal demonstrations for training to learn better patterns for exploration. The trained planner can reason about the partial belief to recognize the potential structure in unknown areas and consider these areas during path planning. Our experiments demonstrate that DARE achieves on-par performance with both conventional and learning-based state-of-the-art exploration planners, as well as good generalizability in both simulations and real-life scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge