Jack Brady
Generation is Required for Data-Efficient Perception
Dec 17, 2025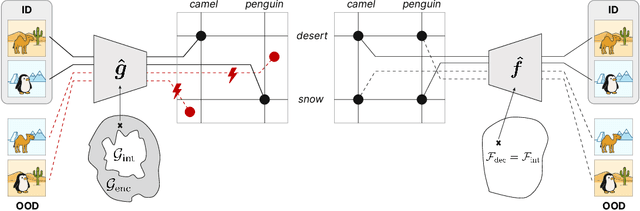
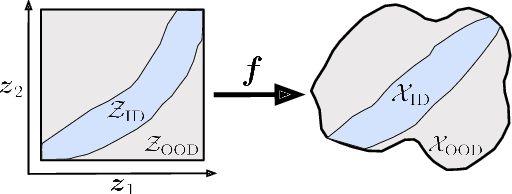
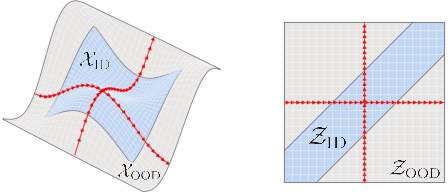
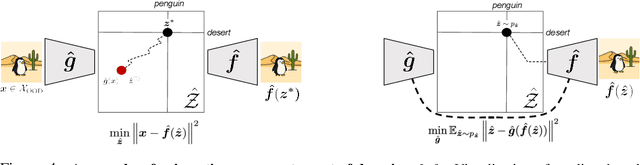
Abstract:It has been hypothesized that human-level visual perception requires a generative approach in which internal representations result from inverting a decoder. Yet today's most successful vision models are non-generative, relying on an encoder that maps images to representations without decoder inversion. This raises the question of whether generation is, in fact, necessary for machines to achieve human-level visual perception. To address this, we study whether generative and non-generative methods can achieve compositional generalization, a hallmark of human perception. Under a compositional data generating process, we formalize the inductive biases required to guarantee compositional generalization in decoder-based (generative) and encoder-based (non-generative) methods. We then show theoretically that enforcing these inductive biases on encoders is generally infeasible using regularization or architectural constraints. In contrast, for generative methods, the inductive biases can be enforced straightforwardly, thereby enabling compositional generalization by constraining a decoder and inverting it. We highlight how this inversion can be performed efficiently, either online through gradient-based search or offline through generative replay. We examine the empirical implications of our theory by training a range of generative and non-generative methods on photorealistic image datasets. We find that, without the necessary inductive biases, non-generative methods often fail to generalize compositionally and require large-scale pretraining or added supervision to improve generalization. By comparison, generative methods yield significant improvements in compositional generalization, without requiring additional data, by leveraging suitable inductive biases on a decoder along with search and replay.
E-CHUM: Event-based Cameras for Human Detection and Urban Monitoring
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Understanding human movement and city dynamics has always been challenging. From traditional methods of manually observing the city's inhabitant, to using cameras, to now using sensors and more complex technology, the field of urban monitoring has evolved greatly. Still, there are more that can be done to unlock better practices for understanding city dynamics. This paper surveys how the landscape of urban dynamics studying has evolved with a particular focus on event-based cameras. Event-based cameras capture changes in light intensity instead of the RGB values that traditional cameras do. They offer unique abilities, like the ability to work in low-light, that can make them advantageous compared to other sensors. Through an analysis of event-based cameras, their applications, their advantages and challenges, and machine learning applications, we propose event-based cameras as a medium for capturing information to study urban dynamics. They offer the ability to capture important information while maintaining privacy. We also suggest multi-sensor fusion of event-based cameras and other sensors in the study of urban dynamics. Combining event-based cameras and infrared, event-LiDAR, or vibration has to potential to enhance the ability of event-based cameras and overcome the challenges that event-based cameras have.
Interaction Asymmetry: A General Principle for Learning Composable Abstractions
Nov 12, 2024Abstract:Learning disentangled representations of concepts and re-composing them in unseen ways is crucial for generalizing to out-of-domain situations. However, the underlying properties of concepts that enable such disentanglement and compositional generalization remain poorly understood. In this work, we propose the principle of interaction asymmetry which states: "Parts of the same concept have more complex interactions than parts of different concepts". We formalize this via block diagonality conditions on the $(n+1)$th order derivatives of the generator mapping concepts to observed data, where different orders of "complexity" correspond to different $n$. Using this formalism, we prove that interaction asymmetry enables both disentanglement and compositional generalization. Our results unify recent theoretical results for learning concepts of objects, which we show are recovered as special cases with $n\!=\!0$ or $1$. We provide results for up to $n\!=\!2$, thus extending these prior works to more flexible generator functions, and conjecture that the same proof strategies generalize to larger $n$. Practically, our theory suggests that, to disentangle concepts, an autoencoder should penalize its latent capacity and the interactions between concepts during decoding. We propose an implementation of these criteria using a flexible Transformer-based VAE, with a novel regularizer on the attention weights of the decoder. On synthetic image datasets consisting of objects, we provide evidence that this model can achieve comparable object disentanglement to existing models that use more explicit object-centric priors.
Provable Compositional Generalization for Object-Centric Learning
Oct 09, 2023



Abstract:Learning representations that generalize to novel compositions of known concepts is crucial for bridging the gap between human and machine perception. One prominent effort is learning object-centric representations, which are widely conjectured to enable compositional generalization. Yet, it remains unclear when this conjecture will be true, as a principled theoretical or empirical understanding of compositional generalization is lacking. In this work, we investigate when compositional generalization is guaranteed for object-centric representations through the lens of identifiability theory. We show that autoencoders that satisfy structural assumptions on the decoder and enforce encoder-decoder consistency will learn object-centric representations that provably generalize compositionally. We validate our theoretical result and highlight the practical relevance of our assumptions through experiments on synthetic image data.
Provably Learning Object-Centric Representations
May 23, 2023



Abstract:Learning structured representations of the visual world in terms of objects promises to significantly improve the generalization abilities of current machine learning models. While recent efforts to this end have shown promising empirical progress, a theoretical account of when unsupervised object-centric representation learning is possible is still lacking. Consequently, understanding the reasons for the success of existing object-centric methods as well as designing new theoretically grounded methods remains challenging. In the present work, we analyze when object-centric representations can provably be learned without supervision. To this end, we first introduce two assumptions on the generative process for scenes comprised of several objects, which we call compositionality and irreducibility. Under this generative process, we prove that the ground-truth object representations can be identified by an invertible and compositional inference model, even in the presence of dependencies between objects. We empirically validate our results through experiments on synthetic data. Finally, we provide evidence that our theory holds predictive power for existing object-centric models by showing a close correspondence between models' compositionality and invertibility and their empirical identifiability.
Embrace the Gap: VAEs Perform Independent Mechanism Analysis
Jun 06, 2022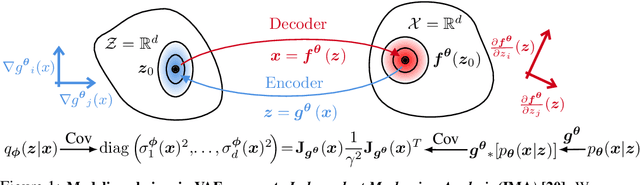
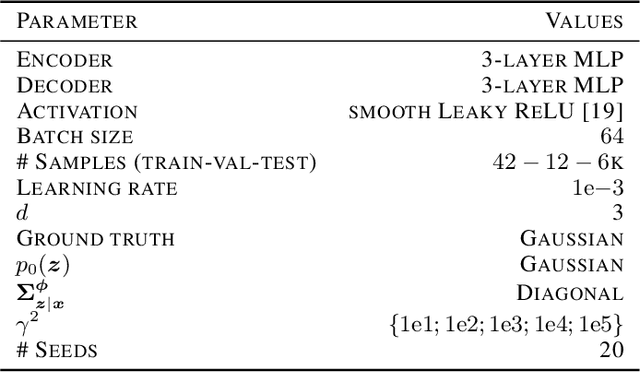
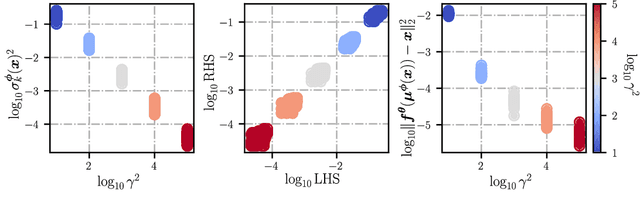
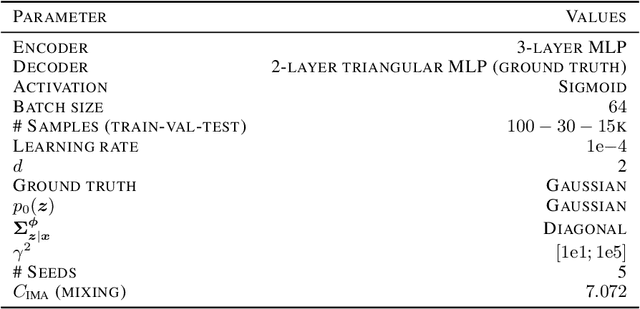
Abstract:Variational autoencoders (VAEs) are a popular framework for modeling complex data distributions; they can be efficiently trained via variational inference by maximizing the evidence lower bound (ELBO), at the expense of a gap to the exact (log-)marginal likelihood. While VAEs are commonly used for representation learning, it is unclear why ELBO maximization would yield useful representations, since unregularized maximum likelihood estimation cannot invert the data-generating process. Yet, VAEs often succeed at this task. We seek to elucidate this apparent paradox by studying nonlinear VAEs in the limit of near-deterministic decoders. We first prove that, in this regime, the optimal encoder approximately inverts the decoder -- a commonly used but unproven conjecture -- which we refer to as {\em self-consistency}. Leveraging self-consistency, we show that the ELBO converges to a regularized log-likelihood. This allows VAEs to perform what has recently been termed independent mechanism analysis (IMA): it adds an inductive bias towards decoders with column-orthogonal Jacobians, which helps recovering the true latent factors. The gap between ELBO and log-likelihood is therefore welcome, since it bears unanticipated benefits for nonlinear representation learning. In experiments on synthetic and image data, we show that VAEs uncover the true latent factors when the data generating process satisfies the IMA assumption.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge