Jüri Keller
LongEval at CLEF 2025: Longitudinal Evaluation of IR Model Performance
Mar 11, 2025
Abstract:This paper presents the third edition of the LongEval Lab, part of the CLEF 2025 conference, which continues to explore the challenges of temporal persistence in Information Retrieval (IR). The lab features two tasks designed to provide researchers with test data that reflect the evolving nature of user queries and document relevance over time. By evaluating how model performance degrades as test data diverge temporally from training data, LongEval seeks to advance the understanding of temporal dynamics in IR systems. The 2025 edition aims to engage the IR and NLP communities in addressing the development of adaptive models that can maintain retrieval quality over time in the domains of web search and scientific retrieval.
Counterfactual Query Rewriting to Use Historical Relevance Feedback
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:When a retrieval system receives a query it has encountered before, previous relevance feedback, such as clicks or explicit judgments can help to improve retrieval results. However, the content of a previously relevant document may have changed, or the document might not be available anymore. Despite this evolved corpus, we counterfactually use these previously relevant documents as relevance signals. In this paper we proposed approaches to rewrite user queries and compare them against a system that directly uses the previous qrels for the ranking. We expand queries with terms extracted from the previously relevant documents or derive so-called keyqueries that rank the previously relevant documents to the top of the current corpus. Our evaluation in the CLEF LongEval scenario shows that rewriting queries with historical relevance feedback improves the retrieval effectiveness and even outperforms computationally expensive transformer-based approaches.
Report on the Workshop on Simulations for Information Access (Sim4IA 2024) at SIGIR 2024
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:This paper is a report of the Workshop on Simulations for Information Access (Sim4IA) workshop at SIGIR 2024. The workshop had two keynotes, a panel discussion, nine lightning talks, and two breakout sessions. Key takeaways were user simulation's importance in academia and industry, the possible bridging of online and offline evaluation, and the issues of organizing a companion shared task around user simulations for information access. We report on how we organized the workshop, provide a brief overview of what happened at the workshop, and summarize the main topics and findings of the workshop and future work.
Replicability Measures for Longitudinal Information Retrieval Evaluation
Sep 09, 2024Abstract:Information Retrieval (IR) systems are exposed to constant changes in most components. Documents are created, updated, or deleted, the information needs are changing, and even relevance might not be static. While it is generally expected that the IR systems retain a consistent utility for the users, test collection evaluations rely on a fixed experimental setup. Based on the LongEval shared task and test collection, this work explores how the effectiveness measured in evolving experiments can be assessed. Specifically, the persistency of effectiveness is investigated as a replicability task. It is observed how the effectiveness progressively deteriorates over time compared to the initial measurement. Employing adapted replicability measures provides further insight into the persistence of effectiveness. The ranking of systems varies across retrieval measures and time. In conclusion, it was found that the most effective systems are not necessarily the ones with the most persistent performance.
Evaluation of Temporal Change in IR Test Collections
Jul 01, 2024



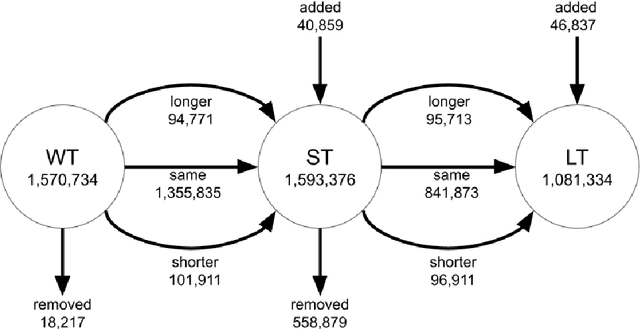
Abstract:Information retrieval systems have been evaluated using the Cranfield paradigm for many years. This paradigm allows a systematic, fair, and reproducible evaluation of different retrieval methods in fixed experimental environments. However, real-world retrieval systems must cope with dynamic environments and temporal changes that affect the document collection, topical trends, and the individual user's perception of what is considered relevant. Yet, the temporal dimension in IR evaluations is still understudied. To this end, this work investigates how the temporal generalizability of effectiveness evaluations can be assessed. As a conceptual model, we generalize Cranfield-type experiments to the temporal context by classifying the change in the essential components according to the create, update, and delete operations of persistent storage known from CRUD. From the different types of change different evaluation scenarios are derived and it is outlined what they imply. Based on these scenarios, renowned state-of-the-art retrieval systems are tested and it is investigated how the retrieval effectiveness changes on different levels of granularity. We show that the proposed measures can be well adapted to describe the changes in the retrieval results. The experiments conducted confirm that the retrieval effectiveness strongly depends on the evaluation scenario investigated. We find that not only the average retrieval performance of single systems but also the relative system performance are strongly affected by the components that change and to what extent these components changed.
Preliminary Results of a Scientometric Analysis of the German Information Retrieval Community 2020-2023
Oct 11, 2023Abstract:The German Information Retrieval community is located in two different sub-fields: Information and computer science. There are no current studies that investigate these communities on a scientometric level. Available studies only focus on the information scientific part of the community. We generated a data set of 401 recent IR-related publications extracted from six core IR conferences from a mainly computer scientific background. We analyze this data set at the institutional and researcher level. The data set is publicly released, and we also demonstrate a mapping use case.
* Data available at https://github.com/irgroup/LWDA2023-IR-community
Evaluating Temporal Persistence Using Replicability Measures
Aug 21, 2023
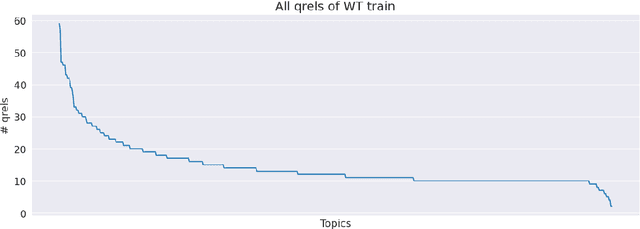

Abstract:In real-world Information Retrieval (IR) experiments, the Evaluation Environment (EE) is exposed to constant change. Documents are added, removed, or updated, and the information need and the search behavior of users is evolving. Simultaneously, IR systems are expected to retain a consistent quality. The LongEval Lab seeks to investigate the longitudinal persistence of IR systems, and in this work, we describe our participation. We submitted runs of five advanced retrieval systems, namely a Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) approach, ColBERT, monoT5, Doc2Query, and E5, to both sub-tasks. Further, we cast the longitudinal evaluation as a replicability study to better understand the temporal change observed. As a result, we quantify the persistence of the submitted runs and see great potential in this evaluation method.
Automated Statement Extraction from Press Briefings
Feb 24, 2023Abstract:Scientific press briefings are a valuable information source. They consist of alternating expert speeches, questions from the audience and their answers. Therefore, they can contribute to scientific and fact-based media coverage. Even though press briefings are highly informative, extracting statements relevant to individual journalistic tasks is challenging and time-consuming. To support this task, an automated statement extraction system is proposed. Claims are used as the main feature to identify statements in press briefing transcripts. The statement extraction task is formulated as a four-step procedure. First, the press briefings are split into sentences and passages, then claim sentences are identified through sequence classification. Subsequently, topics are detected, and the sentences are filtered to improve the coherence and assess the length of the statements. The results indicate that claim detection can be used to identify statements in press briefings. While many statements can be extracted automatically with this system, they are not always as coherent as needed to be understood without context and may need further review by knowledgeable persons.
Evaluating Research Dataset Recommendations in a Living Lab
Sep 30, 2022Abstract:The search for research datasets is as important as laborious. Due to the importance of the choice of research data in further research, this decision must be made carefully. Additionally, because of the growing amounts of data in almost all areas, research data is already a central artifact in empirical sciences. Consequentially, research dataset recommendations can beneficially supplement scientific publication searches. We formulated the recommendation task as a retrieval problem by focussing on broad similarities between research datasets and scientific publications. In a multistage approach, initial recommendations were retrieved by the BM25 ranking function and dynamic queries. Subsequently, the initial ranking was re-ranked utilizing click feedback and document embeddings. The proposed system was evaluated live on real user interaction data using the STELLA infrastructure in the LiLAS Lab at CLEF 2021. Our experimental system could efficiently be fine-tuned before the live evaluation by pre-testing the system with a pseudo test collection based on prior user interaction data from the live system. The results indicate that the experimental system outperforms the other participating systems.
* Best of 2021 Labs: LiLAS
ir_metadata: An Extensible Metadata Schema for IR Experiments
Jul 18, 2022



Abstract:The information retrieval (IR) community has a strong tradition of making the computational artifacts and resources available for future reuse, allowing the validation of experimental results. Besides the actual test collections, the underlying run files are often hosted in data archives as part of conferences like TREC, CLEF, or NTCIR. Unfortunately, the run data itself does not provide much information about the underlying experiment. For instance, the single run file is not of much use without the context of the shared task's website or the run data archive. In other domains, like the social sciences, it is good practice to annotate research data with metadata. In this work, we introduce ir_metadata - an extensible metadata schema for TREC run files based on the PRIMAD model. We propose to align the metadata annotations to PRIMAD, which considers components of computational experiments that can affect reproducibility. Furthermore, we outline important components and information that should be reported in the metadata and give evidence from the literature. To demonstrate the usefulness of these metadata annotations, we implement new features in repro_eval that support the outlined metadata schema for the use case of reproducibility studies. Additionally, we curate a dataset with run files derived from experiments with different instantiations of PRIMAD components and annotate these with the corresponding metadata. In the experiments, we cover reproducibility experiments that are identified by the metadata and classified by PRIMAD. With this work, we enable IR researchers to annotate TREC run files and improve the reuse value of experimental artifacts even further.
* Resource paper
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge