Petr Knoth
LongEval at CLEF 2025: Longitudinal Evaluation of IR Model Performance
Mar 11, 2025
Abstract:This paper presents the third edition of the LongEval Lab, part of the CLEF 2025 conference, which continues to explore the challenges of temporal persistence in Information Retrieval (IR). The lab features two tasks designed to provide researchers with test data that reflect the evolving nature of user queries and document relevance over time. By evaluating how model performance degrades as test data diverge temporally from training data, LongEval seeks to advance the understanding of temporal dynamics in IR systems. The 2025 edition aims to engage the IR and NLP communities in addressing the development of adaptive models that can maintain retrieval quality over time in the domains of web search and scientific retrieval.
CSMeD: Bridging the Dataset Gap in Automated Citation Screening for Systematic Literature Reviews
Nov 21, 2023



Abstract:Systematic literature reviews (SLRs) play an essential role in summarising, synthesising and validating scientific evidence. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in using machine learning techniques to automate the identification of relevant studies for SLRs. However, the lack of standardised evaluation datasets makes comparing the performance of such automated literature screening systems difficult. In this paper, we analyse the citation screening evaluation datasets, revealing that many of the available datasets are either too small, suffer from data leakage or have limited applicability to systems treating automated literature screening as a classification task, as opposed to, for example, a retrieval or question-answering task. To address these challenges, we introduce CSMeD, a meta-dataset consolidating nine publicly released collections, providing unified access to 325 SLRs from the fields of medicine and computer science. CSMeD serves as a comprehensive resource for training and evaluating the performance of automated citation screening models. Additionally, we introduce CSMeD-FT, a new dataset designed explicitly for evaluating the full text publication screening task. To demonstrate the utility of CSMeD, we conduct experiments and establish baselines on new datasets.
CRUISE-Screening: Living Literature Reviews Toolbox
Sep 04, 2023


Abstract:Keeping up with research and finding related work is still a time-consuming task for academics. Researchers sift through thousands of studies to identify a few relevant ones. Automation techniques can help by increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of this task. To this end, we developed CRUISE-Screening, a web-based application for conducting living literature reviews - a type of literature review that is continuously updated to reflect the latest research in a particular field. CRUISE-Screening is connected to several search engines via an API, which allows for updating the search results periodically. Moreover, it can facilitate the process of screening for relevant publications by using text classification and question answering models. CRUISE-Screening can be used both by researchers conducting literature reviews and by those working on automating the citation screening process to validate their algorithms. The application is open-source: https://github.com/ProjectDoSSIER/cruise-screening, and a demo is available under this URL: https://citation-screening.ec.tuwien.ac.at. We discuss the limitations of our tool in Appendix A.
CORE-GPT: Combining Open Access research and large language models for credible, trustworthy question answering
Jul 06, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we present CORE-GPT, a novel question-answering platform that combines GPT-based language models and more than 32 million full-text open access scientific articles from CORE. We first demonstrate that GPT3.5 and GPT4 cannot be relied upon to provide references or citations for generated text. We then introduce CORE-GPT which delivers evidence-based answers to questions, along with citations and links to the cited papers, greatly increasing the trustworthiness of the answers and reducing the risk of hallucinations. CORE-GPT's performance was evaluated on a dataset of 100 questions covering the top 20 scientific domains in CORE, resulting in 100 answers and links to 500 relevant articles. The quality of the provided answers and and relevance of the links were assessed by two annotators. Our results demonstrate that CORE-GPT can produce comprehensive and trustworthy answers across the majority of scientific domains, complete with links to genuine, relevant scientific articles.
Effective Matching of Patients to Clinical Trials using Entity Extraction and Neural Re-ranking
Jul 01, 2023



Abstract:Clinical trials (CTs) often fail due to inadequate patient recruitment. This paper tackles the challenges of CT retrieval by presenting an approach that addresses the patient-to-trials paradigm. Our approach involves two key components in a pipeline-based model: (i) a data enrichment technique for enhancing both queries and documents during the first retrieval stage, and (ii) a novel re-ranking schema that uses a Transformer network in a setup adapted to this task by leveraging the structure of the CT documents. We use named entity recognition and negation detection in both patient description and the eligibility section of CTs. We further classify patient descriptions and CT eligibility criteria into current, past, and family medical conditions. This extracted information is used to boost the importance of disease and drug mentions in both query and index for lexical retrieval. Furthermore, we propose a two-step training schema for the Transformer network used to re-rank the results from the lexical retrieval. The first step focuses on matching patient information with the descriptive sections of trials, while the second step aims to determine eligibility by matching patient information with the criteria section. Our findings indicate that the inclusion criteria section of the CT has a great influence on the relevance score in lexical models, and that the enrichment techniques for queries and documents improve the retrieval of relevant trials. The re-ranking strategy, based on our training schema, consistently enhances CT retrieval and shows improved performance by 15\% in terms of precision at retrieving eligible trials. The results of our experiments suggest the benefit of making use of extracted entities. Moreover, our proposed re-ranking schema shows promising effectiveness compared to larger neural models, even with limited training data.
Outcome-based Evaluation of Systematic Review Automation
Jun 30, 2023

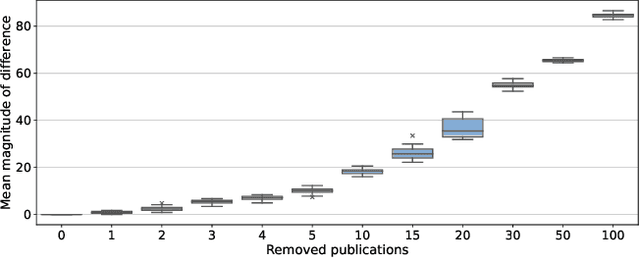

Abstract:Current methods of evaluating search strategies and automated citation screening for systematic literature reviews typically rely on counting the number of relevant and not relevant publications. This established practice, however, does not accurately reflect the reality of conducting a systematic review, because not all included publications have the same influence on the final outcome of the systematic review. More specifically, if an important publication gets excluded or included, this might significantly change the overall review outcome, while not including or excluding less influential studies may only have a limited impact. However, in terms of evaluation measures, all inclusion and exclusion decisions are treated equally and, therefore, failing to retrieve publications with little to no impact on the review outcome leads to the same decrease in recall as failing to retrieve crucial publications. We propose a new evaluation framework that takes into account the impact of the reported study on the overall systematic review outcome. We demonstrate the framework by extracting review meta-analysis data and estimating outcome effects using predictions from ranking runs on systematic reviews of interventions from CLEF TAR 2019 shared task. We further measure how closely the obtained outcomes are to the outcomes of the original review if the arbitrary rankings were used. We evaluate 74 runs using the proposed framework and compare the results with those obtained using standard IR measures. We find that accounting for the difference in review outcomes leads to a different assessment of the quality of a system than if traditional evaluation measures were used. Our analysis provides new insights into the evaluation of retrieval results in the context of systematic review automation, emphasising the importance of assessing the usefulness of each document beyond binary relevance.
Predicting article quality scores with machine learning: The UK Research Excellence Framework
Dec 11, 2022Abstract:National research evaluation initiatives and incentive schemes have previously chosen between simplistic quantitative indicators and time-consuming peer review, sometimes supported by bibliometrics. Here we assess whether artificial intelligence (AI) could provide a third alternative, estimating article quality using more multiple bibliometric and metadata inputs. We investigated this using provisional three-level REF2021 peer review scores for 84,966 articles submitted to the UK Research Excellence Framework 2021, matching a Scopus record 2014-18 and with a substantial abstract. We found that accuracy is highest in the medical and physical sciences Units of Assessment (UoAs) and economics, reaching 42% above the baseline (72% overall) in the best case. This is based on 1000 bibliometric inputs and half of the articles used for training in each UoA. Prediction accuracies above the baseline for the social science, mathematics, engineering, arts, and humanities UoAs were much lower or close to zero. The Random Forest Classifier (standard or ordinal) and Extreme Gradient Boosting Classifier algorithms performed best from the 32 tested. Accuracy was lower if UoAs were merged or replaced by Scopus broad categories. We increased accuracy with an active learning strategy and by selecting articles with higher prediction probabilities, as estimated by the algorithms, but this substantially reduced the number of scores predicted.
Confidence estimation of classification based on the distribution of the neural network output layer
Oct 18, 2022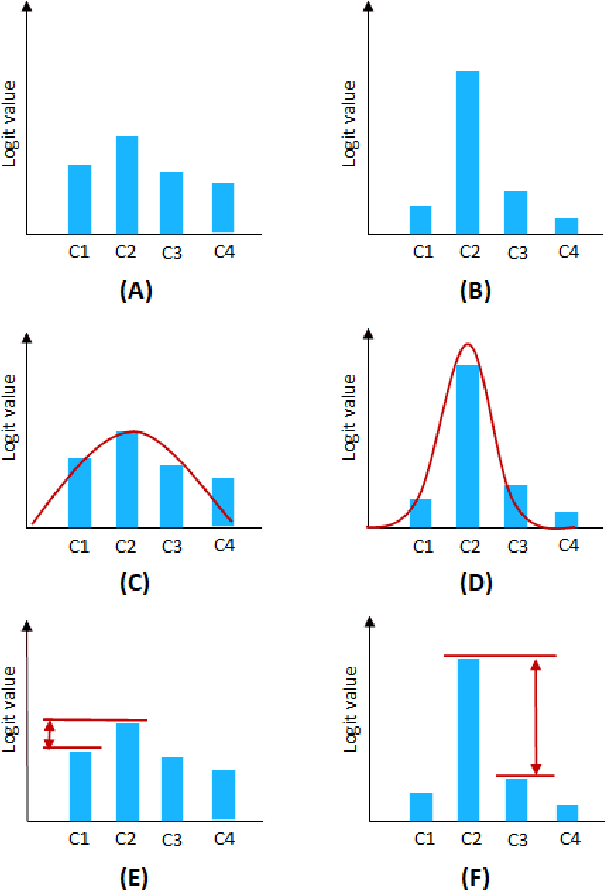
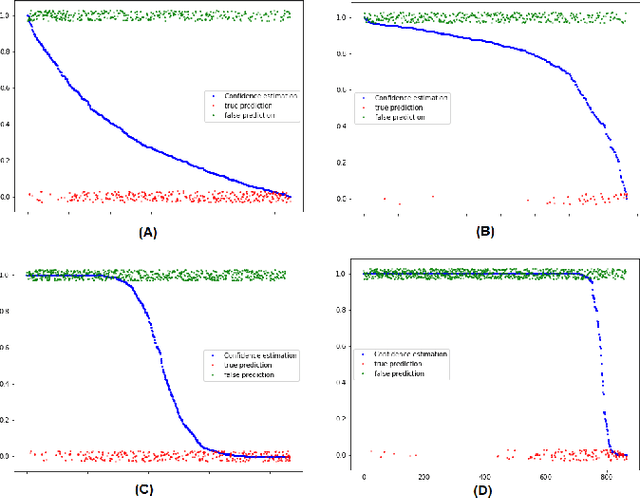
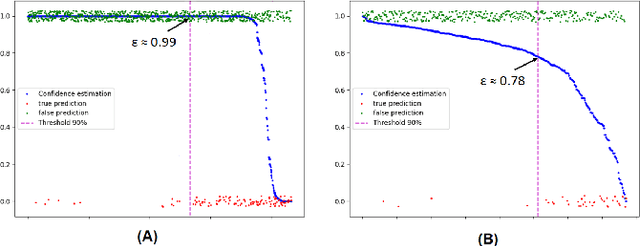
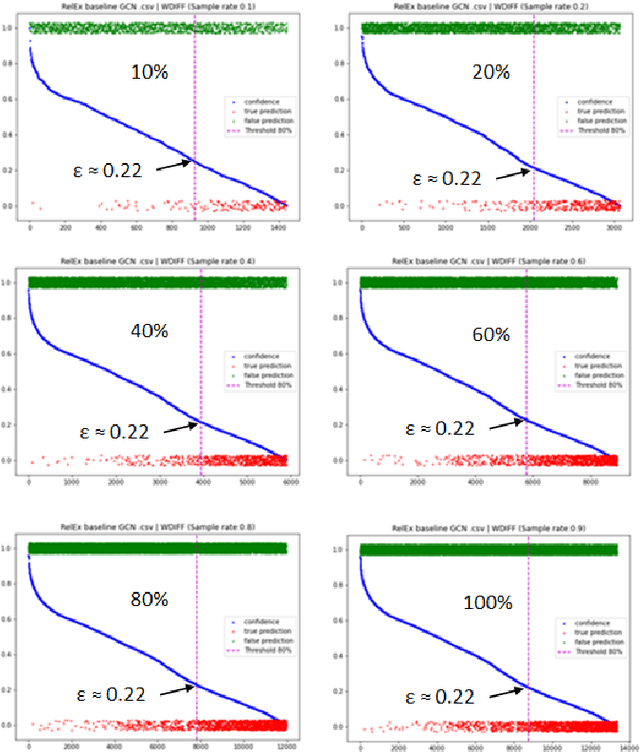
Abstract:One of the most common problems preventing the application of prediction models in the real world is lack of generalization: The accuracy of models, measured in the benchmark does repeat itself on future data, e.g. in the settings of real business. There is relatively little methods exist that estimate the confidence of prediction models. In this paper, we propose novel methods that, given a neural network classification model, estimate uncertainty of particular predictions generated by this model. Furthermore, we propose a method that, given a model and a confidence level, calculates a threshold that separates prediction generated by this model into two subsets, one of them meets the given confidence level. In contrast to other methods, the proposed methods do not require any changes on existing neural networks, because they simply build on the output logit layer of a common neural network. In particular, the methods infer the confidence of a particular prediction based on the distribution of the logit values corresponding to this prediction. The proposed methods constitute a tool that is recommended for filtering predictions in the process of knowledge extraction, e.g. based on web scrapping, where predictions subsets are identified that maximize the precision on cost of the recall, which is less important due to the availability of data. The method has been tested on different tasks including relation extraction, named entity recognition and image classification to show the significant increase of accuracy achieved.
Automation of Citation Screening for Systematic Literature Reviews using Neural Networks: A Replicability Study
Jan 19, 2022



Abstract:In the process of Systematic Literature Review, citation screening is estimated to be one of the most time-consuming steps. Multiple approaches to automate it using various machine learning techniques have been proposed. The first research papers that apply deep neural networks to this problem were published in the last two years. In this work, we conduct a replicability study of the first two deep learning papers for citation screening and evaluate their performance on 23 publicly available datasets. While we succeeded in replicating the results of one of the papers, we were unable to replicate the results of the other. We summarise the challenges involved in the replication, including difficulties in obtaining the datasets to match the experimental setup of the original papers and problems with executing the original source code. Motivated by this experience, we subsequently present a simpler model based on averaging word embeddings that outperforms one of the models on 18 out of 23 datasets and is, on average, 72 times faster than the second replicated approach. Finally, we measure the training time and the invariance of the models when exposed to a variety of input features and random initialisations, demonstrating differences in the robustness of these approaches.
Mr. DLib's Living Lab for Scholarly Recommendations
Jul 19, 2018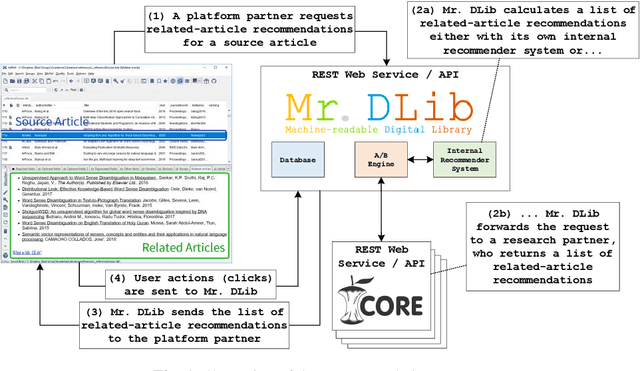
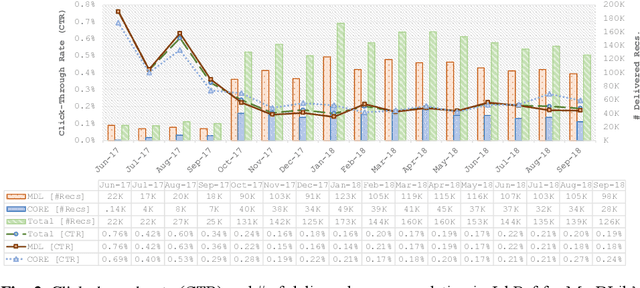
Abstract:We introduce the first living lab for scholarly recommender systems. This lab allows recommender-system researchers to conduct online evaluations of their novel algorithms for scholarly recommendations, i.e., research papers, citations, conferences, research grants etc. Recommendations are delivered through the living lab's API in platforms such as reference management software and digital libraries. The living lab is built on top of the recommender system as-a-service Mr. DLib. Current partners are the reference management software JabRef and the CORE research team. We present the architecture of Mr. DLib's living lab as well as usage statistics on the first ten months of operating it. During this time, 970,517 recommendations were delivered with a mean click-through rate of 0.22%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge