Jérôme Lang
LAMSADE
Fair Railway Network Design
Sep 03, 2024


Abstract:When designing a public transportation network in a country, one may want to minimise the sum of travel duration of all inhabitants. This corresponds to a purely utilitarian view and does not involve any fairness consideration, as the resulting network will typically benefit the capital city and/or large central cities while leaving some peripheral cities behind. On the other hand, a more egalitarian view will allow some people to travel between peripheral cities without having to go through a central city. We define a model, propose algorithms for computing solution networks, and report on experiments based on real data.
Reasoning about unpredicted change and explicit time
Jul 09, 2024Abstract:Reasoning about unpredicted change consists in explaining observations by events; we propose here an approach for explaining time-stamped observations by surprises, which are simple events consisting in the change of the truth value of a fluent. A framework for dealing with surprises is defined. Minimal sets of surprises are provided together with time intervals where each surprise has occurred, and they are characterized from a model-based diagnosis point of view. Then, a probabilistic approach of surprise minimisation is proposed.
Reasoning About Action and Change
Jun 27, 2024Abstract:The purpose of this book is to provide an overview of AI research, ranging from basic work to interfaces and applications, with as much emphasis on results as on current issues. It is aimed at an audience of master students and Ph.D. students, and can be of interest as well for researchers and engineers who want to know more about AI. The book is split into three volumes.
Thou Shalt not Pick all Items if Thou are First: of Strategyproof and Fair Picking Sequences
Jan 11, 2023Abstract:When allocating indivisible items to agents, it is known that the only strategyproof mechanisms that satisfy a set of rather mild conditions are constrained serial dictatorships: given a fixed order over agents, at each step the designated agent chooses a given number of items (depending on her position in the sequence). With these rules, also known as non-interleaving picking sequences, agents who come earlier in the sequence have a larger choice of items. However, this advantage can be compensated by a higher number of items received by those who come later. How to balance priority in the sequence and number of items received is a nontrivial question. We use a previous model, parameterized by a mapping from ranks to scores, a social welfare functional, and a distribution over preference profiles. For several meaningful choices of parameters, we show that the optimal sequence can be computed in polynomial time. Last, we give a simple procedure for eliciting scoring vectors and we study the impact of the assignment from agents to positions on the ex-post social welfare.
Online Approval Committee Elections
Feb 14, 2022Abstract:Assume $k$ candidates need to be selected. The candidates appear over time. Each time one appears, it must be immediately selected or rejected -- a decision that is made by a group of individuals through voting. Assume the voters use approval ballots, i.e., for each candidate they only specify whether they consider it acceptable or not. This setting can be seen as a voting variant of choosing $k$ secretaries. Our contribution is twofold. (1) We assess to what extent the committees that are computed online can proportionally represent the voters. (2) If a prior probability over candidate approvals is available, we show how to compute committees with maximal expected score.
Multi-winner Approval Voting Goes Epistemic
Jan 17, 2022
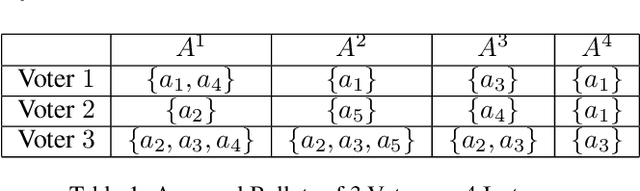
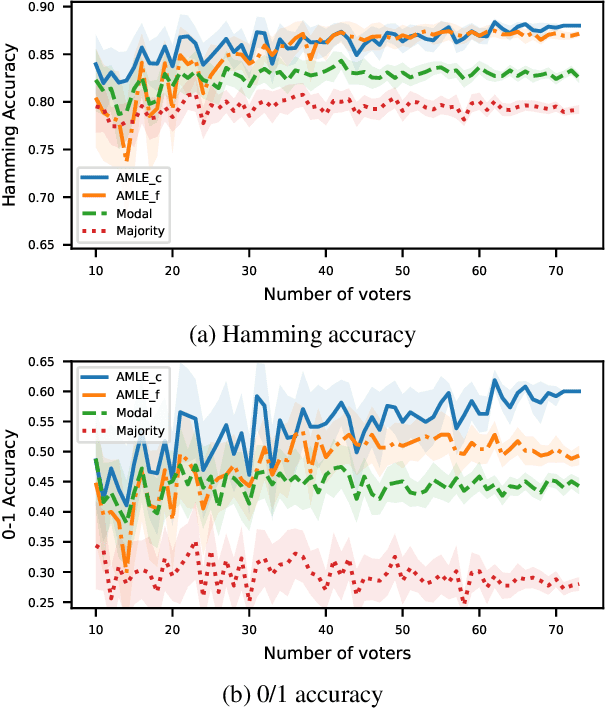
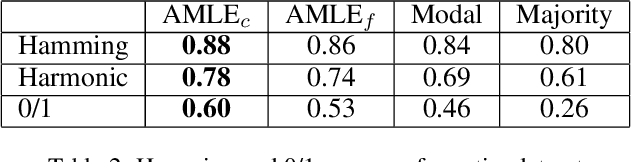
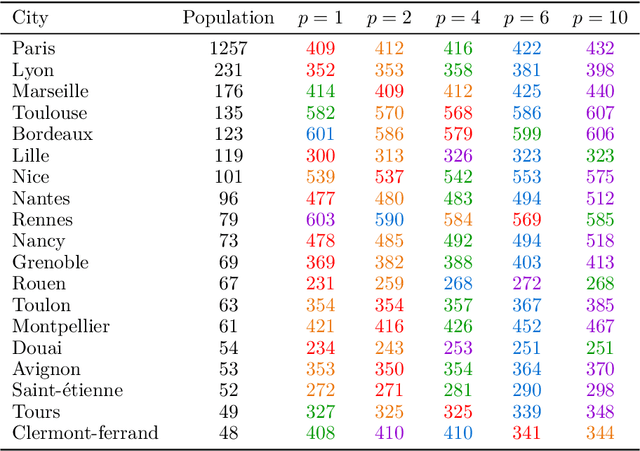
Abstract:Epistemic voting interprets votes as noisy signals about a ground truth. We consider contexts where the truth consists of a set of objective winners, knowing a lower and upper bound on its cardinality. A prototypical problem for this setting is the aggre-gation of multi-label annotations with prior knowledge on the size of the ground truth. We posit noisemodels, for which we define rules that output an optimal set of winners. We report on experiments on multi-label annotations (which we collected).
Truth-tracking via Approval Voting: Size Matters
Dec 07, 2021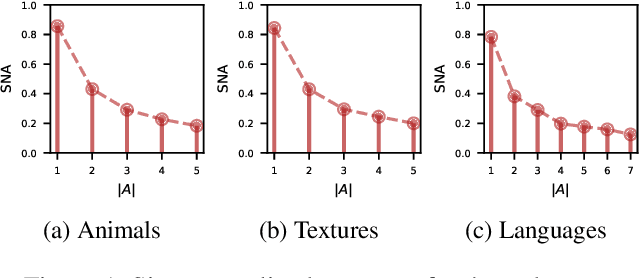
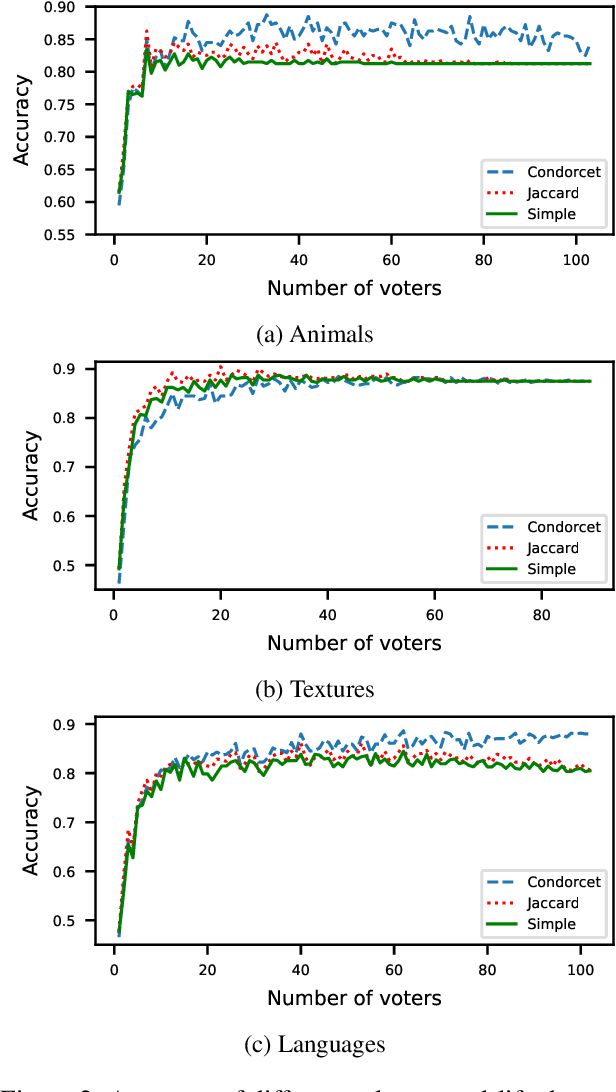
Abstract:Epistemic social choice aims at unveiling a hidden ground truth given votes, which are interpreted as noisy signals about it. We consider here a simple setting where votes consist of approval ballots: each voter approves a set of alternatives which they believe can possibly be the ground truth. Based on the intuitive idea that more reliable votes contain fewer alternatives, we define several noise models that are approval voting variants of the Mallows model. The likelihood-maximizing alternative is then characterized as the winner of a weighted approval rule, where the weight of a ballot decreases with its cardinality. We have conducted an experiment on three image annotation datasets; they conclude that rules based on our noise model outperform standard approval voting; the best performance is obtained by a variant of the Condorcet noise model.
Online Selection of Diverse Committees
May 19, 2021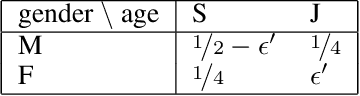


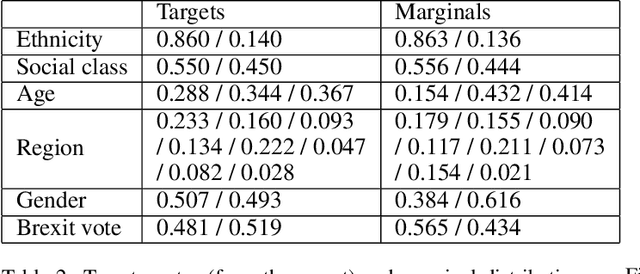
Abstract:Citizens' assemblies need to represent subpopulations according to their proportions in the general population. These large committees are often constructed in an online fashion by contacting people, asking for the demographic features of the volunteers, and deciding to include them or not. This raises a trade-off between the number of people contacted (and the incurring cost) and the representativeness of the committee. We study three methods, theoretically and experimentally: a greedy algorithm that includes volunteers as long as proportionality is not violated; a non-adaptive method that includes a volunteer with a probability depending only on their features, assuming that the joint feature distribution in the volunteer pool is known; and a reinforcement learning based approach when this distribution is not known a priori but learnt online.
Morphologic for knowledge dynamics: revision, fusion, abduction
Feb 14, 2018
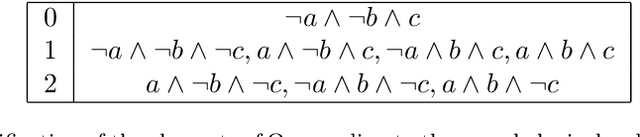
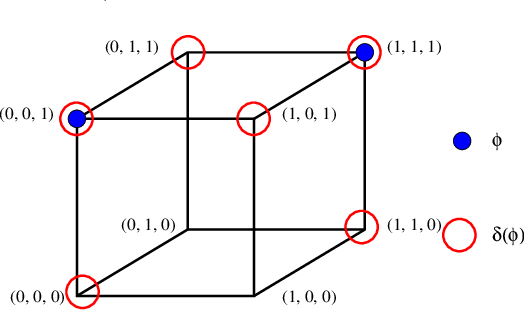
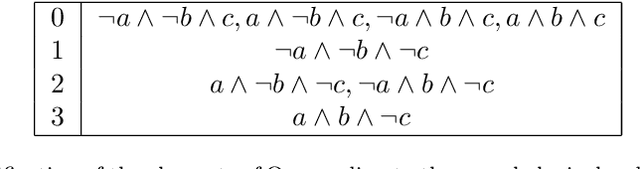
Abstract:Several tasks in artificial intelligence require to be able to find models about knowledge dynamics. They include belief revision, fusion and belief merging, and abduction. In this paper we exploit the algebraic framework of mathematical morphology in the context of propositional logic, and define operations such as dilation or erosion of a set of formulas. We derive concrete operators, based on a semantic approach, that have an intuitive interpretation and that are formally well behaved, to perform revision, fusion and abduction. Computation and tractability are addressed, and simple examples illustrate the typical results that can be obtained.
Proceedings Sixteenth Conference on Theoretical Aspects of Rationality and Knowledge
Jul 25, 2017Abstract:This volume consists of papers presented at the Sixteenth Conference on Theoretical Aspects of Rationality and Knowledge (TARK) held at the University of Liverpool, UK, from July 24 to 26, 2017. TARK conferences bring together researchers from a wide variety of fields, including Computer Science (especially, Artificial Intelligence, Cryptography, Distributed Computing), Economics (especially, Decision Theory, Game Theory, Social Choice Theory), Linguistics, Philosophy (especially, Philosophical Logic), and Cognitive Psychology, in order to further understand the issues involving reasoning about rationality and knowledge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge