Florence Dupin de Saint-Cyr
IRIT-ADRIA
What killed the cat? Towards a logical formalization of curiosity (and suspense, and surprise) in narratives
Oct 11, 2024

Abstract:We provide a unified framework in which the three emotions at the heart of narrative tension (curiosity, suspense and surprise) are formalized. This framework is built on nonmonotonic reasoning which allows us to compactly represent the default behavior of the world and to simulate the affective evolution of an agent receiving a story. After formalizing the notions of awareness, curiosity, surprise and suspense, we explore the properties induced by our definitions and study the computational complexity of detecting them. We finally propose means to evaluate these emotions' intensity for a given agent listening to a story.
Reasoning about unpredicted change and explicit time
Jul 09, 2024Abstract:Reasoning about unpredicted change consists in explaining observations by events; we propose here an approach for explaining time-stamped observations by surprises, which are simple events consisting in the change of the truth value of a fluent. A framework for dealing with surprises is defined. Minimal sets of surprises are provided together with time intervals where each surprise has occurred, and they are characterized from a model-based diagnosis point of view. Then, a probabilistic approach of surprise minimisation is proposed.
Reasoning About Action and Change
Jun 27, 2024Abstract:The purpose of this book is to provide an overview of AI research, ranging from basic work to interfaces and applications, with as much emphasis on results as on current issues. It is aimed at an audience of master students and Ph.D. students, and can be of interest as well for researchers and engineers who want to know more about AI. The book is split into three volumes.
Change in Abstract Argumentation Frameworks: Adding an Argument
Jan 16, 2014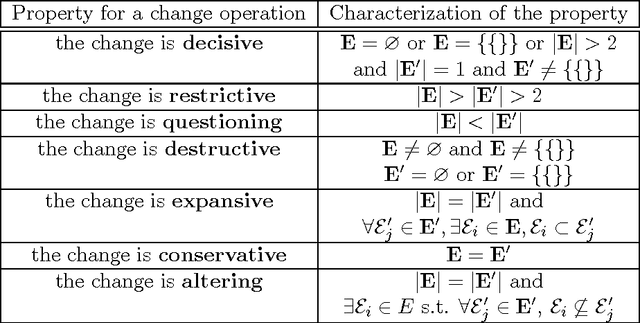
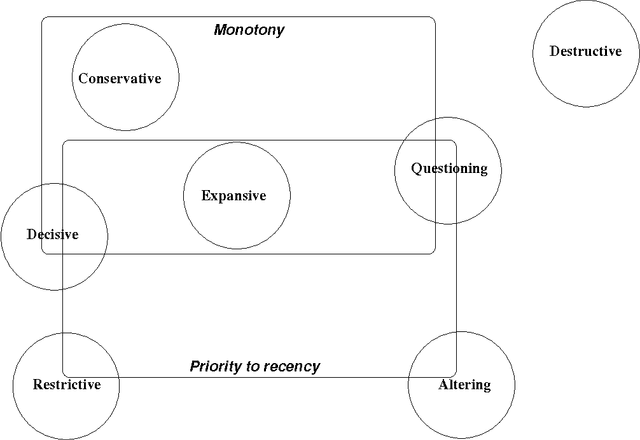
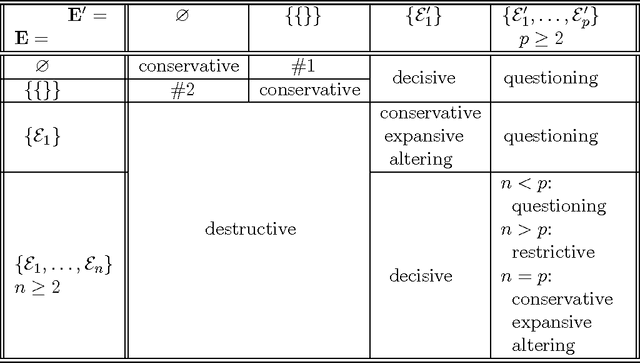

Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of change in an abstract argumentation system. We focus on a particular change: the addition of a new argument which interacts with previous arguments. We study the impact of such an addition on the outcome of the argumentation system, more particularly on the set of its extensions. Several properties for this change operation are defined by comparing the new set of extensions to the initial one, these properties are called structural when the comparisons are based on set-cardinality or set-inclusion relations. Several other properties are proposed where comparisons are based on the status of some particular arguments: the accepted arguments; these properties refer to the evolution of this status during the change, e.g., Monotony and Priority to Recency. All these properties may be more or less desirable according to specific applications. They are studied under two particular semantics: the grounded and preferred semantics.
Penalty logic and its Link with Dempster-Shafer Theory
Feb 27, 2013Abstract:Penalty logic, introduced by Pinkas, associates to each formula of a knowledge base the price to pay if this formula is violated. Penalties may be used as a criterion for selecting preferred consistent subsets in an inconsistent knowledge base, thus inducing a non-monotonic inference relation. A precise formalization and the main properties of penalty logic and of its associated non-monotonic inference relation are given in the first part. We also show that penalty logic and Dempster-Shafer theory are related, especially in the infinitesimal case.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge