Ilia Igashov
DAO
Flow-Based Fragment Identification via Binding Site-Specific Latent Representations
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Fragment-based drug design is a promising strategy leveraging the binding of small chemical moieties that can efficiently guide drug discovery. The initial step of fragment identification remains challenging, as fragments often bind weakly and non-specifically. We developed a protein-fragment encoder that relies on a contrastive learning approach to map both molecular fragments and protein surfaces in a shared latent space. The encoder captures interaction-relevant features and allows to perform virtual screening as well as generative design with our new method LatentFrag. In LatentFrag, fragment embeddings and positions are generated conditioned on the protein surface while being chemically realistic by construction. Our expressive fragment and protein representations allow location of protein-fragment interaction sites with high sensitivity and we observe state-of-the-art fragment recovery rates when sampling from the learned distribution of latent fragment embeddings. Our generative method outperforms common methods such as virtual screening at a fraction of its computational cost providing a valuable starting point for fragment hit discovery. We further show the practical utility of LatentFrag and extend the workflow to full ligand design tasks. Together, these approaches contribute to advancing fragment identification and provide valuable tools for fragment-based drug discovery.
Multi-domain Distribution Learning for De Novo Drug Design
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:We introduce DrugFlow, a generative model for structure-based drug design that integrates continuous flow matching with discrete Markov bridges, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance in learning chemical, geometric, and physical aspects of three-dimensional protein-ligand data. We endow DrugFlow with an uncertainty estimate that is able to detect out-of-distribution samples. To further enhance the sampling process towards distribution regions with desirable metric values, we propose a joint preference alignment scheme applicable to both flow matching and Markov bridge frameworks. Furthermore, we extend our model to also explore the conformational landscape of the protein by jointly sampling side chain angles and molecules.
RetroBridge: Modeling Retrosynthesis with Markov Bridges
Aug 30, 2023



Abstract:Retrosynthesis planning is a fundamental challenge in chemistry which aims at designing reaction pathways from commercially available starting materials to a target molecule. Each step in multi-step retrosynthesis planning requires accurate prediction of possible precursor molecules given the target molecule and confidence estimates to guide heuristic search algorithms. We model single-step retrosynthesis planning as a distribution learning problem in a discrete state space. First, we introduce the Markov Bridge Model, a generative framework aimed to approximate the dependency between two intractable discrete distributions accessible via a finite sample of coupled data points. Our framework is based on the concept of a Markov bridge, a Markov process pinned at its endpoints. Unlike diffusion-based methods, our Markov Bridge Model does not need a tractable noise distribution as a sampling proxy and directly operates on the input product molecules as samples from the intractable prior distribution. We then address the retrosynthesis planning problem with our novel framework and introduce RetroBridge, a template-free retrosynthesis modeling approach that achieves state-of-the-art results on standard evaluation benchmarks.
Structure-based Drug Design with Equivariant Diffusion Models
Oct 24, 2022Abstract:Structure-based drug design (SBDD) aims to design small-molecule ligands that bind with high affinity and specificity to pre-determined protein targets. Traditional SBDD pipelines start with large-scale docking of compound libraries from public databases, thus limiting the exploration of chemical space to existent previously studied regions. Recent machine learning methods approached this problem using an atom-by-atom generation approach, which is computationally expensive. In this paper, we formulate SBDD as a 3D-conditional generation problem and present DiffSBDD, an E(3)-equivariant 3D-conditional diffusion model that generates novel ligands conditioned on protein pockets. Furthermore, we curate a new dataset of experimentally determined binding complex data from Binding MOAD to provide a realistic binding scenario that complements the synthetic CrossDocked dataset. Comprehensive in silico experiments demonstrate the efficiency of DiffSBDD in generating novel and diverse drug-like ligands that engage protein pockets with high binding energies as predicted by in silico docking.
Equivariant 3D-Conditional Diffusion Models for Molecular Linker Design
Oct 11, 2022



Abstract:Fragment-based drug discovery has been an effective paradigm in early-stage drug development. An open challenge in this area is designing linkers between disconnected molecular fragments of interest to obtain chemically-relevant candidate drug molecules. In this work, we propose DiffLinker, an E(3)-equivariant 3D-conditional diffusion model for molecular linker design. Given a set of disconnected fragments, our model places missing atoms in between and designs a molecule incorporating all the initial fragments. Unlike previous approaches that are only able to connect pairs of molecular fragments, our method can link an arbitrary number of fragments. Additionally, the model automatically determines the number of atoms in the linker and its attachment points to the input fragments. We demonstrate that DiffLinker outperforms other methods on the standard datasets generating more diverse and synthetically-accessible molecules. Besides, we experimentally test our method in real-world applications, showing that it can successfully generate valid linkers conditioned on target protein pockets.
6DCNN with roto-translational convolution filters for volumetric data processing
Jul 30, 2021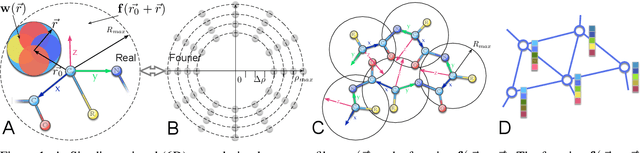
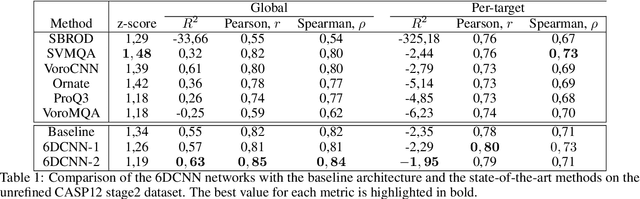
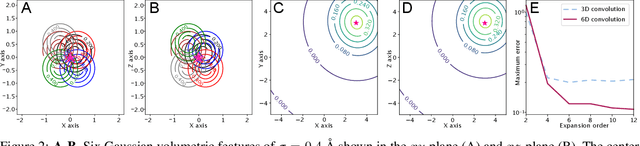
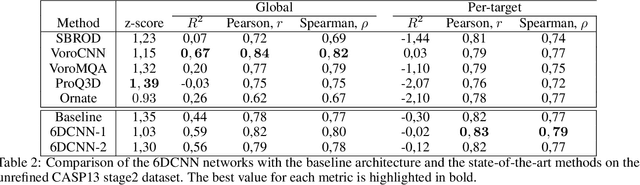
Abstract:In this work, we introduce 6D Convolutional Neural Network (6DCNN) designed to tackle the problem of detecting relative positions and orientations of local patterns when processing three-dimensional volumetric data. 6DCNN also includes SE(3)-equivariant message-passing and nonlinear activation operations constructed in the Fourier space. Working in the Fourier space allows significantly reducing the computational complexity of our operations. We demonstrate the properties of the 6D convolution and its efficiency in the recognition of spatial patterns. We also assess the 6DCNN model on several datasets from the recent CASP protein structure prediction challenges. Here, 6DCNN improves over the baseline architecture and also outperforms the state of the art.
Spherical convolutions on molecular graphs for protein model quality assessment
Nov 16, 2020



Abstract:Processing information on 3D objects requires methods stable to rigid-body transformations, in particular rotations, of the input data. In image processing tasks, convolutional neural networks achieve this property using rotation-equivariant operations. However, contrary to images, graphs generally have irregular topology. This makes it challenging to define a rotation-equivariant convolution operation on these structures. In this work, we propose Spherical Graph Convolutional Network (S-GCN) that processes 3D models of proteins represented as molecular graphs. In a protein molecule, individual amino acids have common topological elements. This allows us to unambiguously associate each amino acid with a local coordinate system and construct rotation-equivariant spherical filters that operate on angular information between graph nodes. Within the framework of the protein model quality assessment problem, we demonstrate that the proposed spherical convolution method significantly improves the quality of model assessment compared to the standard message-passing approach. It is also comparable to state-of-the-art methods, as we demonstrate on Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction (CASP) benchmarks. The proposed technique operates only on geometric features of protein 3D models. This makes it universal and applicable to any other geometric-learning task where the graph structure allows constructing local coordinate systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge