Hugo Jair Escalante
Labeling Comic Mischief Content in Online Videos with a Multimodal Hierarchical-Cross-Attention Model
Jun 12, 2024


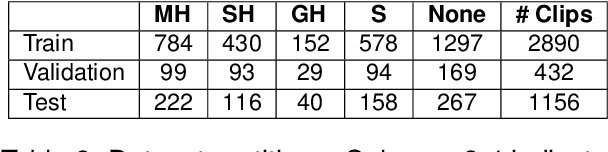
Abstract:We address the challenge of detecting questionable content in online media, specifically the subcategory of comic mischief. This type of content combines elements such as violence, adult content, or sarcasm with humor, making it difficult to detect. Employing a multimodal approach is vital to capture the subtle details inherent in comic mischief content. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel end-to-end multimodal system for the task of comic mischief detection. As part of this contribution, we release a novel dataset for the targeted task consisting of three modalities: video, text (video captions and subtitles), and audio. We also design a HIerarchical Cross-attention model with CAPtions (HICCAP) to capture the intricate relationships among these modalities. The results show that the proposed approach makes a significant improvement over robust baselines and state-of-the-art models for comic mischief detection and its type classification. This emphasizes the potential of our system to empower users, to make informed decisions about the online content they choose to see. In addition, we conduct experiments on the UCF101, HMDB51, and XD-Violence datasets, comparing our model against other state-of-the-art approaches showcasing the outstanding performance of our proposed model in various scenarios.
Unified Physical-Digital Attack Detection Challenge
Apr 09, 2024Abstract:Face Anti-Spoofing (FAS) is crucial to safeguard Face Recognition (FR) Systems. In real-world scenarios, FRs are confronted with both physical and digital attacks. However, existing algorithms often address only one type of attack at a time, which poses significant limitations in real-world scenarios where FR systems face hybrid physical-digital threats. To facilitate the research of Unified Attack Detection (UAD) algorithms, a large-scale UniAttackData dataset has been collected. UniAttackData is the largest public dataset for Unified Attack Detection, with a total of 28,706 videos, where each unique identity encompasses all advanced attack types. Based on this dataset, we organized a Unified Physical-Digital Face Attack Detection Challenge to boost the research in Unified Attack Detections. It attracted 136 teams for the development phase, with 13 qualifying for the final round. The results re-verified by the organizing team were used for the final ranking. This paper comprehensively reviews the challenge, detailing the dataset introduction, protocol definition, evaluation criteria, and a summary of published results. Finally, we focus on the detailed analysis of the highest-performing algorithms and offer potential directions for unified physical-digital attack detection inspired by this competition. Challenge Website: https://sites.google.com/view/face-anti-spoofing-challenge/welcome/challengecvpr2024.
Analysis of Systems' Performance in Natural Language Processing Competitions
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:Collaborative competitions have gained popularity in the scientific and technological fields. These competitions involve defining tasks, selecting evaluation scores, and devising result verification methods. In the standard scenario, participants receive a training set and are expected to provide a solution for a held-out dataset kept by organizers. An essential challenge for organizers arises when comparing algorithms' performance, assessing multiple participants, and ranking them. Statistical tools are often used for this purpose; however, traditional statistical methods often fail to capture decisive differences between systems' performance. This manuscript describes an evaluation methodology for statistically analyzing competition results and competition. The methodology is designed to be universally applicable; however, it is illustrated using eight natural language competitions as case studies involving classification and regression problems. The proposed methodology offers several advantages, including off-the-shell comparisons with correction mechanisms and the inclusion of confidence intervals. Furthermore, we introduce metrics that allow organizers to assess the difficulty of competitions. Our analysis shows the potential usefulness of our methodology for effectively evaluating competition results.
Academic competitions
Dec 01, 2023Abstract:Academic challenges comprise effective means for (i) advancing the state of the art, (ii) putting in the spotlight of a scientific community specific topics and problems, as well as (iii) closing the gap for under represented communities in terms of accessing and participating in the shaping of research fields. Competitions can be traced back for centuries and their achievements have had great influence in our modern world. Recently, they (re)gained popularity, with the overwhelming amounts of data that is being generated in different domains, as well as the need of pushing the barriers of existing methods, and available tools to handle such data. This chapter provides a survey of academic challenges in the context of machine learning and related fields. We review the most influential competitions in the last few years and analyze challenges per area of knowledge. The aims of scientific challenges, their goals, major achievements and expectations for the next few years are reviewed.
TurboGP: A flexible and advanced python based GP library
Aug 31, 2023Abstract:We introduce TurboGP, a Genetic Programming (GP) library fully written in Python and specifically designed for machine learning tasks. TurboGP implements modern features not available in other GP implementations, such as island and cellular population schemes, different types of genetic operations (migration, protected crossovers), online learning, among other features. TurboGP's most distinctive characteristic is its native support for different types of GP nodes to allow different abstraction levels, this makes TurboGP particularly useful for processing a wide variety of data sources.
Continuous Cartesian Genetic Programming based representation for Multi-Objective Neural Architecture Search
Jun 05, 2023Abstract:We propose a novel approach for the challenge of designing less complex yet highly effective convolutional neural networks (CNNs) through the use of cartesian genetic programming (CGP) for neural architecture search (NAS). Our approach combines real-based and block-chained CNNs representations based on CGP for optimization in the continuous domain using multi-objective evolutionary algorithms (MOEAs). Two variants are introduced that differ in the granularity of the search space they consider. The proposed CGP-NASV1 and CGP-NASV2 algorithms were evaluated using the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm II (NSGA-II) on the CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets. The empirical analysis was extended to assess the crossover operator from differential evolution (DE), the multi-objective evolutionary algorithm based on decomposition (MOEA/D) and S metric selection evolutionary multi-objective algorithm (SMS-EMOA) using the same representation. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach is competitive with state-of-the-art proposals in terms of classification performance and model complexity.
Comparison of classifiers in challenge scheme
May 16, 2023Abstract:In recent decades, challenges have become very popular in scientific research as these are crowdsourcing schemes. In particular, challenges are essential for developing machine learning algorithms. For the challenges settings, it is vital to establish the scientific question, the dataset (with adequate quality, quantity, diversity, and complexity), performance metrics, as well as a way to authenticate the participants' results (Gold Standard). This paper addresses the problem of evaluating the performance of different competitors (algorithms) under the restrictions imposed by the challenge scheme, such as the comparison of multiple competitors with a unique dataset (with fixed size), a minimal number of submissions and, a set of metrics chosen to assess performance. The algorithms are sorted according to the performance metric. Still, it is common to observe performance differences among competitors as small as hundredths or even thousandths, so the question is whether the differences are significant. This paper analyzes the results of the MeOffendEs@IberLEF 2021 competition and proposes to make inference through resampling techniques (bootstrap) to support Challenge organizers' decision-making.
Wild Face Anti-Spoofing Challenge 2023: Benchmark and Results
May 05, 2023Abstract:Face anti-spoofing (FAS) is an essential mechanism for safeguarding the integrity of automated face recognition systems. Despite substantial advancements, the generalization of existing approaches to real-world applications remains challenging. This limitation can be attributed to the scarcity and lack of diversity in publicly available FAS datasets, which often leads to overfitting during training or saturation during testing. In terms of quantity, the number of spoof subjects is a critical determinant. Most datasets comprise fewer than 2,000 subjects. With regard to diversity, the majority of datasets consist of spoof samples collected in controlled environments using repetitive, mechanical processes. This data collection methodology results in homogenized samples and a dearth of scenario diversity. To address these shortcomings, we introduce the Wild Face Anti-Spoofing (WFAS) dataset, a large-scale, diverse FAS dataset collected in unconstrained settings. Our dataset encompasses 853,729 images of 321,751 spoof subjects and 529,571 images of 148,169 live subjects, representing a substantial increase in quantity. Moreover, our dataset incorporates spoof data obtained from the internet, spanning a wide array of scenarios and various commercial sensors, including 17 presentation attacks (PAs) that encompass both 2D and 3D forms. This novel data collection strategy markedly enhances FAS data diversity. Leveraging the WFAS dataset and Protocol 1 (Known-Type), we host the Wild Face Anti-Spoofing Challenge at the CVPR2023 workshop. Additionally, we meticulously evaluate representative methods using Protocol 1 and Protocol 2 (Unknown-Type). Through an in-depth examination of the challenge outcomes and benchmark baselines, we provide insightful analyses and propose potential avenues for future research. The dataset is released under Insightface.
Surveillance Face Presentation Attack Detection Challenge
Apr 15, 2023Abstract:Face Anti-spoofing (FAS) is essential to secure face recognition systems from various physical attacks. However, most of the studies lacked consideration of long-distance scenarios. Specifically, compared with FAS in traditional scenes such as phone unlocking, face payment, and self-service security inspection, FAS in long-distance such as station squares, parks, and self-service supermarkets are equally important, but it has not been sufficiently explored yet. In order to fill this gap in the FAS community, we collect a large-scale Surveillance High-Fidelity Mask (SuHiFiMask). SuHiFiMask contains $10,195$ videos from $101$ subjects of different age groups, which are collected by $7$ mainstream surveillance cameras. Based on this dataset and protocol-$3$ for evaluating the robustness of the algorithm under quality changes, we organized a face presentation attack detection challenge in surveillance scenarios. It attracted 180 teams for the development phase with a total of 37 teams qualifying for the final round. The organization team re-verified and re-ran the submitted code and used the results as the final ranking. In this paper, we present an overview of the challenge, including an introduction to the dataset used, the definition of the protocol, the evaluation metrics, and the announcement of the competition results. Finally, we present the top-ranked algorithms and the research ideas provided by the competition for attack detection in long-range surveillance scenarios.
Multi-Branch Deep Radial Basis Function Networks for Facial Emotion Recognition
Sep 07, 2021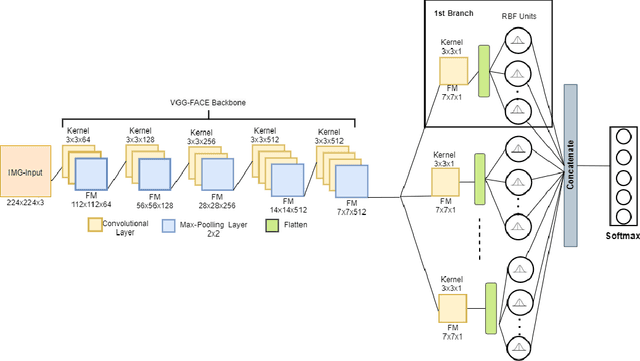
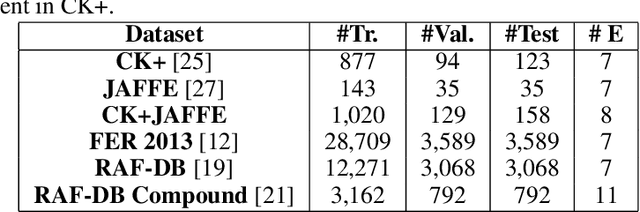
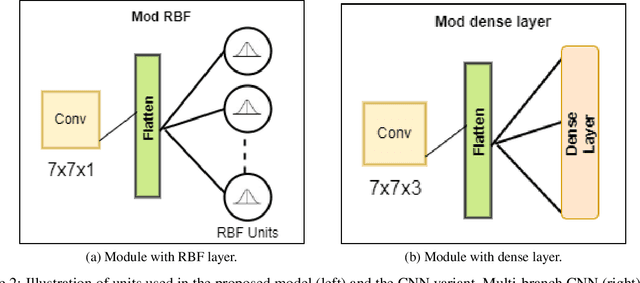
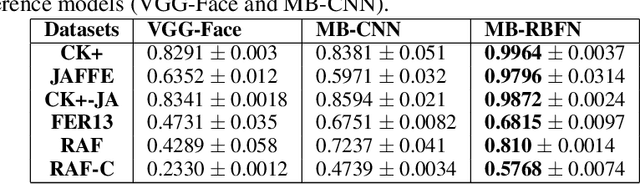
Abstract:Emotion recognition (ER) from facial images is one of the landmark tasks in affective computing with major developments in the last decade. Initial efforts on ER relied on handcrafted features that were used to characterize facial images and then feed to standard predictive models. Recent methodologies comprise end-to-end trainable deep learning methods that simultaneously learn both, features and predictive model. Perhaps the most successful models are based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). While these models have excelled at this task, they still fail at capturing local patterns that could emerge in the learning process. We hypothesize these patterns could be captured by variants based on locally weighted learning. Specifically, in this paper we propose a CNN based architecture enhanced with multiple branches formed by radial basis function (RBF) units that aims at exploiting local information at the final stage of the learning process. Intuitively, these RBF units capture local patterns shared by similar instances using an intermediate representation, then the outputs of the RBFs are feed to a softmax layer that exploits this information to improve the predictive performance of the model. This feature could be particularly advantageous in ER as cultural / ethnicity differences may be identified by the local units. We evaluate the proposed method in several ER datasets and show the proposed methodology achieves state-of-the-art in some of them, even when we adopt a pre-trained VGG-Face model as backbone. We show it is the incorporation of local information what makes the proposed model competitive.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge