Hongwei Xu
Compressive Toeplitz Covariance Estimation From Few-Bit Quantized Measurements With Applications to DOA Estimation
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of estimating the Hermitian Toeplitz covariance matrix under practical hardware constraints of sparse observations and coarse quantization. Within the triangular-dithered quantization framework, we propose an estimator called Toeplitz-projected sample covariance matrix (Q-TSCM) to compensate for the quantization-induced bias, together with its finite-bit counterpart termed the $2k$-bit Toeplitz-projected sample covariance matrix ($2k$-TSCM), obtained by truncating the pre-quantization observations. Under the complex Gaussian assumption, we derive non-asymptotic error bounds of the estimators that reveal a quadratic dependence on the quantization level and capture the effect of sparse sampling patterns through the so-called coverage coefficient. To further improve performance, we propose the quantized sparse and parametric approach (Q-SPA) based on a covariance-fitting criterion, which enforces additionally positive semidefiniteness at the cost of solving a semidefinite program. Numerical experiments are presented that corroborate our theoretical findings and demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed estimators in the application to direction-of-arrival estimation.
NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image Generation Model Quality Assessment
May 22, 2025Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image (T2I) generation model quality assessment, which will be held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement Workshop (NTIRE) at CVPR 2025. The aim of this challenge is to address the fine-grained quality assessment of text-to-image generation models. This challenge evaluates text-to-image models from two aspects: image-text alignment and image structural distortion detection, and is divided into the alignment track and the structural track. The alignment track uses the EvalMuse-40K, which contains around 40K AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) generated by 20 popular generative models. The alignment track has a total of 371 registered participants. A total of 1,883 submissions are received in the development phase, and 507 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 12 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. The structure track uses the EvalMuse-Structure, which contains 10,000 AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) with corresponding structural distortion mask. A total of 211 participants have registered in the structure track. A total of 1155 submissions are received in the development phase, and 487 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 8 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Almost all methods have achieved better results than baseline methods, and the winning methods in both tracks have demonstrated superior prediction performance on T2I model quality assessment.
Bit Efficient Toeplitz Covariance Estimation
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of Toeplitz covariance matrix estimation from partial entries of random quantized samples. To balance trade-offs among the number of samples, the number of entries observed per sample, and the data resolution, we propose a ruler-based quantized Toeplitz covariance estimator. We derive non-asymptotic error bounds and analyze the convergence rates of the proposed estimator. Our results show that the estimator is near-optimal and imply that reducing data resolution within a certain range has a limited impact on the estimation accuracy. Numerical experiments are provided that validate our theoretical findings and show effectiveness of the proposed estimator.
MMFace4D: A Large-Scale Multi-Modal 4D Face Dataset for Audio-Driven 3D Face Animation
Mar 17, 2023



Abstract:Audio-Driven Face Animation is an eagerly anticipated technique for applications such as VR/AR, games, and movie making. With the rapid development of 3D engines, there is an increasing demand for driving 3D faces with audio. However, currently available 3D face animation datasets are either scale-limited or quality-unsatisfied, which hampers further developments of audio-driven 3D face animation. To address this challenge, we propose MMFace4D, a large-scale multi-modal 4D (3D sequence) face dataset consisting of 431 identities, 35,904 sequences, and 3.9 million frames. MMFace4D has three appealing characteristics: 1) highly diversified subjects and corpus, 2) synchronized audio and 3D mesh sequence with high-resolution face details, and 3) low storage cost with a new efficient compression algorithm on 3D mesh sequences. These characteristics enable the training of high-fidelity, expressive, and generalizable face animation models. Upon MMFace4D, we construct a challenging benchmark of audio-driven 3D face animation with a strong baseline, which enables non-autoregressive generation with fast inference speed and outperforms the state-of-the-art autoregressive method. The whole benchmark will be released.
SubFace: Learning with Softmax Approximation for Face Recognition
Aug 24, 2022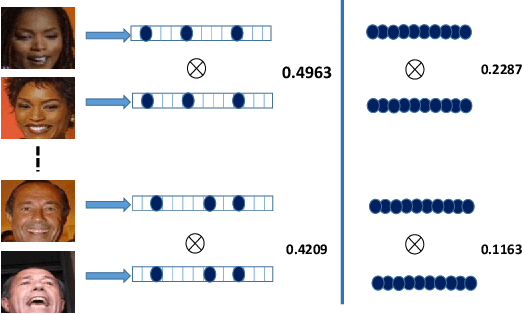

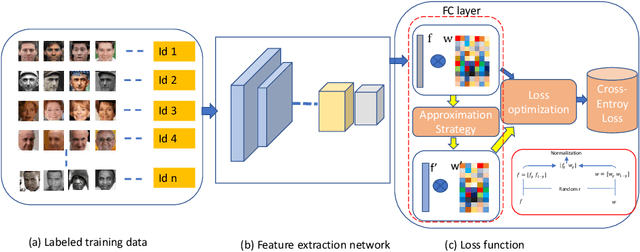

Abstract:The softmax-based loss functions and its variants (e.g., cosface, sphereface, and arcface) significantly improve the face recognition performance in wild unconstrained scenes. A common practice of these algorithms is to perform optimizations on the multiplication between the embedding features and the linear transformation matrix. However in most cases, the dimension of embedding features is given based on traditional design experience, and there is less-studied on improving performance using the feature itself when giving a fixed size. To address this challenge, this paper presents a softmax approximation method called SubFace, which employs the subspace feature to promote the performance of face recognition. Specifically, we dynamically select the non-overlapping subspace features in each batch during training, and then use the subspace features to approximate full-feature among softmax-based loss, so the discriminability of the deep model can be significantly enhanced for face recognition. Comprehensive experiments conducted on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method can significantly improve the performance of vanilla CNN baseline, which strongly proves the effectiveness of subspace strategy with the margin-based loss.
High-Quality Real Time Facial Capture Based on Single Camera
Nov 15, 2021



Abstract:We propose a real time deep learning framework for video-based facial expression capture. Our process uses a high-end facial capture pipeline based on FACEGOOD to capture facial expression. We train a convolutional neural network to produce high-quality continuous blendshape weight output from video training. Since this facial capture is fully automated, our system can drastically reduce the amount of labor involved in the development of modern narrative-driven video games or films involving realistic digital doubles of actors and potentially hours of animated dialogue per character. We demonstrate compelling animation inference in challenging areas such as eyes and lips.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge