Hongwei Lin
HOMURA: Taming the Sand-Glass for Time-Constrained LLM Translation via Reinforcement Learning
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable strides in multilingual translation but are hindered by a systemic cross-lingual verbosity bias, rendering them unsuitable for strict time-constrained tasks like subtitling and dubbing. Current prompt-engineering approaches struggle to resolve this conflict between semantic fidelity and rigid temporal feasibility. To bridge this gap, we first introduce Sand-Glass, a benchmark specifically designed to evaluate translation under syllable-level duration constraints. Furthermore, we propose HOMURA, a reinforcement learning framework that explicitly optimizes the trade-off between semantic preservation and temporal compliance. By employing a KL-regularized objective with a novel dynamic syllable-ratio reward, HOMURA effectively "tames" the output length. Experimental results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms strong LLM baselines, achieving precise length control that respects linguistic density hierarchies without compromising semantic adequacy.
Predicting Region of Interest in Human Visual Search Based on Statistical Texture and Gabor Features
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Understanding human visual search behavior is a fundamental problem in vision science and computer vision, with direct implications for modeling how observers allocate attention in location-unknown search tasks. In this study, we investigate the relationship between Gabor-based features and gray-level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM) based texture features in modeling early-stage visual search behavior. Two feature-combination pipelines are proposed to integrate Gabor and GLCM features for narrowing the region of possible human fixations. The pipelines are evaluated using simulated digital breast tomosynthesis images. Results show qualitative agreement among fixation candidates predicted by the proposed pipelines and a threshold-based model observer. A strong correlation is observed between GLCM mean and Gabor feature responses, indicating that these features encode related image information despite their different formulations. Eye-tracking data from human observers further suggest consistency between predicted fixation regions and early-stage gaze behavior. These findings highlight the value of combining structural and texture-based features for modeling visual search and support the development of perceptually informed observer models.
Application of Ideal Observer for Thresholded Data in Search Task
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:This study advances task-based image quality assessment by developing an anthropomorphic thresholded visual-search model observer. The model is an ideal observer for thresholded data inspired by the human visual system, allowing selective processing of high-salience features to improve discrimination performance. By filtering out irrelevant variability, the model enhances diagnostic accuracy and computational efficiency. The observer employs a two-stage framework: candidate selection and decision-making. Using thresholded data during candidate selection refines regions of interest, while stage-specific feature processing optimizes performance. Simulations were conducted to evaluate the effects of thresholding on feature maps, candidate localization, and multi-feature scenarios. Results demonstrate that thresholding improves observer performance by excluding low-salience features, particularly in noisy environments. Intermediate thresholds often outperform no thresholding, indicating that retaining only relevant features is more effective than keeping all features. Additionally, the model demonstrates effective training with fewer images while maintaining alignment with human performance. These findings suggest that the proposed novel framework can predict human visual search performance in clinically realistic tasks and provide solutions for model observer training with limited resources. Our novel approach has applications in other areas where human visual search and detection tasks are modeled such as in computer vision, machine learning, defense and security image analysis.
TUN: Detecting Significant Points in Persistence Diagrams with Deep Learning
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Persistence diagrams (PDs) provide a powerful tool for understanding the topology of the underlying shape of a point cloud. However, identifying which points in PDs encode genuine signals remains challenging. This challenge directly hinders the practical adoption of topological data analysis in many applications, where automated and reliable interpretation of persistence diagrams is essential for downstream decision-making. In this paper, we study automatic significance detection for one-dimensional persistence diagrams. Specifically, we propose Topology Understanding Net (TUN), a multi-modal network that combines enhanced PD descriptors with self-attention, a PointNet-style point cloud encoder, learned fusion, and per-point classification, alongside stable preprocessing and imbalance-aware training. It provides an automated and effective solution for identifying significant points in PDs, which are critical for downstream applications. Experiments show that TUN outperforms classic methods in detecting significant points in PDs, illustrating its effectiveness in real-world applications.
OC3D: Weakly Supervised Outdoor 3D Object Detection with Only Coarse Click Annotation
Aug 15, 2024



Abstract:LiDAR-based outdoor 3D object detection has received widespread attention. However, training 3D detectors from the LiDAR point cloud typically relies on expensive bounding box annotations. This paper presents OC3D, an innovative weakly supervised method requiring only coarse clicks on the bird' s eye view of the 3D point cloud. A key challenge here is the absence of complete geometric descriptions of the target objects from such simple click annotations. To address this problem, our proposed OC3D adopts a two-stage strategy. In the first stage, we initially design a novel dynamic and static classification strategy and then propose the Click2Box and Click2Mask modules to generate box-level and mask-level pseudo-labels for static and dynamic instances, respectively. In the second stage, we design a Mask2Box module, leveraging the learning capabilities of neural networks to update mask-level pseudo-labels, which contain less information, to box level pseudo-labels. Experimental results on the widely used KITTI and nuScenes datasets demonstrate that our OC3D with only coarse clicks achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to weakly-supervised 3D detection methods. Combining OC3D with a missing click mining strategy, we propose a OC3D++ pipeline, which requires only 0.2% annotation cost in the KITTI dataset to achieve performance comparable to fully supervised methods.
Functional Network: A Novel Framework for Interpretability of Deep Neural Networks
May 24, 2022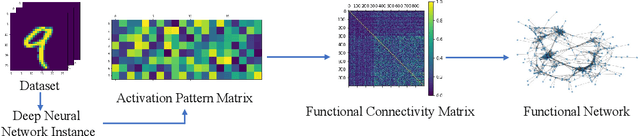
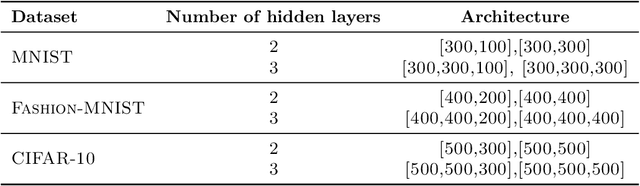
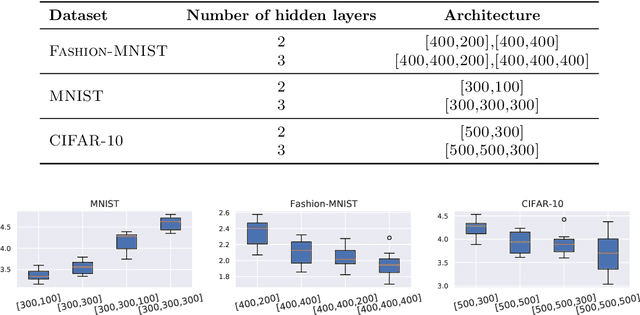
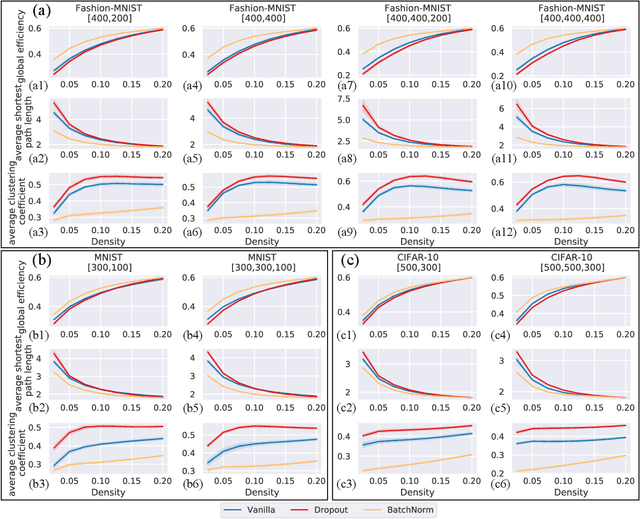
Abstract:The layered structure of deep neural networks hinders the use of numerous analysis tools and thus the development of its interpretability. Inspired by the success of functional brain networks, we propose a novel framework for interpretability of deep neural networks, that is, the functional network. We construct the functional network of fully connected networks and explore its small-worldness. In our experiments, the mechanisms of regularization methods, namely, batch normalization and dropout, are revealed using graph theoretical analysis and topological data analysis. Our empirical analysis shows the following: (1) Batch normalization enhances model performance by increasing the global e ciency and the number of loops but reduces adversarial robustness by lowering the fault tolerance. (2) Dropout improves generalization and robustness of models by improving the functional specialization and fault tolerance. (3) The models with dierent regularizations can be clustered correctly according to their functional topological dierences, re ecting the great potential of the functional network and topological data analysis in interpretability.
High-Dimensional Data Set Simplification by Laplace-Beltrami Operator
Mar 23, 2020
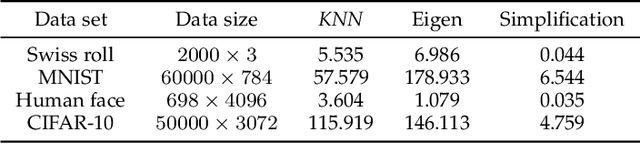
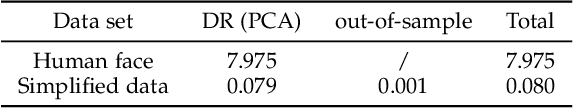
Abstract:With the development of the Internet and other digital technologies, the speed of data generation has become considerably faster than the speed of data processing. Because big data typically contain massive redundant information, it is possible to significantly simplify a big data set while maintaining the key information it contains. In this paper, we develop a big data simplification method based on the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of the Laplace-Beltrami operator (LBO). Specifically, given a data set that can be considered as an unorganized data point set in high-dimensional space, a discrete LBO defined on the big data set is constructed and its eigenvalues and eigenvectors are calculated. Then, the local extremum and the saddle points of the eigenfunctions are proposed to be the feature points of a data set in high-dimensional space, constituting a simplified data set. Moreover, we develop feature point detection methods for the functions defined on an unorganized data point set in high-dimensional space, and devise metrics for measuring the fidelity of the simplified data set to the original set. Finally, examples and applications are demonstrated to validate the efficiency and effectiveness of the proposed methods, demonstrating that data set simplification is a method for processing a maximum-sized data set using a limited data processing capability.
Persistence B-Spline Grids: Stable Vector Representation of Persistence Diagrams Based on Data Fitting
Sep 17, 2019
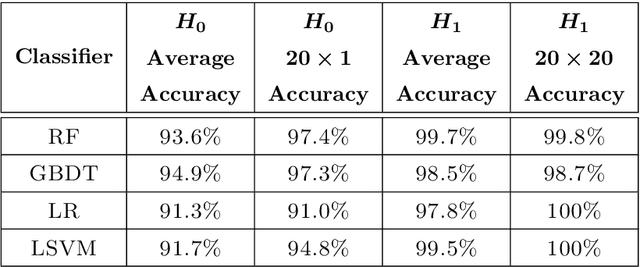

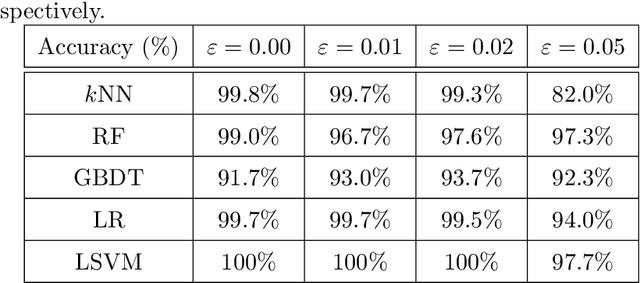
Abstract:Over the last decades, many attempts have been made to optimally integrate machine learning (ML) and topological data analysis. A prominent problem in applying persistent homology to ML tasks is finding a vector representation of a persistence diagram (PD), which is a summary diagram for representing topological features. From the perspective of data fitting, a stable vector representation, persistence B-spline grid (PB), is proposed based on the efficient technique of progressive-iterative approximation for least-squares B-spline surface fitting. Meanwhile, we theoretically prove that the PB method is stable with respect to the metrics defined on the PD space, i.e., the $p$-Wasserstein distance and the bottleneck distance. The proposed method was tested on a synthetic dataset, datasets of randomly generated PDs, data of a dynamical system, and 3D CAD models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge