Holger Voos
Human Interaction for Collaborative Semantic SLAM using Extended Reality
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Semantic SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) systems enrich robot maps with structural and semantic information, enabling robots to operate more effectively in complex environments. However, these systems struggle in real-world scenarios with occlusions, incomplete data, or ambiguous geometries, as they cannot fully leverage the higher-level spatial and semantic knowledge humans naturally apply. We introduce HICS-SLAM, a Human-in-the-Loop semantic SLAM framework that uses a shared extended reality environment for real-time collaboration. The system allows human operators to directly interact with and visualize the robot's 3D scene graph, and add high-level semantic concepts (e.g., rooms or structural entities) into the mapping process. We propose a graph-based semantic fusion methodology that integrates these human interventions with robot perception, enabling scalable collaboration for enhanced situational awareness. Experimental evaluations on real-world construction site datasets demonstrate improvements in room detection accuracy, map precision, and semantic completeness compared to automated baselines, demonstrating both the effectiveness of the approach and its potential for future extensions.
BIM Informed Visual SLAM for Construction Monitoring
Sep 17, 2025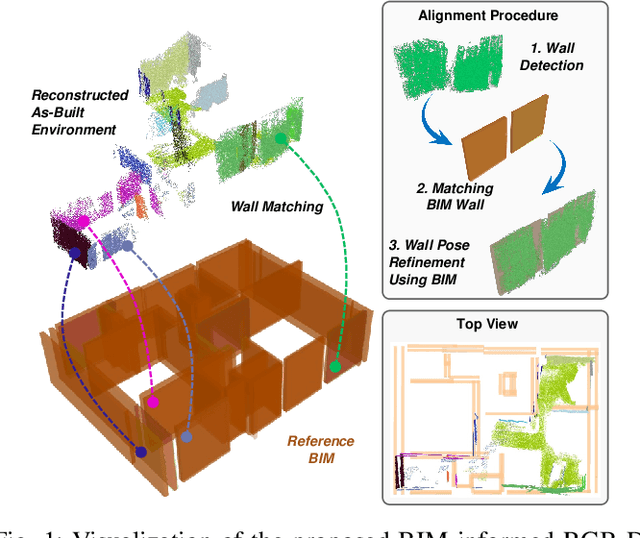

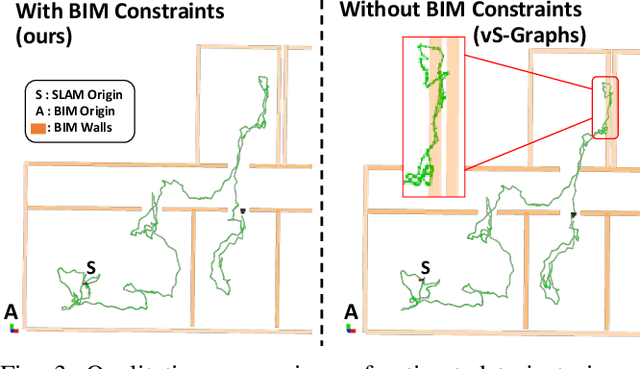

Abstract:Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) is a key tool for monitoring construction sites, where aligning the evolving as-built state with the as-planned design enables early error detection and reduces costly rework. LiDAR-based SLAM achieves high geometric precision, but its sensors are typically large and power-demanding, limiting their use on portable platforms. Visual SLAM offers a practical alternative with lightweight cameras already embedded in most mobile devices. however, visually mapping construction environments remains challenging: repetitive layouts, occlusions, and incomplete or low-texture structures often cause drift in the trajectory map. To mitigate this, we propose an RGB-D SLAM system that incorporates the Building Information Model (BIM) as structural prior knowledge. Instead of relying solely on visual cues, our system continuously establishes correspondences between detected wall and their BIM counterparts, which are then introduced as constraints in the back-end optimization. The proposed method operates in real time and has been validated on real construction sites, reducing trajectory error by an average of 23.71% and map RMSE by 7.14% compared to visual SLAM baselines. These results demonstrate that BIM constraints enable reliable alignment of the digital plan with the as-built scene, even under partially constructed conditions.
SMapper: A Multi-Modal Data Acquisition Platform for SLAM Benchmarking
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Advancing research in fields like Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) and autonomous navigation critically depends on reliable and reproducible multimodal datasets. While several influential datasets have driven progress in these domains, they often suffer from limitations in sensing modalities, environmental diversity, and the reproducibility of the underlying hardware setups. To address these challenges, this paper introduces SMapper, a novel open-hardware, multi-sensor platform designed explicitly for, though not limited to, SLAM research. The device integrates synchronized LiDAR, multi-camera, and inertial sensing, supported by a robust calibration and synchronization pipeline that ensures precise spatio-temporal alignment across modalities. Its open and replicable design allows researchers to extend its capabilities and reproduce experiments across both handheld and robot-mounted scenarios. To demonstrate its practicality, we additionally release SMapper-light, a publicly available SLAM dataset containing representative indoor and outdoor sequences. The dataset includes tightly synchronized multimodal data and ground-truth trajectories derived from offline LiDAR-based SLAM with sub-centimeter accuracy, alongside dense 3D reconstructions. Furthermore, the paper contains benchmarking results on state-of-the-art LiDAR and visual SLAM frameworks using the SMapper-light dataset. By combining open-hardware design, reproducible data collection, and comprehensive benchmarking, SMapper establishes a robust foundation for advancing SLAM algorithm development, evaluation, and reproducibility.
Situationally-aware Path Planning Exploiting 3D Scene Graphs
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:3D Scene Graphs integrate both metric and semantic information, yet their structure remains underutilized for improving path planning efficiency and interpretability. In this work, we present S-Path, a situationally-aware path planner that leverages the metric-semantic structure of indoor 3D Scene Graphs to significantly enhance planning efficiency. S-Path follows a two-stage process: it first performs a search over a semantic graph derived from the scene graph to yield a human-understandable high-level path. This also identifies relevant regions for planning, which later allows the decomposition of the problem into smaller, independent subproblems that can be solved in parallel. We also introduce a replanning mechanism that, in the event of an infeasible path, reuses information from previously solved subproblems to update semantic heuristics and prioritize reuse to further improve the efficiency of future planning attempts. Extensive experiments on both real-world and simulated environments show that S-Path achieves average reductions of 5.7x in planning time while maintaining comparable path optimality to classical sampling-based planners and surpassing them in complex scenarios, making it an efficient and interpretable path planner for environments represented by indoor 3D Scene Graphs.
Barrier Method for Inequality Constrained Factor Graph Optimization with Application to Model Predictive Control
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:Factor graphs have demonstrated remarkable efficiency for robotic perception tasks, particularly in localization and mapping applications. However, their application to optimal control problems -- especially Model Predictive Control (MPC) -- has remained limited due to fundamental challenges in constraint handling. This paper presents a novel integration of the Barrier Interior Point Method (BIPM) with factor graphs, implemented as an open-source extension to the widely adopted g2o framework. Our approach introduces specialized inequality factor nodes that encode logarithmic barrier functions, thereby overcoming the quadratic-form limitations of conventional factor graph formulations. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first g2o-based implementation capable of efficiently handling both equality and inequality constraints within a unified optimization backend. We validate the method through a multi-objective adaptive cruise control application for autonomous vehicles. Benchmark comparisons with state-of-the-art constraint-handling techniques demonstrate faster convergence and improved computational efficiency. (Code repository: https://github.com/snt-arg/bipm_g2o)
BIM-Constrained Optimization for Accurate Localization and Deviation Correction in Construction Monitoring
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Augmented reality (AR) applications for construction monitoring rely on real-time environmental tracking to visualize architectural elements. However, construction sites present significant challenges for traditional tracking methods due to featureless surfaces, dynamic changes, and drift accumulation, leading to misalignment between digital models and the physical world. This paper proposes a BIM-aware drift correction method to address these challenges. Instead of relying solely on SLAM-based localization, we align ``as-built" detected planes from the real-world environment with ``as-planned" architectural planes in BIM. Our method performs robust plane matching and computes a transformation (TF) between SLAM (S) and BIM (B) origin frames using optimization techniques, minimizing drift over time. By incorporating BIM as prior structural knowledge, we can achieve improved long-term localization and enhanced AR visualization accuracy in noisy construction environments. The method is evaluated through real-world experiments, showing significant reductions in drift-induced errors and optimized alignment consistency. On average, our system achieves a reduction of 52.24% in angular deviations and a reduction of 60.8% in the distance error of the matched walls compared to the initial manual alignment by the user.
Hardware, Algorithms, and Applications of the Neuromorphic Vision Sensor: a Review
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Neuromorphic, or event, cameras represent a transformation in the classical approach to visual sensing encodes detected instantaneous per-pixel illumination changes into an asynchronous stream of event packets. Their novelty compared to standard cameras lies in the transition from capturing full picture frames at fixed time intervals to a sparse data format which, with its distinctive qualities, offers potential improvements in various applications. However, these advantages come at the cost of reinventing algorithmic procedures or adapting them to effectively process the new data format. In this survey, we systematically examine neuromorphic vision along three main dimensions. First, we highlight the technological evolution and distinctive hardware features of neuromorphic cameras from their inception to recent models. Second, we review image processing algorithms developed explicitly for event-based data, covering key works on feature detection, tracking, and optical flow -which form the basis for analyzing image elements and transformations -as well as depth and pose estimation or object recognition, which interpret more complex scene structures and components. These techniques, drawn from classical computer vision and modern data-driven approaches, are examined to illustrate the breadth of applications for event-based cameras. Third, we present practical application case studies demonstrating how event cameras have been successfully used across various industries and scenarios. Finally, we analyze the challenges limiting widespread adoption, identify significant research gaps compared to standard imaging techniques, and outline promising future directions and opportunities that neuromorphic vision offers.
Reinforcement Learning-Based Neuroadaptive Control of Robotic Manipulators under Deferred Constraints
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a reinforcement learning-based neuroadaptive control framework for robotic manipulators operating under deferred constraints. The proposed approach improves traditional barrier Lyapunov functions by introducing a smooth constraint enforcement mechanism that offers two key advantages: (i) it minimizes control effort in unconstrained regions and progressively increases it near constraints, improving energy efficiency, and (ii) it enables gradual constraint activation through a prescribed-time shifting function, allowing safe operation even when initial conditions violate constraints. To address system uncertainties and improve adaptability, an actor-critic reinforcement learning framework is employed. The critic network estimates the value function, while the actor network learns an optimal control policy in real time, enabling adaptive constraint handling without requiring explicit system modeling. Lyapunov-based stability analysis guarantees the boundedness of all closed-loop signals. The effectiveness of the proposed method is validated through numerical simulations.
Category-level Meta-learned NeRF Priors for Efficient Object Mapping
Mar 05, 2025



Abstract:In 3D object mapping, category-level priors enable efficient object reconstruction and canonical pose estimation, requiring only a single prior per semantic category (e.g., chair, book, laptop). Recently, DeepSDF has predominantly been used as a category-level shape prior, but it struggles to reconstruct sharp geometry and is computationally expensive. In contrast, NeRFs capture fine details but have yet to be effectively integrated with category-level priors in a real-time multi-object mapping framework. To bridge this gap, we introduce PRENOM, a Prior-based Efficient Neural Object Mapper that integrates category-level priors with object-level NeRFs to enhance reconstruction efficiency while enabling canonical object pose estimation. PRENOM gets to know objects on a first-name basis by meta-learning on synthetic reconstruction tasks generated from open-source shape datasets. To account for object category variations, it employs a multi-objective genetic algorithm to optimize the NeRF architecture for each category, balancing reconstruction quality and training time. Additionally, prior-based probabilistic ray sampling directs sampling toward expected object regions, accelerating convergence and improving reconstruction quality under constrained resources. Experimental results on a low-end GPU highlight the ability of PRENOM to achieve high-quality reconstructions while maintaining computational feasibility. Specifically, comparisons with prior-free NeRF-based approaches on a synthetic dataset show a 21% lower Chamfer distance, demonstrating better reconstruction quality. Furthermore, evaluations against other approaches using shape priors on a noisy real-world dataset indicate a 13% improvement averaged across all reconstruction metrics, and comparable pose and size estimation accuracy, while being trained for 5x less time.
ecg2o: A Seamless Extension of g2o for Equality-Constrained Factor Graph Optimization
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Factor graph optimization serves as a fundamental framework for robotic perception, enabling applications such as pose estimation, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), structure-from-motion (SfM), and situational awareness. Traditionally, these methods solve unconstrained least squares problems using algorithms such as Gauss-Newton and Levenberg-Marquardt. However, extending factor graphs with native support for equality constraints can improve solution accuracy and broaden their applicability, particularly in optimal control. In this paper, we propose a novel extension of factor graphs that seamlessly incorporates equality constraints without requiring additional optimization algorithms. Our approach maintains the efficiency and flexibility of existing second-order optimization techniques while ensuring constraint feasibility. To validate our method, we apply it to an optimal control problem for velocity tracking in autonomous vehicles and benchmark our results against state-of-the-art constraint handling techniques. Additionally, we introduce ecg2o, a header-only C++ library that extends the widely used g2o factor graph library by adding full support for equality-constrained optimization. This library, along with demonstrative examples and the optimal control problem, is available as open source at https://github.com/snt-arg/ecg2o
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge