Claudio Cimarelli
Hardware, Algorithms, and Applications of the Neuromorphic Vision Sensor: a Review
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Neuromorphic, or event, cameras represent a transformation in the classical approach to visual sensing encodes detected instantaneous per-pixel illumination changes into an asynchronous stream of event packets. Their novelty compared to standard cameras lies in the transition from capturing full picture frames at fixed time intervals to a sparse data format which, with its distinctive qualities, offers potential improvements in various applications. However, these advantages come at the cost of reinventing algorithmic procedures or adapting them to effectively process the new data format. In this survey, we systematically examine neuromorphic vision along three main dimensions. First, we highlight the technological evolution and distinctive hardware features of neuromorphic cameras from their inception to recent models. Second, we review image processing algorithms developed explicitly for event-based data, covering key works on feature detection, tracking, and optical flow -which form the basis for analyzing image elements and transformations -as well as depth and pose estimation or object recognition, which interpret more complex scene structures and components. These techniques, drawn from classical computer vision and modern data-driven approaches, are examined to illustrate the breadth of applications for event-based cameras. Third, we present practical application case studies demonstrating how event cameras have been successfully used across various industries and scenarios. Finally, we analyze the challenges limiting widespread adoption, identify significant research gaps compared to standard imaging techniques, and outline promising future directions and opportunities that neuromorphic vision offers.
Graph-Based vs. Error State Kalman Filter-Based Fusion Of 5G And Inertial Data For MAV Indoor Pose Estimation
Mar 31, 2024Abstract:5G New Radio Time of Arrival (ToA) data has the potential to revolutionize indoor localization for micro aerial vehicles (MAVs). However, its performance under varying network setups, especially when combined with IMU data for real-time localization, has not been fully explored so far. In this study, we develop an error state Kalman filter (ESKF) and a pose graph optimization (PGO) approach to address this gap. We systematically evaluate the performance of the derived approaches for real-time MAV localization in realistic scenarios with 5G base stations in Line-Of-Sight (LOS), demonstrating the potential of 5G technologies in this domain. In order to experimentally test and compare our localization approaches, we augment the EuRoC MAV benchmark dataset for visual-inertial odometry with simulated yet highly realistic 5G ToA measurements. Our experimental results comprehensively assess the impact of varying network setups, including varying base station numbers and network configurations, on ToA-based MAV localization performance. The findings show promising results for seamless and robust localization using 5G ToA measurements, achieving an accuracy of 15 cm throughout the entire trajectory within a graph-based framework with five 5G base stations, and an accuracy of up to 34 cm in the case of ESKF-based localization. Additionally, we measure the run time of both algorithms and show that they are both fast enough for real-time implementation.
Pose Graph Optimization for a MAV Indoor Localization Fusing 5GNR TOA with an IMU
Jun 16, 2023



Abstract:This paper explores the potential of 5G new radio (NR) Time-of-Arrival (TOA) data for indoor drone localization under different scenarios and conditions when fused with inertial measurement unit (IMU) data. Our approach involves performing graph-based optimization to estimate the drone's position and orientation from the multiple sensor measurements. Due to the lack of real-world data, we use Matlab 5G toolbox and QuaDRiGa (quasi-deterministic radio channel generator) channel simulator to generate TOA measurements for the EuRoC MAV indoor dataset that provides IMU readings and ground truths 6DoF poses of a flying drone. Hence, we create twelve sequences combining three predefined indoor scenarios setups of QuaDRiGa with 2 to 5 base station antennas. Therefore, experimental results demonstrate that, for a sufficient number of base stations and a high bandwidth 5G configuration, the pose graph optimization approach achieves accurate drone localization, with an average error of less than 15 cm on the overall trajectory. Furthermore, the adopted graph-based optimization algorithm is fast and can be easily implemented for onboard real-time pose tracking on a micro aerial vehicle (MAV).
A Review of Radio Frequency Based Localization for Aerial and Ground Robots with 5G Future Perspectives
Dec 13, 2022Abstract:Efficient localization plays a vital role in many modern applications of Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGV) and Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), which would contribute to improved control, safety, power economy, etc. The ubiquitous 5G NR (New Radio) cellular network will provide new opportunities for enhancing localization of UAVs and UGVs. In this paper, we review the radio frequency (RF) based approaches for localization. We review the RF features that can be utilized for localization and investigate the current methods suitable for Unmanned vehicles under two general categories: range-based and fingerprinting. The existing state-of-the-art literature on RF-based localization for both UAVs and UGVs is examined, and the envisioned 5G NR for localization enhancement, and the future research direction are explored.
RAUM-VO: Rotational Adjusted Unsupervised Monocular Visual Odometry
Mar 14, 2022
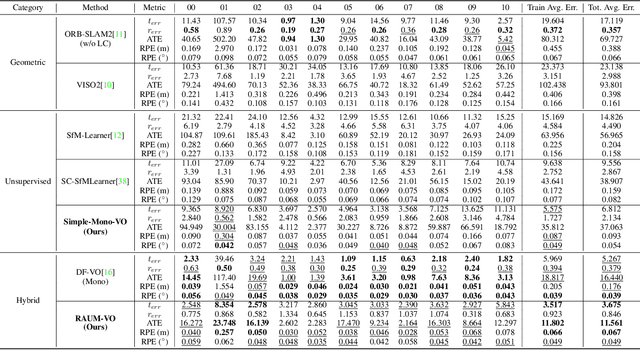
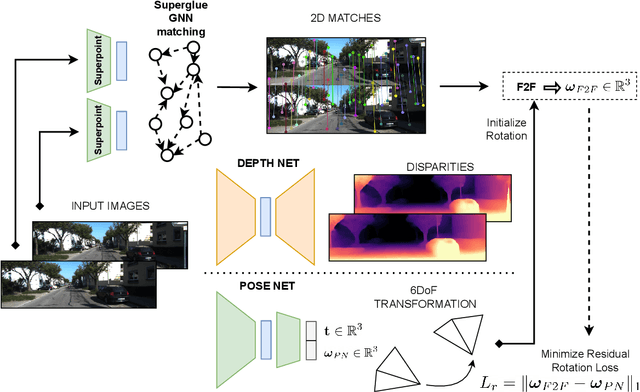
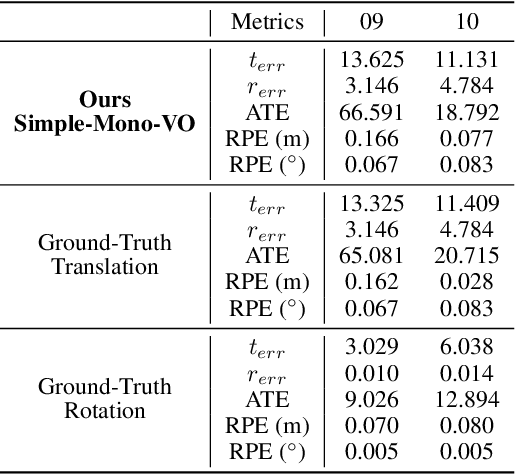
Abstract:Unsupervised learning for monocular camera motion and 3D scene understanding has gained popularity over traditional methods, relying on epipolar geometry or non-linear optimization. Notably, deep learning can overcome many issues of monocular vision, such as perceptual aliasing, low-textured areas, scale-drift, and degenerate motions. Also, concerning supervised learning, we can fully leverage video streams data without the need for depth or motion labels. However, in this work, we note that rotational motion can limit the accuracy of the unsupervised pose networks more than the translational component. Therefore, we present RAUM-VO, an approach based on a model-free epipolar constraint for frame-to-frame motion estimation (F2F) to adjust the rotation during training and online inference. To this end, we match 2D keypoints between consecutive frames using pre-trained deep networks, Superpoint and Superglue, while training a network for depth and pose estimation using an unsupervised training protocol. Then, we adjust the predicted rotation with the motion estimated by F2F using the 2D matches and initializing the solver with the pose network prediction. Ultimately, RAUM-VO shows a considerable accuracy improvement compared to other unsupervised pose networks on the KITTI dataset while reducing the complexity of other hybrid or traditional approaches and achieving comparable state-of-the-art results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge