Hojun Choi
FinDER: Financial Dataset for Question Answering and Evaluating Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:In the fast-paced financial domain, accurate and up-to-date information is critical to addressing ever-evolving market conditions. Retrieving this information correctly is essential in financial Question-Answering (QA), since many language models struggle with factual accuracy in this domain. We present FinDER, an expert-generated dataset tailored for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) in finance. Unlike existing QA datasets that provide predefined contexts and rely on relatively clear and straightforward queries, FinDER focuses on annotating search-relevant evidence by domain experts, offering 5,703 query-evidence-answer triplets derived from real-world financial inquiries. These queries frequently include abbreviations, acronyms, and concise expressions, capturing the brevity and ambiguity common in the realistic search behavior of professionals. By challenging models to retrieve relevant information from large corpora rather than relying on readily determined contexts, FinDER offers a more realistic benchmark for evaluating RAG systems. We further present a comprehensive evaluation of multiple state-of-the-art retrieval models and Large Language Models, showcasing challenges derived from a realistic benchmark to drive future research on truthful and precise RAG in the financial domain.
Sampling Bag of Views for Open-Vocabulary Object Detection
Dec 24, 2024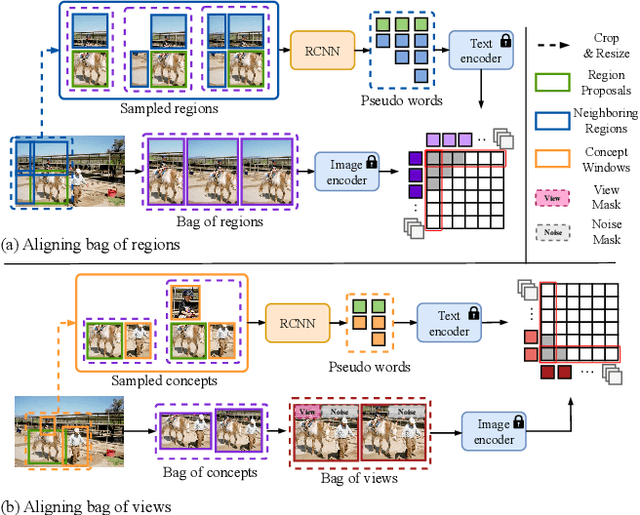
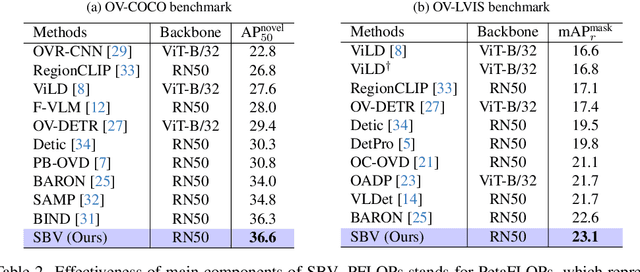


Abstract:Existing open-vocabulary object detection (OVD) develops methods for testing unseen categories by aligning object region embeddings with corresponding VLM features. A recent study leverages the idea that VLMs implicitly learn compositional structures of semantic concepts within the image. Instead of using an individual region embedding, it utilizes a bag of region embeddings as a new representation to incorporate compositional structures into the OVD task. However, this approach often fails to capture the contextual concepts of each region, leading to noisy compositional structures. This results in only marginal performance improvements and reduced efficiency. To address this, we propose a novel concept-based alignment method that samples a more powerful and efficient compositional structure. Our approach groups contextually related ``concepts'' into a bag and adjusts the scale of concepts within the bag for more effective embedding alignment. Combined with Faster R-CNN, our method achieves improvements of 2.6 box AP50 and 0.5 mask AP over prior work on novel categories in the open-vocabulary COCO and LVIS benchmarks. Furthermore, our method reduces CLIP computation in FLOPs by 80.3% compared to previous research, significantly enhancing efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms previous state-of-the-art models on the OVD datasets.
Explore, Select, Derive, and Recall: Augmenting LLM with Human-like Memory for Mobile Task Automation
Dec 04, 2023


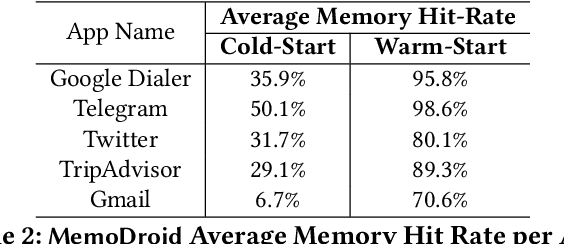
Abstract:The advent of large language models (LLMs) has opened up new opportunities in the field of mobile task automation. Their superior language understanding and reasoning capabilities allow users to automate complex and repetitive tasks. However, due to the inherent unreliability and high operational cost of LLMs, their practical applicability is quite limited. To address these issues, this paper introduces MemoDroid, an innovative LLM-based mobile task automator enhanced with a unique app memory. MemoDroid emulates the cognitive process of humans interacting with a mobile app -- explore, select, derive, and recall. This approach allows for a more precise and efficient learning of a task's procedure by breaking it down into smaller, modular components that can be re-used, re-arranged, and adapted for various objectives. We implement MemoDroid using online LLMs services (GPT-3.5 and GPT-4) and evaluate its performance on 50 unique mobile tasks across 5 widely used mobile apps. The results indicate that MemoDroid can adapt learned tasks to varying contexts with 100% accuracy and reduces their latency and cost by 69.22% and 77.36% compared to a GPT-4 powered baseline.
Knowledge-preserving Pruning for Pre-trained Language Models without Retraining
Aug 07, 2023



Abstract:Given a pre-trained language model, how can we efficiently compress it without retraining? Retraining-free structured pruning algorithms are crucial in pre-trained language model compression due to their significantly reduced pruning cost and capability to prune large language models. However, existing retraining-free algorithms encounter severe accuracy degradation, as they fail to preserve the useful knowledge of pre-trained models. In this paper, we propose K-pruning (Knowledge-preserving pruning), an accurate retraining-free structured pruning algorithm for pre-trained language models. K-pruning identifies and prunes attention heads and neurons deemed to be superfluous, based on the amount of their inherent knowledge. K-pruning applies an iterative process of pruning followed by knowledge reconstruction for each sub-layer to preserve the knowledge of the pre-trained models. Consequently, K-pruning shows up to 58.02%p higher F1 score than existing retraining-free pruning algorithms under a high compression rate of 80% on the SQuAD benchmark.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge