Hessam Bagherinezhad
OpenAI o1 System Card
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:The o1 model series is trained with large-scale reinforcement learning to reason using chain of thought. These advanced reasoning capabilities provide new avenues for improving the safety and robustness of our models. In particular, our models can reason about our safety policies in context when responding to potentially unsafe prompts, through deliberative alignment. This leads to state-of-the-art performance on certain benchmarks for risks such as generating illicit advice, choosing stereotyped responses, and succumbing to known jailbreaks. Training models to incorporate a chain of thought before answering has the potential to unlock substantial benefits, while also increasing potential risks that stem from heightened intelligence. Our results underscore the need for building robust alignment methods, extensively stress-testing their efficacy, and maintaining meticulous risk management protocols. This report outlines the safety work carried out for the OpenAI o1 and OpenAI o1-mini models, including safety evaluations, external red teaming, and Preparedness Framework evaluations.
Who Let The Dogs Out? Modeling Dog Behavior From Visual Data
May 17, 2018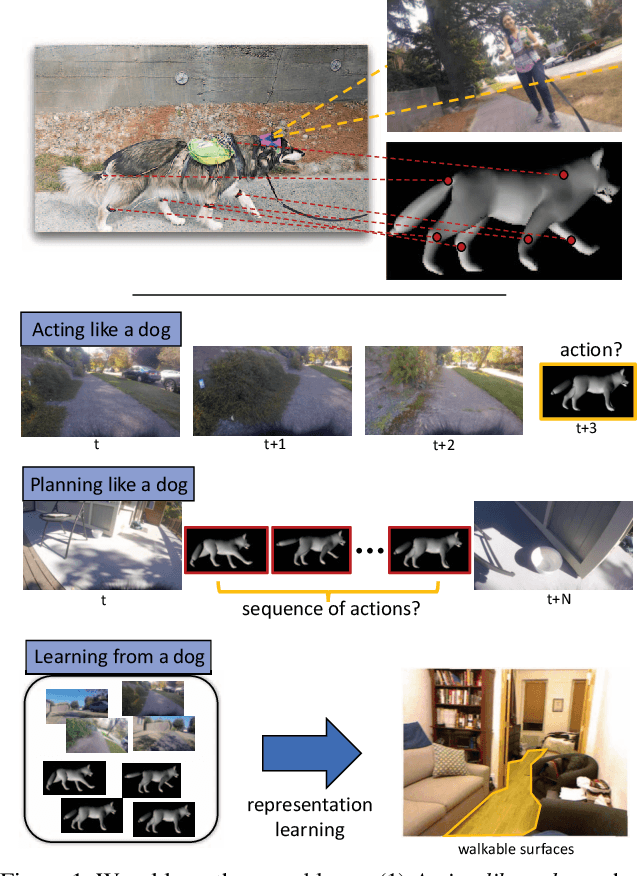
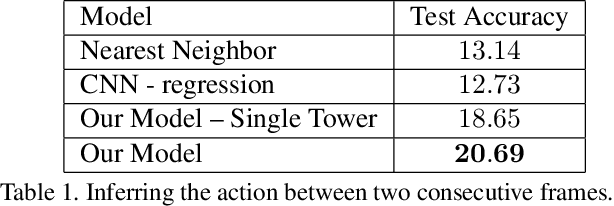
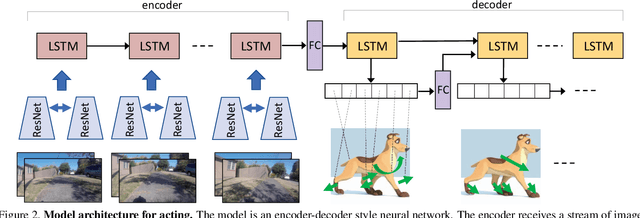
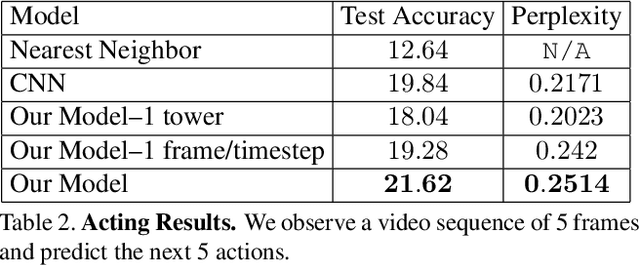
Abstract:We introduce the task of directly modeling a visually intelligent agent. Computer vision typically focuses on solving various subtasks related to visual intelligence. We depart from this standard approach to computer vision; instead we directly model a visually intelligent agent. Our model takes visual information as input and directly predicts the actions of the agent. Toward this end we introduce DECADE, a large-scale dataset of ego-centric videos from a dog's perspective as well as her corresponding movements. Using this data we model how the dog acts and how the dog plans her movements. We show under a variety of metrics that given just visual input we can successfully model this intelligent agent in many situations. Moreover, the representation learned by our model encodes distinct information compared to representations trained on image classification, and our learned representation can generalize to other domains. In particular, we show strong results on the task of walkable surface estimation by using this dog modeling task as representation learning.
Label Refinery: Improving ImageNet Classification through Label Progression
May 07, 2018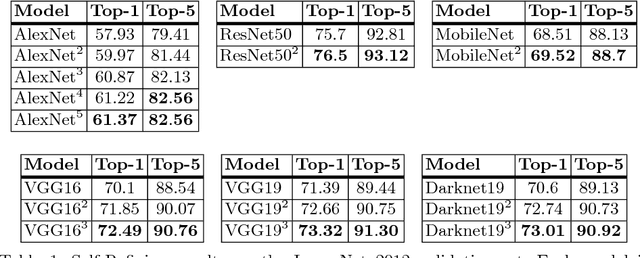



Abstract:Among the three main components (data, labels, and models) of any supervised learning system, data and models have been the main subjects of active research. However, studying labels and their properties has received very little attention. Current principles and paradigms of labeling impose several challenges to machine learning algorithms. Labels are often incomplete, ambiguous, and redundant. In this paper we study the effects of various properties of labels and introduce the Label Refinery: an iterative procedure that updates the ground truth labels after examining the entire dataset. We show significant gain using refined labels across a wide range of models. Using a Label Refinery improves the state-of-the-art top-1 accuracy of (1) AlexNet from 59.3 to 67.2, (2) MobileNet from 70.6 to 73.39, (3) MobileNet-0.25 from 50.6 to 55.59, (4) VGG19 from 72.7 to 75.46, and (5) Darknet19 from 72.9 to 74.47.
LCNN: Lookup-based Convolutional Neural Network
Jun 13, 2017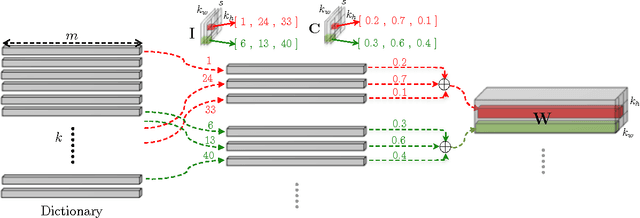

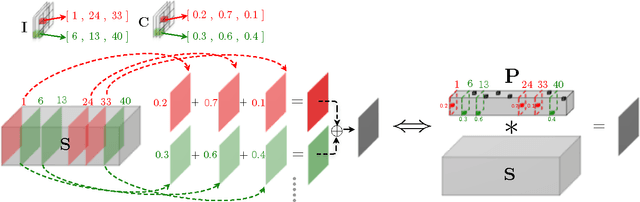

Abstract:Porting state of the art deep learning algorithms to resource constrained compute platforms (e.g. VR, AR, wearables) is extremely challenging. We propose a fast, compact, and accurate model for convolutional neural networks that enables efficient learning and inference. We introduce LCNN, a lookup-based convolutional neural network that encodes convolutions by few lookups to a dictionary that is trained to cover the space of weights in CNNs. Training LCNN involves jointly learning a dictionary and a small set of linear combinations. The size of the dictionary naturally traces a spectrum of trade-offs between efficiency and accuracy. Our experimental results on ImageNet challenge show that LCNN can offer 3.2x speedup while achieving 55.1% top-1 accuracy using AlexNet architecture. Our fastest LCNN offers 37.6x speed up over AlexNet while maintaining 44.3% top-1 accuracy. LCNN not only offers dramatic speed ups at inference, but it also enables efficient training. In this paper, we show the benefits of LCNN in few-shot learning and few-iteration learning, two crucial aspects of on-device training of deep learning models.
Are Elephants Bigger than Butterflies? Reasoning about Sizes of Objects
Feb 02, 2016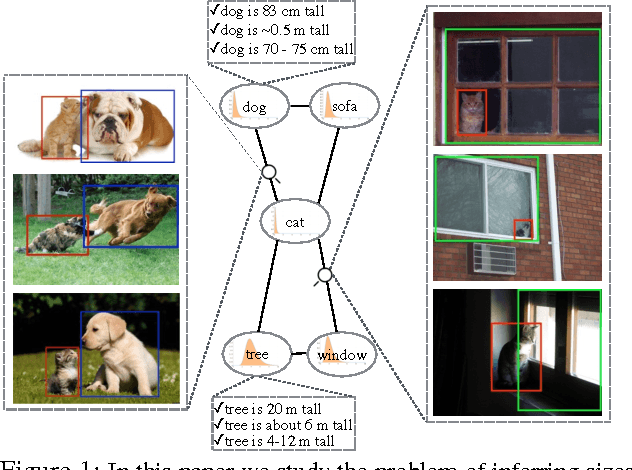

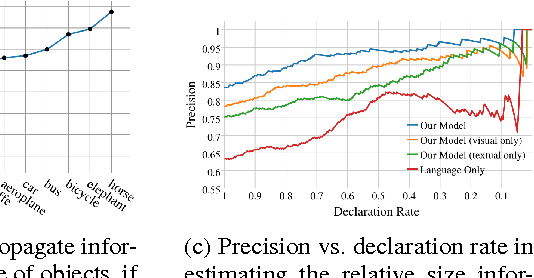
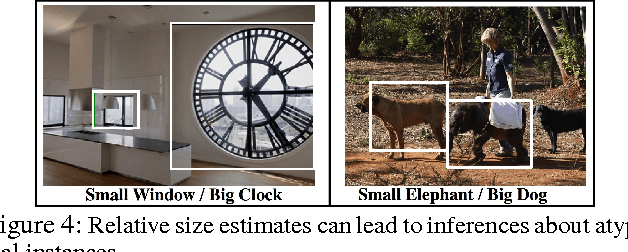
Abstract:Human vision greatly benefits from the information about sizes of objects. The role of size in several visual reasoning tasks has been thoroughly explored in human perception and cognition. However, the impact of the information about sizes of objects is yet to be determined in AI. We postulate that this is mainly attributed to the lack of a comprehensive repository of size information. In this paper, we introduce a method to automatically infer object sizes, leveraging visual and textual information from web. By maximizing the joint likelihood of textual and visual observations, our method learns reliable relative size estimates, with no explicit human supervision. We introduce the relative size dataset and show that our method outperforms competitive textual and visual baselines in reasoning about size comparisons.
Newtonian Image Understanding: Unfolding the Dynamics of Objects in Static Images
Nov 12, 2015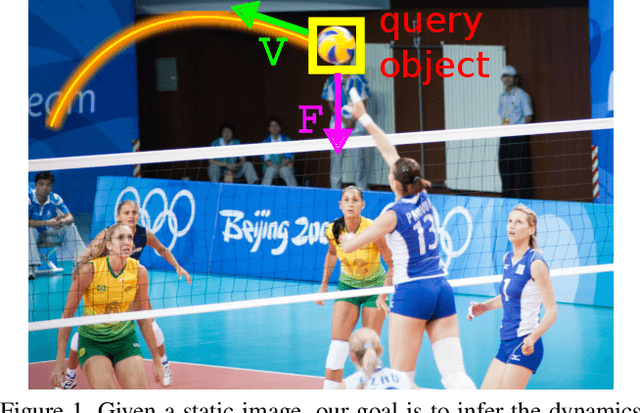



Abstract:In this paper, we study the challenging problem of predicting the dynamics of objects in static images. Given a query object in an image, our goal is to provide a physical understanding of the object in terms of the forces acting upon it and its long term motion as response to those forces. Direct and explicit estimation of the forces and the motion of objects from a single image is extremely challenging. We define intermediate physical abstractions called Newtonian scenarios and introduce Newtonian Neural Network ($N^3$) that learns to map a single image to a state in a Newtonian scenario. Our experimental evaluations show that our method can reliably predict dynamics of a query object from a single image. In addition, our approach can provide physical reasoning that supports the predicted dynamics in terms of velocity and force vectors. To spur research in this direction we compiled Visual Newtonian Dynamics (VIND) dataset that includes 6806 videos aligned with Newtonian scenarios represented using game engines, and 4516 still images with their ground truth dynamics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge