Hangqi Zhou
Learning Concept-Driven Logical Rules for Interpretable and Generalizable Medical Image Classification
May 20, 2025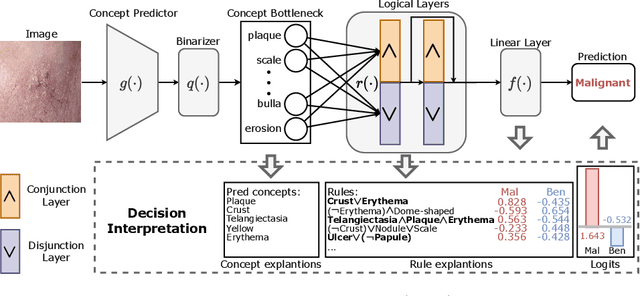
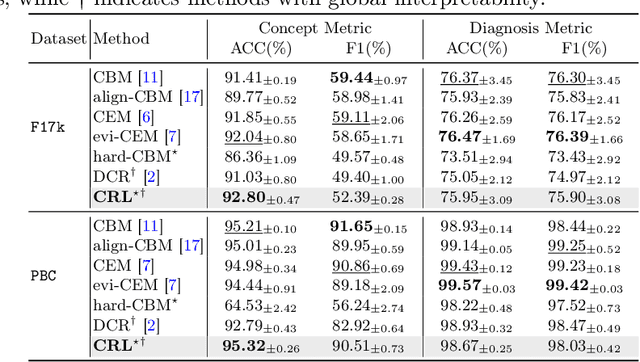
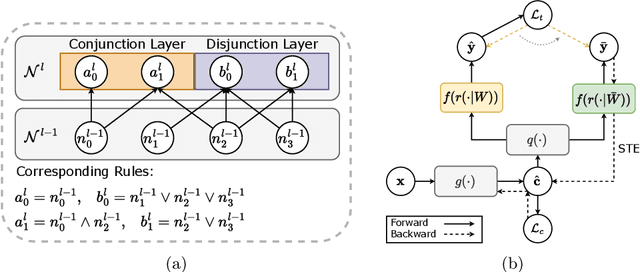
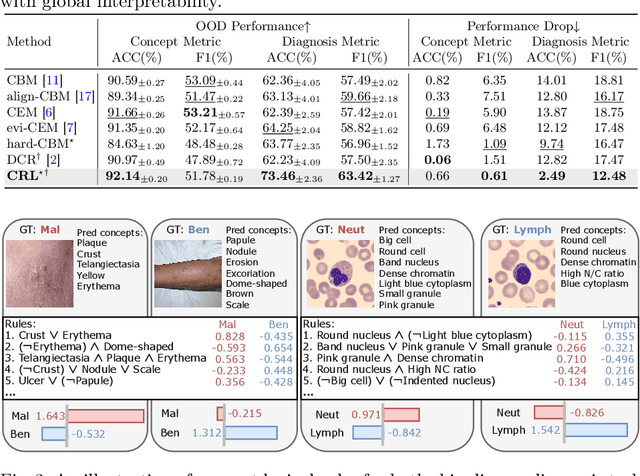
Abstract:The pursuit of decision safety in clinical applications highlights the potential of concept-based methods in medical imaging. While these models offer active interpretability, they often suffer from concept leakages, where unintended information within soft concept representations undermines both interpretability and generalizability. Moreover, most concept-based models focus solely on local explanations (instance-level), neglecting the global decision logic (dataset-level). To address these limitations, we propose Concept Rule Learner (CRL), a novel framework to learn Boolean logical rules from binarized visual concepts. CRL employs logical layers to capture concept correlations and extract clinically meaningful rules, thereby providing both local and global interpretability. Experiments on two medical image classification tasks show that CRL achieves competitive performance with existing methods while significantly improving generalizability to out-of-distribution data. The code of our work is available at https://github.com/obiyoag/crl.
Multi-Center Fetal Brain Tissue Annotation (FeTA) Challenge 2022 Results
Feb 08, 2024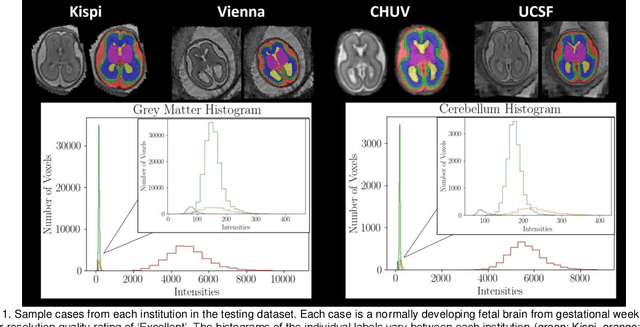
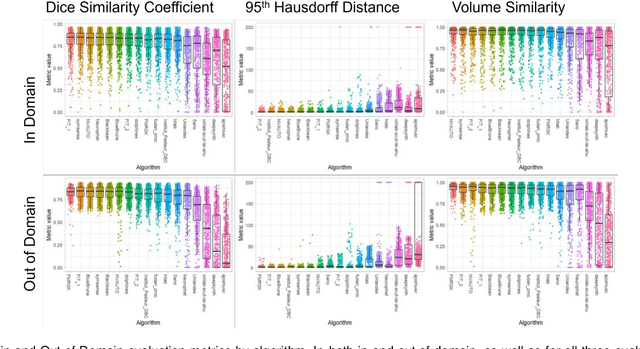
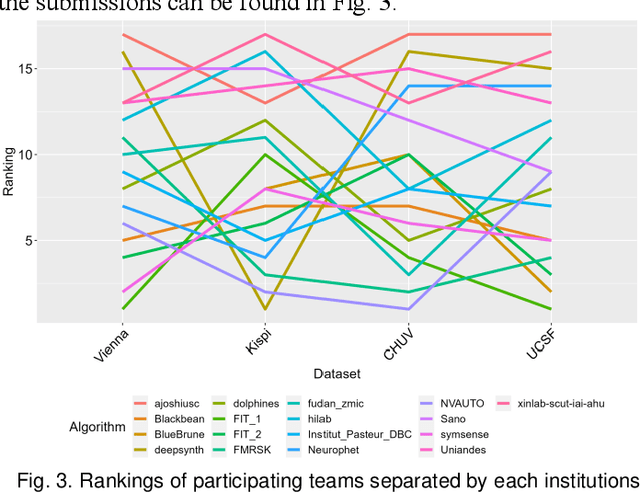
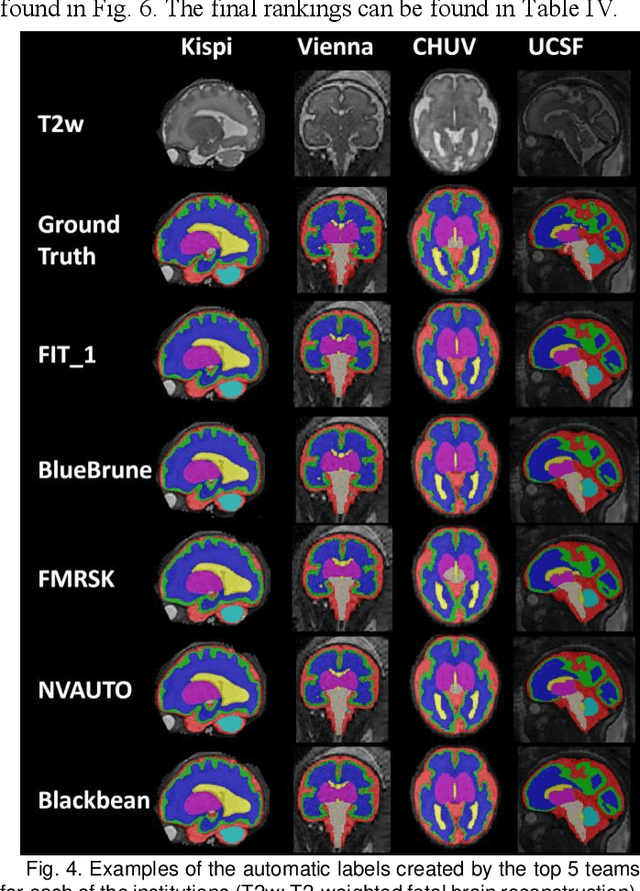
Abstract:Segmentation is a critical step in analyzing the developing human fetal brain. There have been vast improvements in automatic segmentation methods in the past several years, and the Fetal Brain Tissue Annotation (FeTA) Challenge 2021 helped to establish an excellent standard of fetal brain segmentation. However, FeTA 2021 was a single center study, and the generalizability of algorithms across different imaging centers remains unsolved, limiting real-world clinical applicability. The multi-center FeTA Challenge 2022 focuses on advancing the generalizability of fetal brain segmentation algorithms for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In FeTA 2022, the training dataset contained images and corresponding manually annotated multi-class labels from two imaging centers, and the testing data contained images from these two imaging centers as well as two additional unseen centers. The data from different centers varied in many aspects, including scanners used, imaging parameters, and fetal brain super-resolution algorithms applied. 16 teams participated in the challenge, and 17 algorithms were evaluated. Here, a detailed overview and analysis of the challenge results are provided, focusing on the generalizability of the submissions. Both in- and out of domain, the white matter and ventricles were segmented with the highest accuracy, while the most challenging structure remains the cerebral cortex due to anatomical complexity. The FeTA Challenge 2022 was able to successfully evaluate and advance generalizability of multi-class fetal brain tissue segmentation algorithms for MRI and it continues to benchmark new algorithms. The resulting new methods contribute to improving the analysis of brain development in utero.
BayeSeg: Bayesian Modeling for Medical Image Segmentation with Interpretable Generalizability
Mar 03, 2023Abstract:Due to the cross-domain distribution shift aroused from diverse medical imaging systems, many deep learning segmentation methods fail to perform well on unseen data, which limits their real-world applicability. Recent works have shown the benefits of extracting domain-invariant representations on domain generalization. However, the interpretability of domain-invariant features remains a great challenge. To address this problem, we propose an interpretable Bayesian framework (BayeSeg) through Bayesian modeling of image and label statistics to enhance model generalizability for medical image segmentation. Specifically, we first decompose an image into a spatial-correlated variable and a spatial-variant variable, assigning hierarchical Bayesian priors to explicitly force them to model the domain-stable shape and domain-specific appearance information respectively. Then, we model the segmentation as a locally smooth variable only related to the shape. Finally, we develop a variational Bayesian framework to infer the posterior distributions of these explainable variables. The framework is implemented with neural networks, and thus is referred to as deep Bayesian segmentation. Quantitative and qualitative experimental results on prostate segmentation and cardiac segmentation tasks have shown the effectiveness of our proposed method. Moreover, we investigated the interpretability of BayeSeg by explaining the posteriors and analyzed certain factors that affect the generalization ability through further ablation studies. Our code will be released via https://zmiclab.github.io/projects.html, once the manuscript is accepted for publication.
Joint Modeling of Image and Label Statistics for Enhancing Model Generalizability of Medical Image Segmentation
Jun 09, 2022
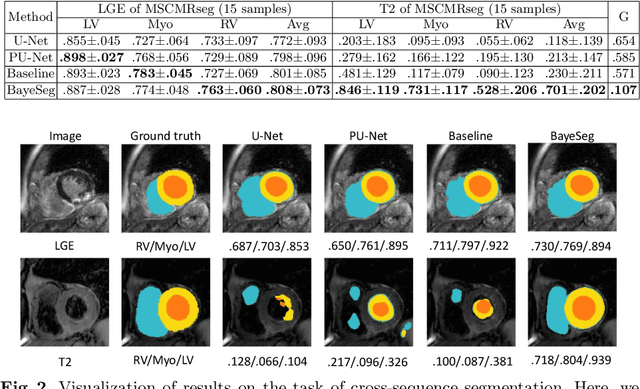
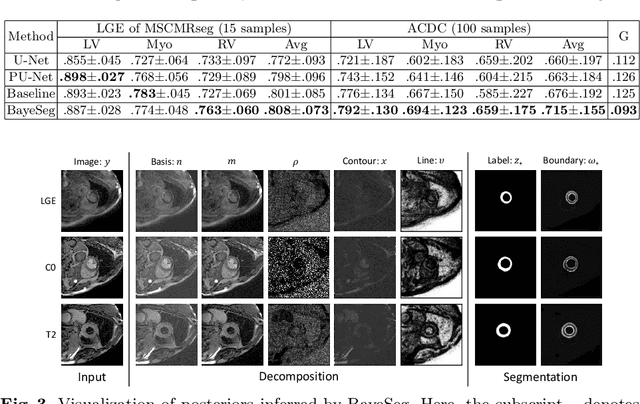
Abstract:Although supervised deep-learning has achieved promising performance in medical image segmentation, many methods cannot generalize well on unseen data, limiting their real-world applicability. To address this problem, we propose a deep learning-based Bayesian framework, which jointly models image and label statistics, utilizing the domain-irrelevant contour of a medical image for segmentation. Specifically, we first decompose an image into components of contour and basis. Then, we model the expected label as a variable only related to the contour. Finally, we develop a variational Bayesian framework to infer the posterior distributions of these variables, including the contour, the basis, and the label. The framework is implemented with neural networks, thus is referred to as deep Bayesian segmentation. Results on the task of cross-sequence cardiac MRI segmentation show that our method set a new state of the art for model generalizability. Particularly, the BayeSeg model trained with LGE MRI generalized well on T2 images and outperformed other models with great margins, i.e., over 0.47 in terms of average Dice. Our code is available at https://zmiclab.github.io/projects.html.
VSpSR: Explorable Super-Resolution via Variational Sparse Representation
Apr 17, 2021



Abstract:Super-resolution (SR) is an ill-posed problem, which means that infinitely many high-resolution (HR) images can be degraded to the same low-resolution (LR) image. To study the one-to-many stochastic SR mapping, we implicitly represent the non-local self-similarity of natural images and develop a Variational Sparse framework for Super-Resolution (VSpSR) via neural networks. Since every small patch of a HR image can be well approximated by the sparse representation of atoms in an over-complete dictionary, we design a two-branch module, i.e., VSpM, to explore the SR space. Concretely, one branch of VSpM extracts patch-level basis from the LR input, and the other branch infers pixel-wise variational distributions with respect to the sparse coefficients. By repeatedly sampling coefficients, we could obtain infinite sparse representations, and thus generate diverse HR images. According to the preliminary results of NTIRE 2021 challenge on learning SR space, our team (FudanZmic21) ranks 7-th in terms of released scores. The implementation of VSpSR is released at https://zmiclab.github.io/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge