Guorong Cai
DS$^2$Net: Detail-Semantic Deep Supervision Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Deep Supervision Networks exhibit significant efficacy for the medical imaging community. Nevertheless, existing work merely supervises either the coarse-grained semantic features or fine-grained detailed features in isolation, which compromises the fact that these two types of features hold vital relationships in medical image analysis. We advocate the powers of complementary feature supervision for medical image segmentation, by proposing a Detail-Semantic Deep Supervision Network (DS$^2$Net). DS$^2$Net navigates both low-level detailed and high-level semantic feature supervision through Detail Enhance Module (DEM) and Semantic Enhance Module (SEM). DEM and SEM respectively harness low-level and high-level feature maps to create detail and semantic masks for enhancing feature supervision. This is a novel shift from single-view deep supervision to multi-view deep supervision. DS$^2$Net is also equipped with a novel uncertainty-based supervision loss that adaptively assigns the supervision strength of features within distinct scales based on their uncertainty, thus circumventing the sub-optimal heuristic design that typifies previous works. Through extensive experiments on six benchmarks captured under either colonoscopy, ultrasound and microscope, we demonstrate that DS$^2$Net consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods for medical image analysis.
Leveraging Depth and Language for Open-Vocabulary Domain-Generalized Semantic Segmentation
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Open-Vocabulary semantic segmentation (OVSS) and domain generalization in semantic segmentation (DGSS) highlight a subtle complementarity that motivates Open-Vocabulary Domain-Generalized Semantic Segmentation (OV-DGSS). OV-DGSS aims to generate pixel-level masks for unseen categories while maintaining robustness across unseen domains, a critical capability for real-world scenarios such as autonomous driving in adverse conditions. We introduce Vireo, a novel single-stage framework for OV-DGSS that unifies the strengths of OVSS and DGSS for the first time. Vireo builds upon the frozen Visual Foundation Models (VFMs) and incorporates scene geometry via Depth VFMs to extract domain-invariant structural features. To bridge the gap between visual and textual modalities under domain shift, we propose three key components: (1) GeoText Prompts, which align geometric features with language cues and progressively refine VFM encoder representations; (2) Coarse Mask Prior Embedding (CMPE) for enhancing gradient flow for faster convergence and stronger textual influence; and (3) the Domain-Open-Vocabulary Vector Embedding Head (DOV-VEH), which fuses refined structural and semantic features for robust prediction. Comprehensive evaluation on these components demonstrates the effectiveness of our designs. Our proposed Vireo achieves the state-of-the-art performance and surpasses existing methods by a large margin in both domain generalization and open-vocabulary recognition, offering a unified and scalable solution for robust visual understanding in diverse and dynamic environments. Code is available at https://github.com/anonymouse-9c53tp182bvz/Vireo.
Stronger, Steadier & Superior: Geometric Consistency in Depth VFM Forges Domain Generalized Semantic Segmentation
Apr 17, 2025



Abstract:Vision Foundation Models (VFMs) have delivered remarkable performance in Domain Generalized Semantic Segmentation (DGSS). However, recent methods often overlook the fact that visual cues are susceptible, whereas the underlying geometry remains stable, rendering depth information more robust. In this paper, we investigate the potential of integrating depth information with features from VFMs, to improve the geometric consistency within an image and boost the generalization performance of VFMs. We propose a novel fine-tuning DGSS framework, named DepthForge, which integrates the visual cues from frozen DINOv2 or EVA02 and depth cues from frozen Depth Anything V2. In each layer of the VFMs, we incorporate depth-aware learnable tokens to continuously decouple domain-invariant visual and spatial information, thereby enhancing depth awareness and attention of the VFMs. Finally, we develop a depth refinement decoder and integrate it into the model architecture to adaptively refine multi-layer VFM features and depth-aware learnable tokens. Extensive experiments are conducted based on various DGSS settings and five different datsets as unseen target domains. The qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms alternative approaches with stronger performance, steadier visual-spatial attention, and superior generalization ability. In particular, DepthForge exhibits outstanding performance under extreme conditions (e.g., night and snow). Code is available at https://github.com/anonymouse-xzrptkvyqc/DepthForge.
Depth Matters: Exploring Deep Interactions of RGB-D for Semantic Segmentation in Traffic Scenes
Sep 12, 2024



Abstract:RGB-D has gradually become a crucial data source for understanding complex scenes in assisted driving. However, existing studies have paid insufficient attention to the intrinsic spatial properties of depth maps. This oversight significantly impacts the attention representation, leading to prediction errors caused by attention shift issues. To this end, we propose a novel learnable Depth interaction Pyramid Transformer (DiPFormer) to explore the effectiveness of depth. Firstly, we introduce Depth Spatial-Aware Optimization (Depth SAO) as offset to represent real-world spatial relationships. Secondly, the similarity in the feature space of RGB-D is learned by Depth Linear Cross-Attention (Depth LCA) to clarify spatial differences at the pixel level. Finally, an MLP Decoder is utilized to effectively fuse multi-scale features for meeting real-time requirements. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed DiPFormer significantly addresses the issue of attention misalignment in both road detection (+7.5%) and semantic segmentation (+4.9% / +1.5%) tasks. DiPFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance on the KITTI (97.57% F-score on KITTI road and 68.74% mIoU on KITTI-360) and Cityscapes (83.4% mIoU) datasets.
Evolutionary Reinforcement Learning: A Systematic Review and Future Directions
Feb 20, 2024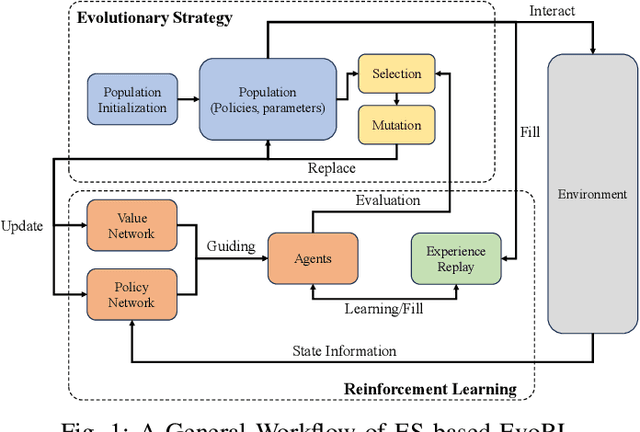

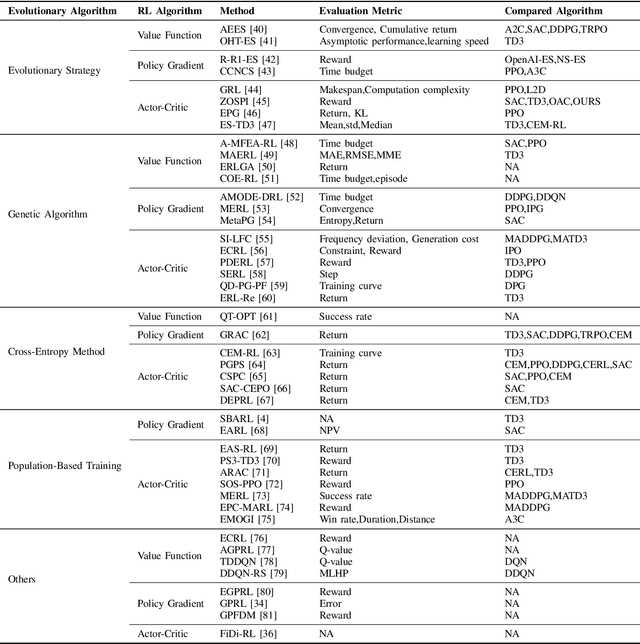

Abstract:In response to the limitations of reinforcement learning and evolutionary algorithms (EAs) in complex problem-solving, Evolutionary Reinforcement Learning (EvoRL) has emerged as a synergistic solution. EvoRL integrates EAs and reinforcement learning, presenting a promising avenue for training intelligent agents. This systematic review firstly navigates through the technological background of EvoRL, examining the symbiotic relationship between EAs and reinforcement learning algorithms. We then delve into the challenges faced by both EAs and reinforcement learning, exploring their interplay and impact on the efficacy of EvoRL. Furthermore, the review underscores the need for addressing open issues related to scalability, adaptability, sample efficiency, adversarial robustness, ethic and fairness within the current landscape of EvoRL. Finally, we propose future directions for EvoRL, emphasizing research avenues that strive to enhance self-adaptation and self-improvement, generalization, interpretability, explainability, and so on. Serving as a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners, this systematic review provides insights into the current state of EvoRL and offers a guide for advancing its capabilities in the ever-evolving landscape of artificial intelligence.
Toronto-3D: A Large-scale Mobile LiDAR Dataset for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Roadways
Apr 16, 2020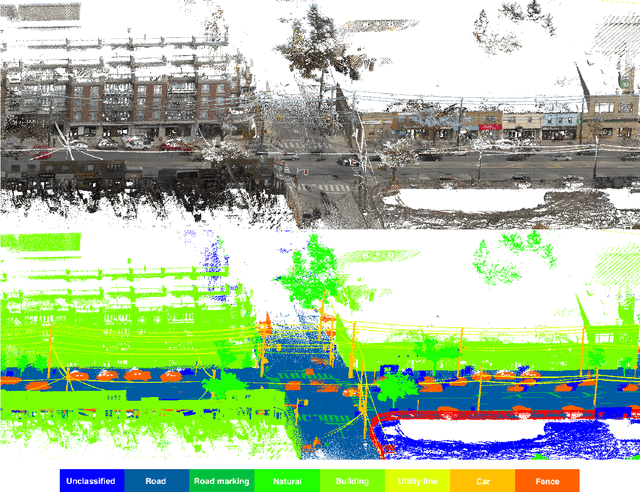
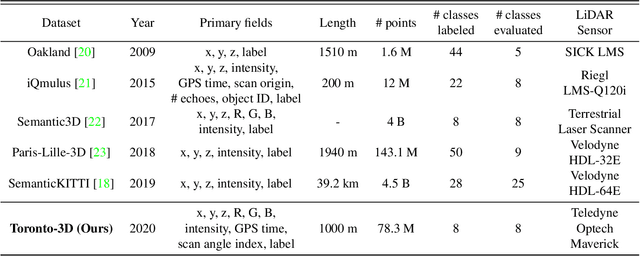
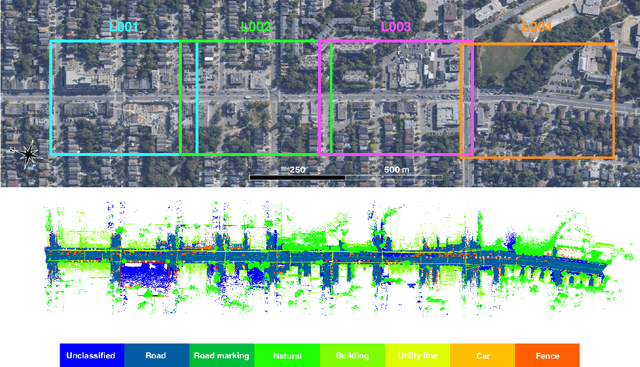
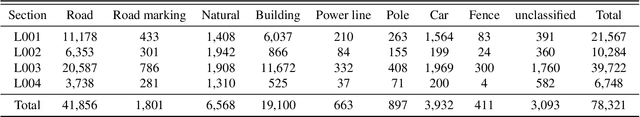
Abstract:Semantic segmentation of large-scale outdoor point clouds is essential for urban scene understanding in various applications, especially autonomous driving and urban high-definition (HD) mapping. With rapid developments of mobile laser scanning (MLS) systems, massive point clouds are available for scene understanding, but publicly accessible large-scale labeled datasets, which are essential for developing learning-based methods, are still limited. This paper introduces Toronto-3D, a large-scale urban outdoor point cloud dataset acquired by a MLS system in Toronto, Canada for semantic segmentation. This dataset covers approximately 1 km of point clouds and consists of about 78.3 million points with 8 labeled object classes. Baseline experiments for semantic segmentation were conducted and the results confirmed the capability of this dataset to train deep learning models effectively. Toronto-3D is released to encourage new research, and the labels will be improved and updated with feedback from the research community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge