Guang-Tong Zhou
Time Perception Machine: Temporal Point Processes for the When, Where and What of Activity Prediction
Aug 14, 2018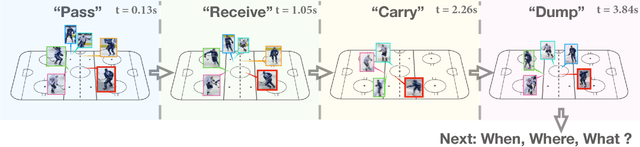
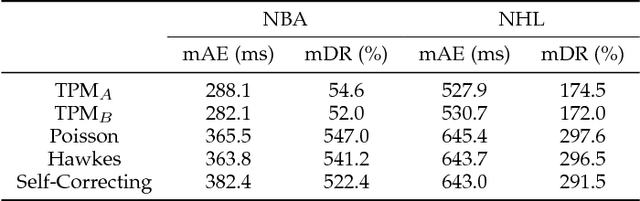
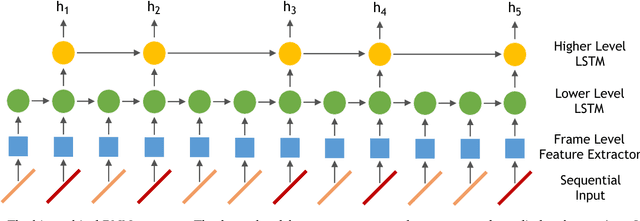
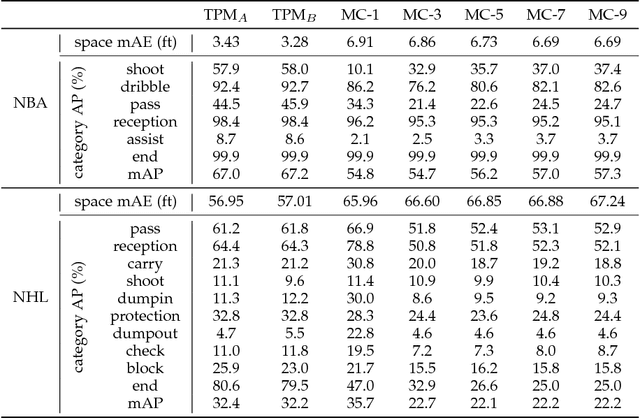
Abstract:Numerous powerful point process models have been developed to understand temporal patterns in sequential data from fields such as health-care, electronic commerce, social networks, and natural disaster forecasting. In this paper, we develop novel models for learning the temporal distribution of human activities in streaming data (e.g., videos and person trajectories). We propose an integrated framework of neural networks and temporal point processes for predicting when the next activity will happen. Because point processes are limited to taking event frames as input, we propose a simple yet effective mechanism to extract features at frames of interest while also preserving the rich information in the remaining frames. We evaluate our model on two challenging datasets. The results show that our model outperforms traditional statistical point process approaches significantly, demonstrating its effectiveness in capturing the underlying temporal dynamics as well as the correlation within sequential activities. Furthermore, we also extend our model to a joint estimation framework for predicting the timing, spatial location, and category of the activity simultaneously, to answer the when, where, and what of activity prediction.
Structured Label Inference for Visual Understanding
Feb 18, 2018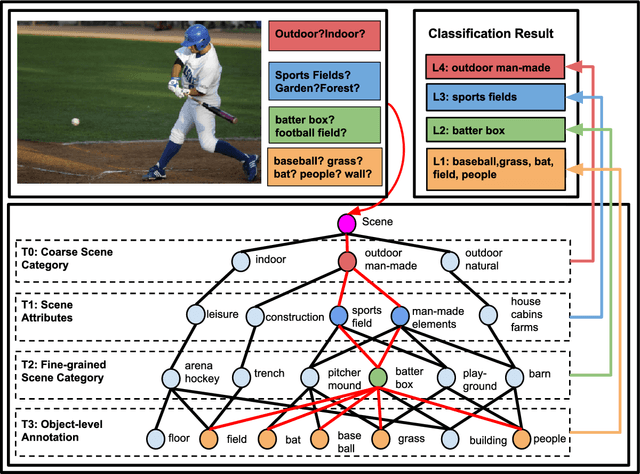
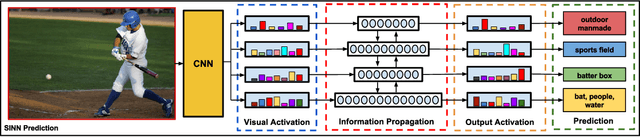
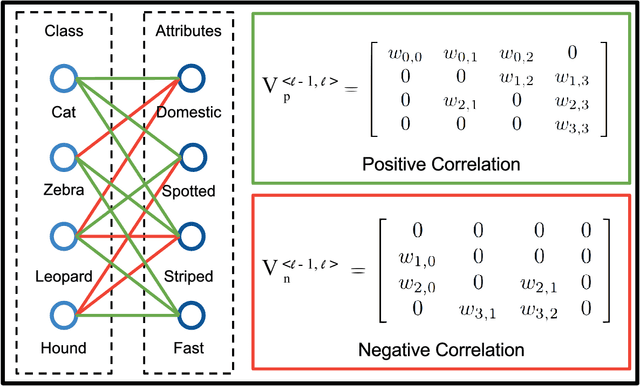
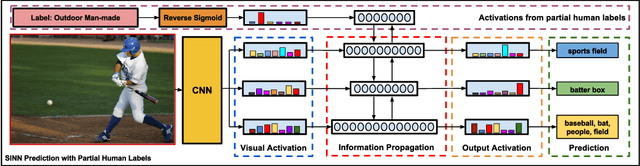
Abstract:Visual data such as images and videos contain a rich source of structured semantic labels as well as a wide range of interacting components. Visual content could be assigned with fine-grained labels describing major components, coarse-grained labels depicting high level abstractions, or a set of labels revealing attributes. Such categorization over different, interacting layers of labels evinces the potential for a graph-based encoding of label information. In this paper, we exploit this rich structure for performing graph-based inference in label space for a number of tasks: multi-label image and video classification and action detection in untrimmed videos. We consider the use of the Bidirectional Inference Neural Network (BINN) and Structured Inference Neural Network (SINN) for performing graph-based inference in label space and propose a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) based extension for exploiting activity progression on untrimmed videos. The methods were evaluated on (i) the Animal with Attributes (AwA), Scene Understanding (SUN) and NUS-WIDE datasets for multi-label image classification, (ii) the first two releases of the YouTube-8M large scale dataset for multi-label video classification, and (iii) the THUMOS'14 and MultiTHUMOS video datasets for action detection. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of structured label inference in these challenging tasks, achieving significant improvements against baselines.
LabelBank: Revisiting Global Perspectives for Semantic Segmentation
Mar 29, 2017



Abstract:Semantic segmentation requires a detailed labeling of image pixels by object category. Information derived from local image patches is necessary to describe the detailed shape of individual objects. However, this information is ambiguous and can result in noisy labels. Global inference of image content can instead capture the general semantic concepts present. We advocate that holistic inference of image concepts provides valuable information for detailed pixel labeling. We propose a generic framework to leverage holistic information in the form of a LabelBank for pixel-level segmentation. We show the ability of our framework to improve semantic segmentation performance in a variety of settings. We learn models for extracting a holistic LabelBank from visual cues, attributes, and/or textual descriptions. We demonstrate improvements in semantic segmentation accuracy on standard datasets across a range of state-of-the-art segmentation architectures and holistic inference approaches.
Learning Structured Inference Neural Networks with Label Relations
Oct 24, 2016


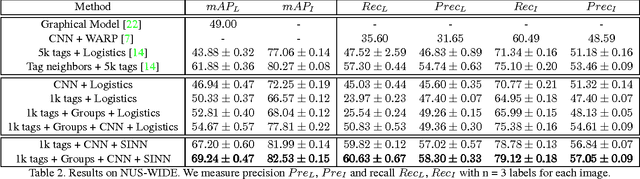
Abstract:Images of scenes have various objects as well as abundant attributes, and diverse levels of visual categorization are possible. A natural image could be assigned with fine-grained labels that describe major components, coarse-grained labels that depict high level abstraction or a set of labels that reveal attributes. Such categorization at different concept layers can be modeled with label graphs encoding label information. In this paper, we exploit this rich information with a state-of-art deep learning framework, and propose a generic structured model that leverages diverse label relations to improve image classification performance. Our approach employs a novel stacked label prediction neural network, capturing both inter-level and intra-level label semantics. We evaluate our method on benchmark image datasets, and empirical results illustrate the efficacy of our model.
Discovering Human Interactions in Videos with Limited Data Labeling
Feb 12, 2015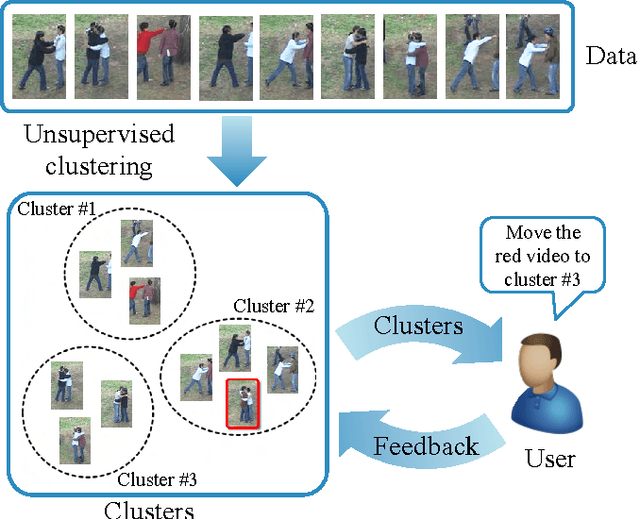
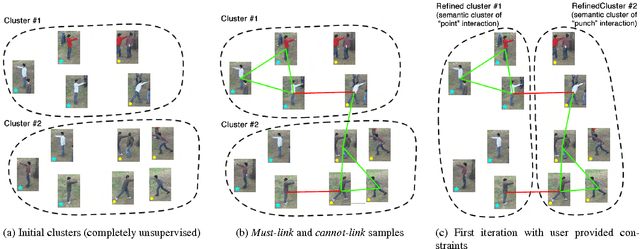
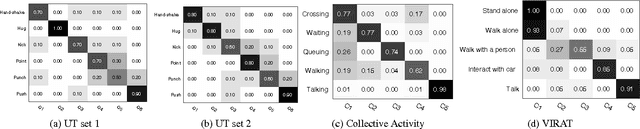
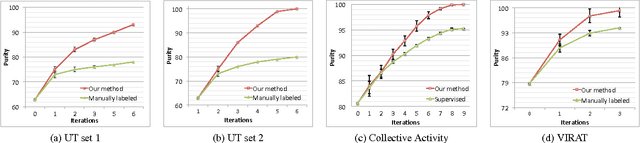
Abstract:We present a novel approach for discovering human interactions in videos. Activity understanding techniques usually require a large number of labeled examples, which are not available in many practical cases. Here, we focus on recovering semantically meaningful clusters of human-human and human-object interaction in an unsupervised fashion. A new iterative solution is introduced based on Maximum Margin Clustering (MMC), which also accepts user feedback to refine clusters. This is achieved by formulating the whole process as a unified constrained latent max-margin clustering problem. Extensive experiments have been carried out over three challenging datasets, Collective Activity, VIRAT, and UT-interaction. Empirical results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can efficiently discover perfect semantic clusters of human interactions with only a small amount of labeling effort.
Hierarchical Maximum-Margin Clustering
Feb 06, 2015



Abstract:We present a hierarchical maximum-margin clustering method for unsupervised data analysis. Our method extends beyond flat maximum-margin clustering, and performs clustering recursively in a top-down manner. We propose an effective greedy splitting criteria for selecting which cluster to split next, and employ regularizers that enforce feature sharing/competition for capturing data semantics. Experimental results obtained on four standard datasets show that our method outperforms flat and hierarchical clustering baselines, while forming clean and semantically meaningful cluster hierarchies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge