Nelson Nauata
Structured Outdoor Architecture Reconstruction by Exploration and Classification
Aug 18, 2021



Abstract:This paper presents an explore-and-classify framework for structured architectural reconstruction from an aerial image. Starting from a potentially imperfect building reconstruction by an existing algorithm, our approach 1) explores the space of building models by modifying the reconstruction via heuristic actions; 2) learns to classify the correctness of building models while generating classification labels based on the ground-truth, and 3) repeat. At test time, we iterate exploration and classification, seeking for a result with the best classification score. We evaluate the approach using initial reconstructions by two baselines and two state-of-the-art reconstruction algorithms. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations demonstrate that our approach consistently improves the reconstruction quality from every initial reconstruction.
House-GAN++: Generative Adversarial Layout Refinement Networks
Mar 03, 2021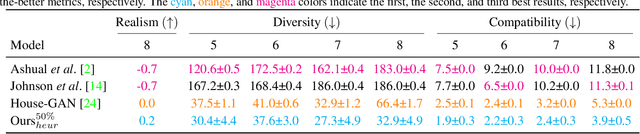
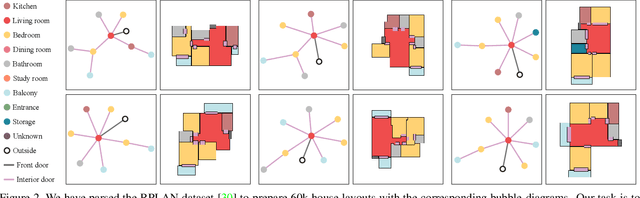
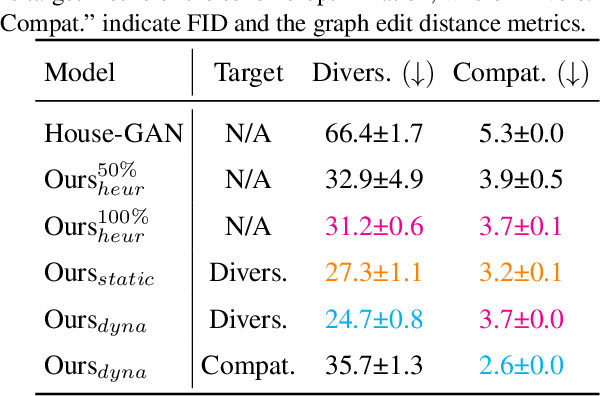
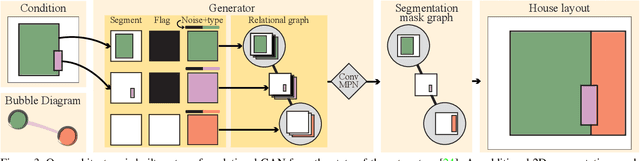
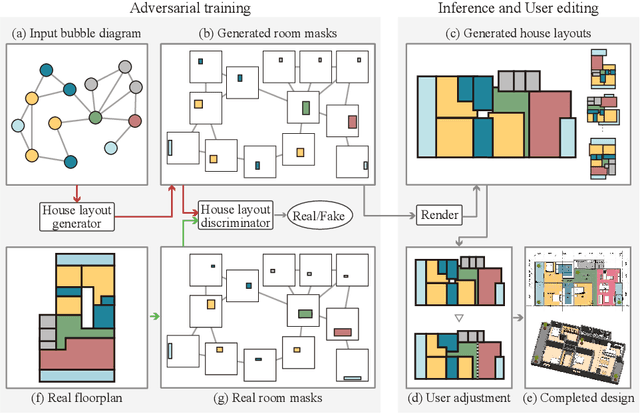
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel generative adversarial layout refinement network for automated floorplan generation. Our architecture is an integration of a graph-constrained relational GAN and a conditional GAN, where a previously generated layout becomes the next input constraint, enabling iterative refinement. A surprising discovery of our research is that a simple non-iterative training process, dubbed component-wise GT-conditioning, is effective in learning such a generator. The iterative generator also creates a new opportunity in further improving a metric of choice via meta-optimization techniques by controlling when to pass which input constraints during iterative layout refinement. Our qualitative and quantitative evaluation based on the three standard metrics demonstrate that the proposed system makes significant improvements over the current state-of-the-art, even competitive against the ground-truth floorplans, designed by professional architects.
House-GAN: Relational Generative Adversarial Networks for Graph-constrained House Layout Generation
Mar 16, 2020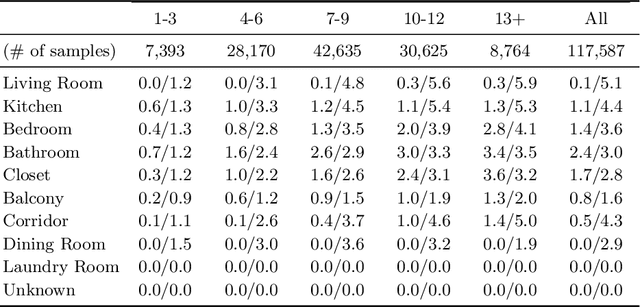

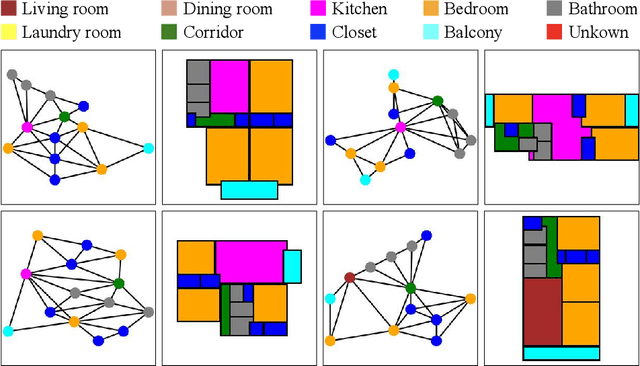
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel graph-constrained generative adversarial network, whose generator and discriminator are built upon relational architecture. The main idea is to encode the constraint into the graph structure of its relational networks. We have demonstrated the proposed architecture for a new house layout generation problem, whose task is to take an architectural constraint as a graph (i.e., the number and types of rooms with their spatial adjacency) and produce a set of axis-aligned bounding boxes of rooms. We measure the quality of generated house layouts with the three metrics: the realism, the diversity, and the compatibility with the input graph constraint. Our qualitative and quantitative evaluations over 117,000 real floorplan images demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms existing methods and baselines. We will publicly share all our code and data.
Vectorizing World Buildings: Planar Graph Reconstruction by Primitive Detection and Relationship Classification
Dec 12, 2019



Abstract:This paper tackles a 2D architecture vectorization problem, whose task is to infer an outdoor building architecture as a 2D planar graph from a single RGB image. We provide a new benchmark with ground-truth annotations for 2,001 complex buildings across the cities of Atlanta, Paris, and Las Vegas. We also propose a novel algorithm utilizing 1) convolutional neural networks (CNNs) that detects geometric primitives and classifies their relationships and 2) an integer programming (IP) that assembles the information into a 2D planar graph. While being a trivial task for human vision, the inference of a graph structure with an arbitrary topology is still an open problem for computer vision. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations demonstrate that our algorithm makes significant improvements over the current state-of-the-art, towards an intelligent system at the level of human perception. We will share code and data to promote further research.
Conv-MPN: Convolutional Message Passing Neural Network for Structured Outdoor Architecture Reconstruction
Dec 04, 2019



Abstract:This paper proposes a novel message passing neural (MPN) architecture Conv-MPN, which reconstructs an outdoor building as a planar graph from a single RGB image. Conv-MPN is specifically designed for cases where nodes of a graph have explicit spatial embedding. In our problem, nodes correspond to building edges in an image. Conv-MPN is different from MPN in that 1) the feature associated with a node is represented as a feature volume instead of a 1D vector; and 2) convolutions encode messages instead of fully connected layers. Conv-MPN learns to select a true subset of nodes (i.e., building edges) to reconstruct a building planar graph. Our qualitative and quantitative evaluations over 2,000 buildings show that Conv-MPN makes significant improvements over the existing fully neural solutions. We believe that the paper has a potential to open a new line of graph neural network research for structured geometry reconstruction.
Structured Label Inference for Visual Understanding
Feb 18, 2018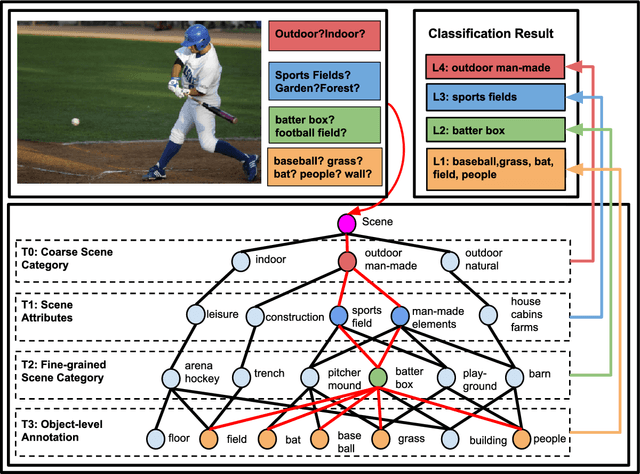
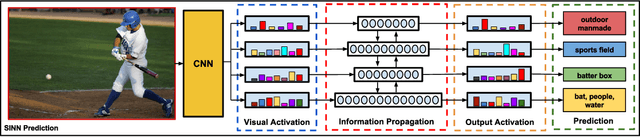
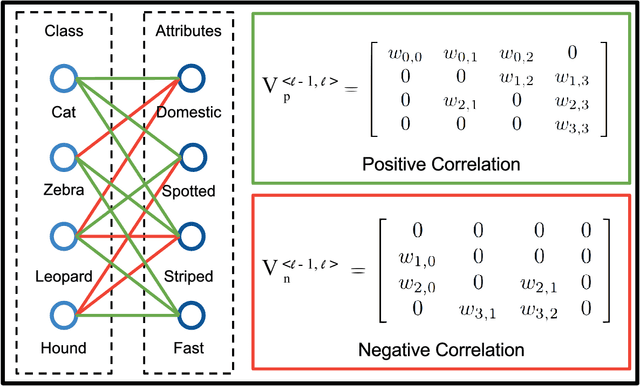
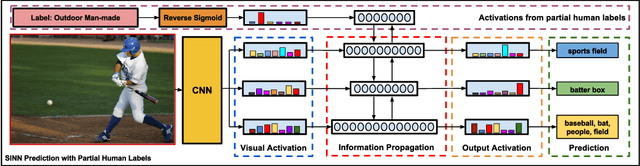
Abstract:Visual data such as images and videos contain a rich source of structured semantic labels as well as a wide range of interacting components. Visual content could be assigned with fine-grained labels describing major components, coarse-grained labels depicting high level abstractions, or a set of labels revealing attributes. Such categorization over different, interacting layers of labels evinces the potential for a graph-based encoding of label information. In this paper, we exploit this rich structure for performing graph-based inference in label space for a number of tasks: multi-label image and video classification and action detection in untrimmed videos. We consider the use of the Bidirectional Inference Neural Network (BINN) and Structured Inference Neural Network (SINN) for performing graph-based inference in label space and propose a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) based extension for exploiting activity progression on untrimmed videos. The methods were evaluated on (i) the Animal with Attributes (AwA), Scene Understanding (SUN) and NUS-WIDE datasets for multi-label image classification, (ii) the first two releases of the YouTube-8M large scale dataset for multi-label video classification, and (iii) the THUMOS'14 and MultiTHUMOS video datasets for action detection. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of structured label inference in these challenging tasks, achieving significant improvements against baselines.
Hierarchical Label Inference for Video Classification
Jan 21, 2018

Abstract:Videos are a rich source of high-dimensional structured data, with a wide range of interacting components at varying levels of granularity. In order to improve understanding of unconstrained internet videos, it is important to consider the role of labels at separate levels of abstraction. In this paper, we consider the use of the Bidirectional Inference Neural Network (BINN) for performing graph-based inference in label space for the task of video classification. We take advantage of the inherent hierarchy between labels at increasing granularity. The BINN is evaluated on the first and second release of the YouTube-8M large scale multilabel video dataset. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of BINN, achieving significant improvements against baseline models.
Learning Genomic Representations to Predict Clinical Outcomes in Cancer
Sep 27, 2016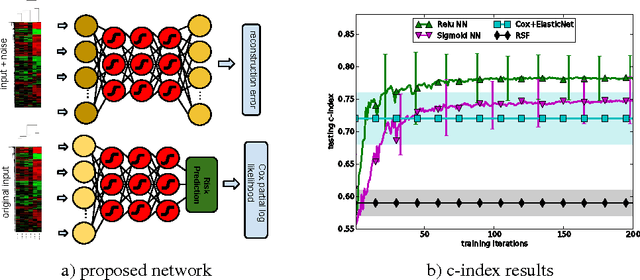
Abstract:Genomics are rapidly transforming medical practice and basic biomedical research, providing insights into disease mechanisms and improving therapeutic strategies, particularly in cancer. The ability to predict the future course of a patient's disease from high-dimensional genomic profiling will be essential in realizing the promise of genomic medicine, but presents significant challenges for state-of-the-art survival analysis methods. In this abstract we present an investigation in learning genomic representations with neural networks to predict patient survival in cancer. We demonstrate the advantages of this approach over existing survival analysis methods using brain tumor data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge