Genlang Chen
Dataset Ownership Verification in Contrastive Pre-trained Models
Feb 11, 2025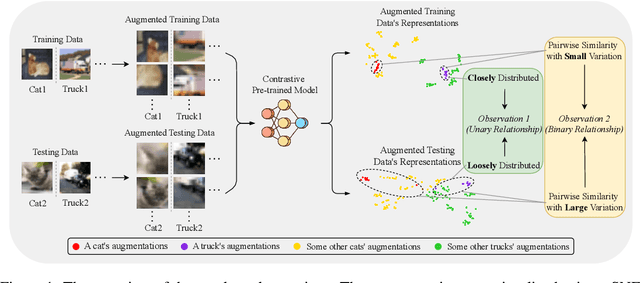
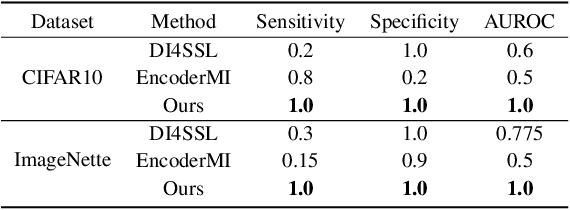
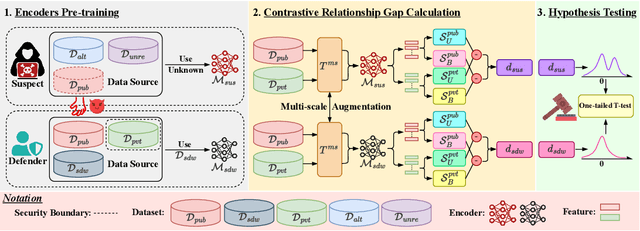
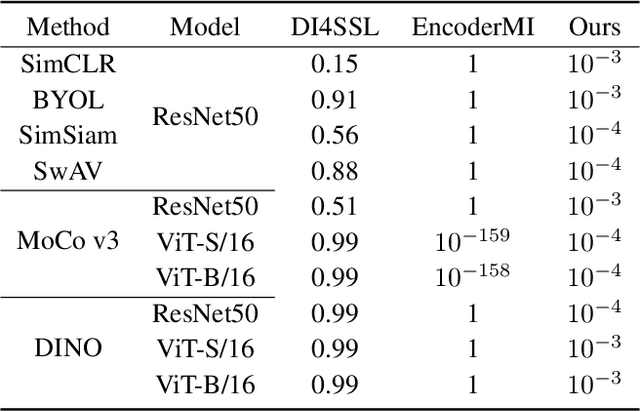
Abstract:High-quality open-source datasets, which necessitate substantial efforts for curation, has become the primary catalyst for the swift progress of deep learning. Concurrently, protecting these datasets is paramount for the well-being of the data owner. Dataset ownership verification emerges as a crucial method in this domain, but existing approaches are often limited to supervised models and cannot be directly extended to increasingly popular unsupervised pre-trained models. In this work, we propose the first dataset ownership verification method tailored specifically for self-supervised pre-trained models by contrastive learning. Its primary objective is to ascertain whether a suspicious black-box backbone has been pre-trained on a specific unlabeled dataset, aiding dataset owners in upholding their rights. The proposed approach is motivated by our empirical insights that when models are trained with the target dataset, the unary and binary instance relationships within the embedding space exhibit significant variations compared to models trained without the target dataset. We validate the efficacy of this approach across multiple contrastive pre-trained models including SimCLR, BYOL, SimSiam, MOCO v3, and DINO. The results demonstrate that our method rejects the null hypothesis with a $p$-value markedly below $0.05$, surpassing all previous methodologies. Our code is available at https://github.com/xieyc99/DOV4CL.
Knowledge Distillation with Refined Logits
Aug 14, 2024



Abstract:Recent research on knowledge distillation has increasingly focused on logit distillation because of its simplicity, effectiveness, and versatility in model compression. In this paper, we introduce Refined Logit Distillation (RLD) to address the limitations of current logit distillation methods. Our approach is motivated by the observation that even high-performing teacher models can make incorrect predictions, creating a conflict between the standard distillation loss and the cross-entropy loss. This conflict can undermine the consistency of the student model's learning objectives. Previous attempts to use labels to empirically correct teacher predictions may undermine the class correlation. In contrast, our RLD employs labeling information to dynamically refine teacher logits. In this way, our method can effectively eliminate misleading information from the teacher while preserving crucial class correlations, thus enhancing the value and efficiency of distilled knowledge. Experimental results on CIFAR-100 and ImageNet demonstrate its superiority over existing methods. The code is provided at \text{https://github.com/zju-SWJ/RLD}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge