Fred Pauling
Present and Future of SLAM in Extreme Underground Environments
Aug 02, 2022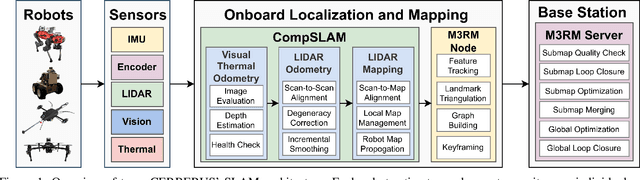
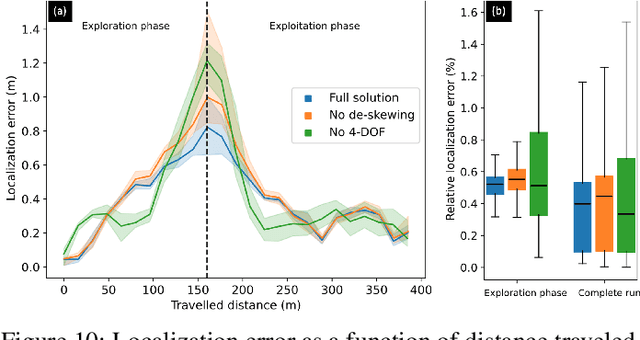
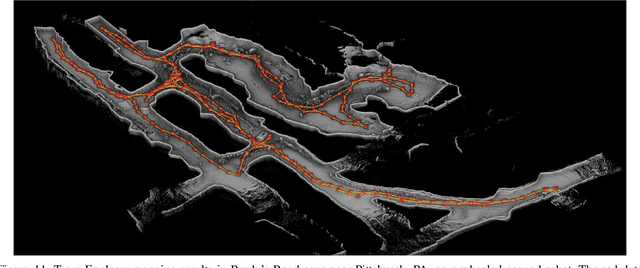
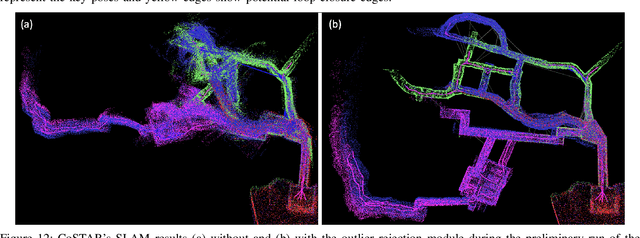
Abstract:This paper reports on the state of the art in underground SLAM by discussing different SLAM strategies and results across six teams that participated in the three-year-long SubT competition. In particular, the paper has four main goals. First, we review the algorithms, architectures, and systems adopted by the teams; particular emphasis is put on lidar-centric SLAM solutions (the go-to approach for virtually all teams in the competition), heterogeneous multi-robot operation (including both aerial and ground robots), and real-world underground operation (from the presence of obscurants to the need to handle tight computational constraints). We do not shy away from discussing the dirty details behind the different SubT SLAM systems, which are often omitted from technical papers. Second, we discuss the maturity of the field by highlighting what is possible with the current SLAM systems and what we believe is within reach with some good systems engineering. Third, we outline what we believe are fundamental open problems, that are likely to require further research to break through. Finally, we provide a list of open-source SLAM implementations and datasets that have been produced during the SubT challenge and related efforts, and constitute a useful resource for researchers and practitioners.
Wildcat: Online Continuous-Time 3D Lidar-Inertial SLAM
May 25, 2022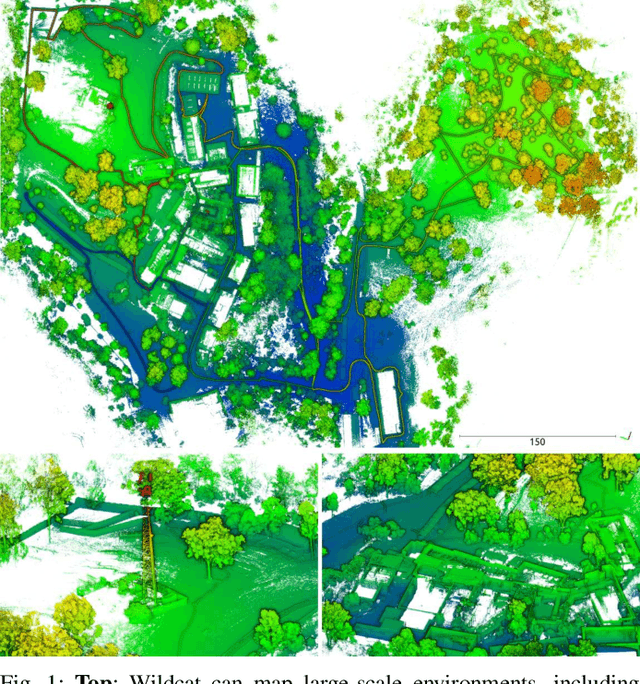
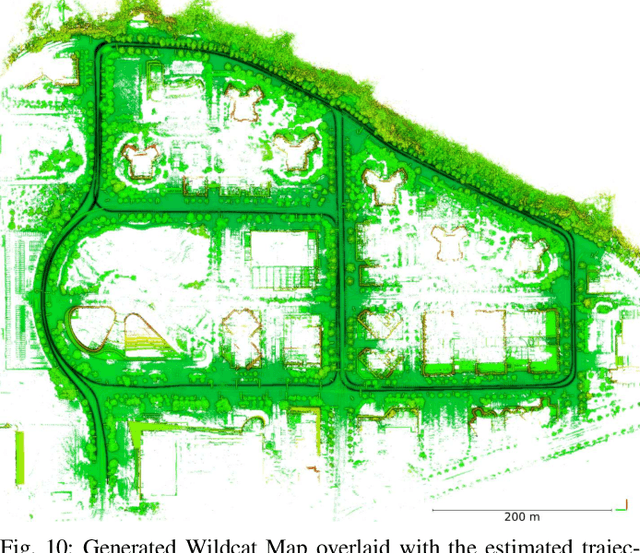
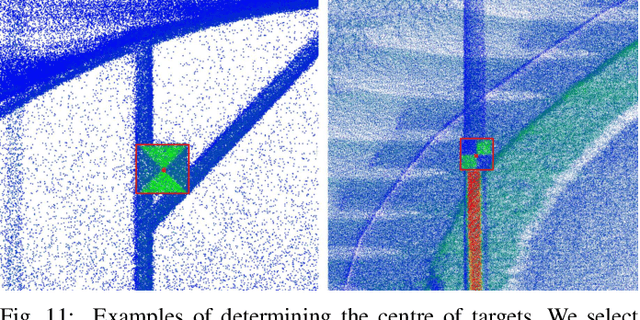
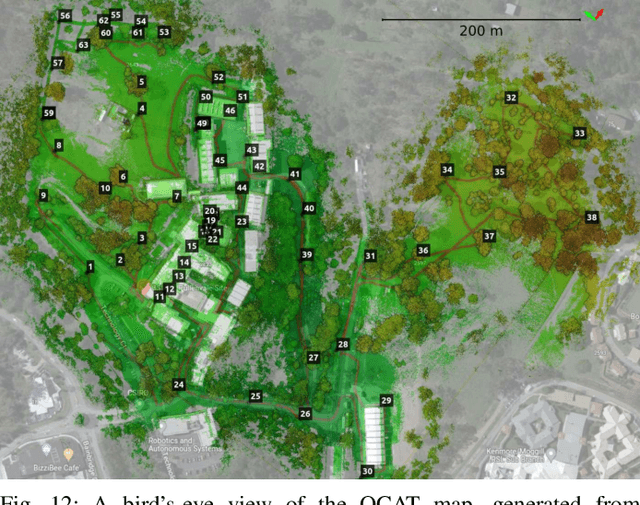
Abstract:We present Wildcat, a novel online 3D lidar-inertial SLAM system with exceptional versatility and robustness. At its core, Wildcat combines a robust real-time lidar-inertial odometry module, utilising a continuous-time trajectory representation, with an efficient pose-graph optimisation module that seamlessly supports both the single- and multi-agent settings. The robustness of Wildcat was recently demonstrated in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge where it outperformed other SLAM systems across various types of sensing-degraded and perceptually challenging environments. In this paper, we extensively evaluate Wildcat in a diverse set of new and publicly available real-world datasets and showcase its superior robustness and versatility over two existing state-of-the-art lidar-inertial SLAM systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge