Florian Boyer
A Study of Transducer based End-to-End ASR with ESPnet: Architecture, Auxiliary Loss and Decoding Strategies
Jan 14, 2022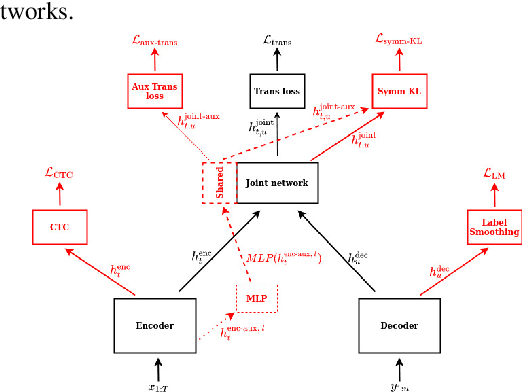
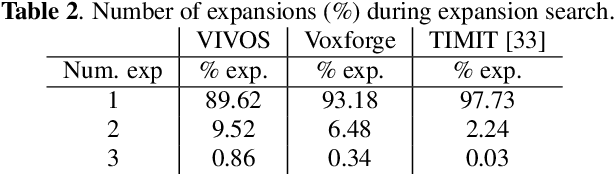
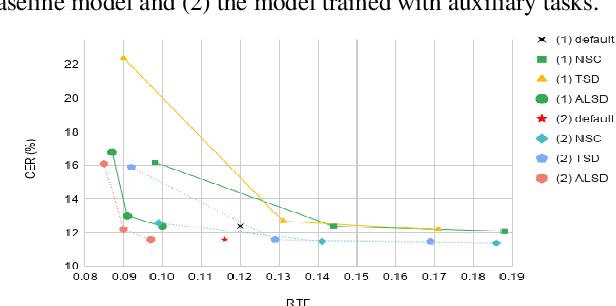
Abstract:In this study, we present recent developments of models trained with the RNN-T loss in ESPnet. It involves the use of various architectures such as recently proposed Conformer, multi-task learning with different auxiliary criteria and multiple decoding strategies, including our own proposition. Through experiments and benchmarks, we show that our proposed systems can be competitive against other state-of-art systems on well-known datasets such as LibriSpeech and AISHELL-1. Additionally, we demonstrate that these models are promising against other already implemented systems in ESPnet in regards to both performance and decoding speed, enabling the possibility to have powerful systems for a streaming task. With these additions, we hope to expand the usefulness of the ESPnet toolkit for the research community and also give tools for the ASR industry to deploy our systems in realistic and production environments.
The 2020 ESPnet update: new features, broadened applications, performance improvements, and future plans
Dec 23, 2020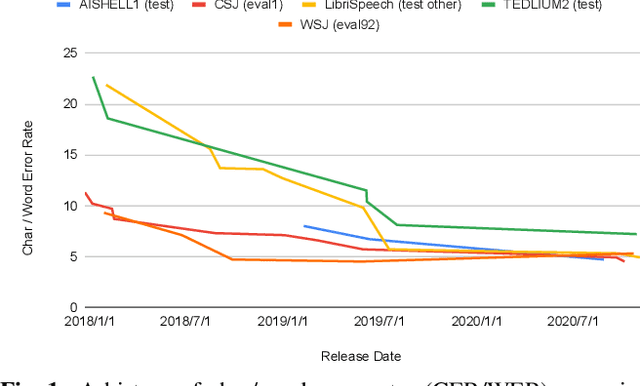
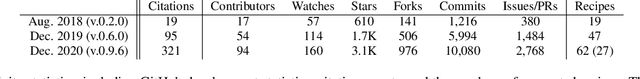
Abstract:This paper describes the recent development of ESPnet (https://github.com/espnet/espnet), an end-to-end speech processing toolkit. This project was initiated in December 2017 to mainly deal with end-to-end speech recognition experiments based on sequence-to-sequence modeling. The project has grown rapidly and now covers a wide range of speech processing applications. Now ESPnet also includes text to speech (TTS), voice conversation (VC), speech translation (ST), and speech enhancement (SE) with support for beamforming, speech separation, denoising, and dereverberation. All applications are trained in an end-to-end manner, thanks to the generic sequence to sequence modeling properties, and they can be further integrated and jointly optimized. Also, ESPnet provides reproducible all-in-one recipes for these applications with state-of-the-art performance in various benchmarks by incorporating transformer, advanced data augmentation, and conformer. This project aims to provide up-to-date speech processing experience to the community so that researchers in academia and various industry scales can develop their technologies collaboratively.
End-to-End Speech Recognition: A review for the French Language
Oct 23, 2019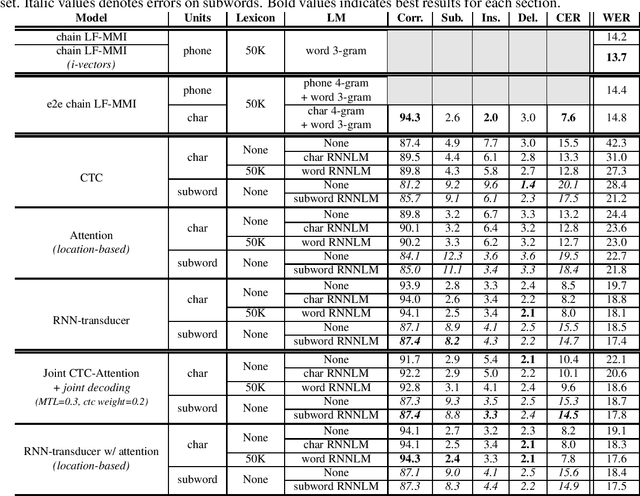
Abstract:Recently, end-to-end ASR based either on sequence-to-sequence networks or on the CTC objective function gained a lot of interest from the community, achieving competitive results over traditional systems using robust but complex pipelines. One of the main features of end-to-end systems, in addition to the ability to free themselves from extra linguistic resources such as dictionaries or language models, is the capacity to model acoustic units such as characters, subwords or directly words; opening up the capacity to directly translate speech with different representations or levels of knowledge depending on the target language. In this paper we propose a review of the existing end-to-end ASR approaches for the French language. We compare results to conventional state-of-the-art ASR systems and discuss which units are more suited to model the French language.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge