End-to-End Speech Recognition: A review for the French Language
Paper and Code
Oct 23, 2019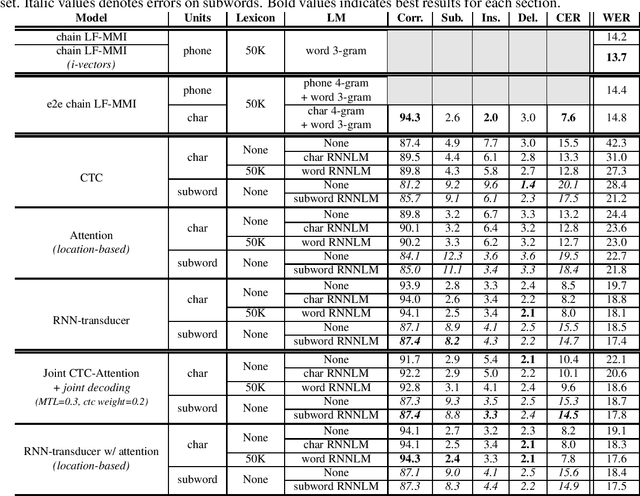
Recently, end-to-end ASR based either on sequence-to-sequence networks or on the CTC objective function gained a lot of interest from the community, achieving competitive results over traditional systems using robust but complex pipelines. One of the main features of end-to-end systems, in addition to the ability to free themselves from extra linguistic resources such as dictionaries or language models, is the capacity to model acoustic units such as characters, subwords or directly words; opening up the capacity to directly translate speech with different representations or levels of knowledge depending on the target language. In this paper we propose a review of the existing end-to-end ASR approaches for the French language. We compare results to conventional state-of-the-art ASR systems and discuss which units are more suited to model the French language.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge