Yusuke Shinohara
Bagpiper: Solving Open-Ended Audio Tasks via Rich Captions
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Current audio foundation models typically rely on rigid, task-specific supervision, addressing isolated factors of audio rather than the whole. In contrast, human intelligence processes audio holistically, seamlessly bridging physical signals with abstract cognitive concepts to execute complex tasks. Grounded in this philosophy, we introduce Bagpiper, an 8B audio foundation model that interprets physical audio via rich captions, i.e., comprehensive natural language descriptions that encapsulate the critical cognitive concepts inherent in the signal (e.g., transcription, audio events). By pre-training on a massive corpus of 600B tokens, the model establishes a robust bidirectional mapping between raw audio and this high-level conceptual space. During fine-tuning, Bagpiper adopts a caption-then-process workflow, simulating an intermediate cognitive reasoning step to solve diverse tasks without task-specific priors. Experimentally, Bagpiper outperforms Qwen-2.5-Omni on MMAU and AIRBench for audio understanding and surpasses CosyVoice3 and TangoFlux in generation quality, capable of synthesizing arbitrary compositions of speech, music, and sound effects. To the best of our knowledge, Bagpiper is among the first works that achieve unified understanding generation for general audio. Model, data, and code are available at Bagpiper Home Page.
Video Consistency Distance: Enhancing Temporal Consistency for Image-to-Video Generation via Reward-Based Fine-Tuning
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Reward-based fine-tuning of video diffusion models is an effective approach to improve the quality of generated videos, as it can fine-tune models without requiring real-world video datasets. However, it can sometimes be limited to specific performances because conventional reward functions are mainly aimed at enhancing the quality across the whole generated video sequence, such as aesthetic appeal and overall consistency. Notably, the temporal consistency of the generated video often suffers when applying previous approaches to image-to-video (I2V) generation tasks. To address this limitation, we propose Video Consistency Distance (VCD), a novel metric designed to enhance temporal consistency, and fine-tune a model with the reward-based fine-tuning framework. To achieve coherent temporal consistency relative to a conditioning image, VCD is defined in the frequency space of video frame features to capture frame information effectively through frequency-domain analysis. Experimental results across multiple I2V datasets demonstrate that fine-tuning a video generation model with VCD significantly enhances temporal consistency without degrading other performance compared to the previous method.
Evaluating Self-Supervised Speech Models via Text-Based LLMS
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) has gained traction for its ability to learn rich representations with low labeling costs, applicable across diverse downstream tasks. However, assessing the downstream-task performance remains challenging due to the cost of extra training and evaluation. Existing methods for task-agnostic evaluation also require extra training or hyperparameter tuning. We propose a novel evaluation metric using large language models (LLMs). By inputting discrete token sequences and minimal domain cues derived from SSL models into LLMs, we obtain the mean log-likelihood; these cues guide in-context learning, rendering the score more reliable without extra training or hyperparameter tuning. Experimental results show a correlation between LLM-based scores and automatic speech recognition task. Additionally, our findings reveal that LLMs not only functions as an SSL evaluation tools but also provides inference-time embeddings that are useful for speaker verification task.
Minimum Latency Training of Sequence Transducers for Streaming End-to-End Speech Recognition
Nov 04, 2022Abstract:Sequence transducers, such as the RNN-T and the Conformer-T, are one of the most promising models of end-to-end speech recognition, especially in streaming scenarios where both latency and accuracy are important. Although various methods, such as alignment-restricted training and FastEmit, have been studied to reduce the latency, latency reduction is often accompanied with a significant degradation in accuracy. We argue that this suboptimal performance might be caused because none of the prior methods explicitly model and reduce the latency. In this paper, we propose a new training method to explicitly model and reduce the latency of sequence transducer models. First, we define the expected latency at each diagonal line on the lattice, and show that its gradient can be computed efficiently within the forward-backward algorithm. Then we augment the transducer loss with this expected latency, so that an optimal trade-off between latency and accuracy is achieved. Experimental results on the WSJ dataset show that the proposed minimum latency training reduces the latency of causal Conformer-T from 220 ms to 27 ms within a WER degradation of 0.7%, and outperforms conventional alignment-restricted training (110 ms) and FastEmit (67 ms) methods.
A Study of Transducer based End-to-End ASR with ESPnet: Architecture, Auxiliary Loss and Decoding Strategies
Jan 14, 2022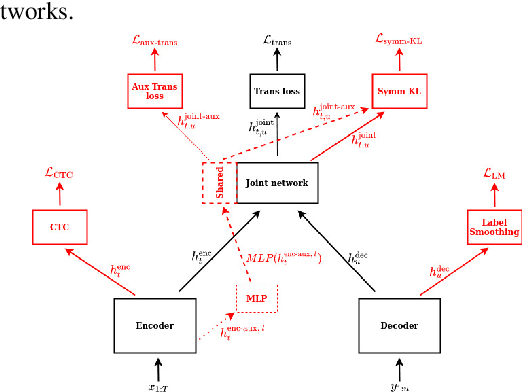
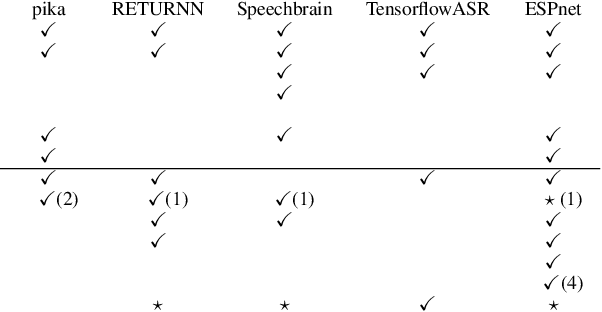
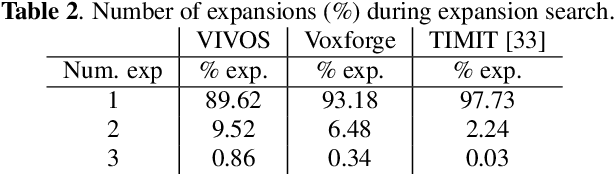
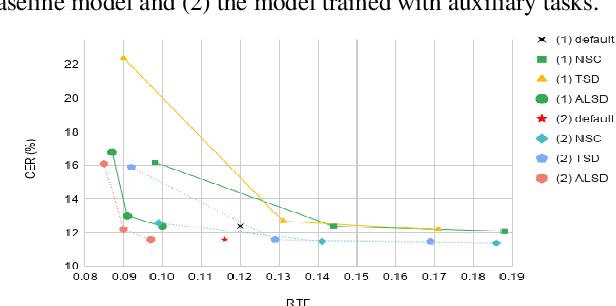
Abstract:In this study, we present recent developments of models trained with the RNN-T loss in ESPnet. It involves the use of various architectures such as recently proposed Conformer, multi-task learning with different auxiliary criteria and multiple decoding strategies, including our own proposition. Through experiments and benchmarks, we show that our proposed systems can be competitive against other state-of-art systems on well-known datasets such as LibriSpeech and AISHELL-1. Additionally, we demonstrate that these models are promising against other already implemented systems in ESPnet in regards to both performance and decoding speed, enabling the possibility to have powerful systems for a streaming task. With these additions, we hope to expand the usefulness of the ESPnet toolkit for the research community and also give tools for the ASR industry to deploy our systems in realistic and production environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge