A Study of Transducer based End-to-End ASR with ESPnet: Architecture, Auxiliary Loss and Decoding Strategies
Paper and Code
Jan 14, 2022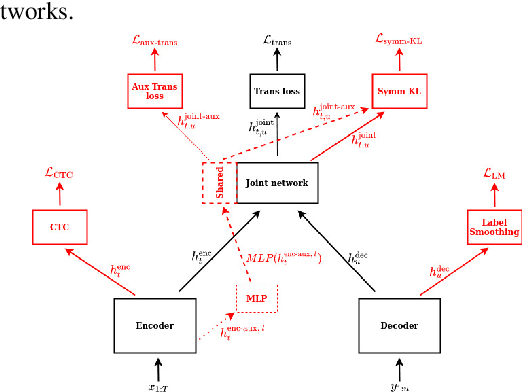
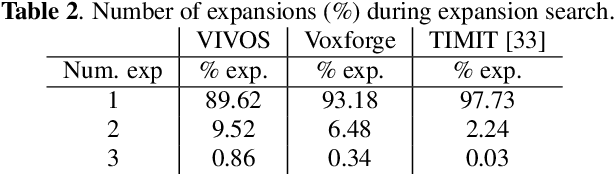
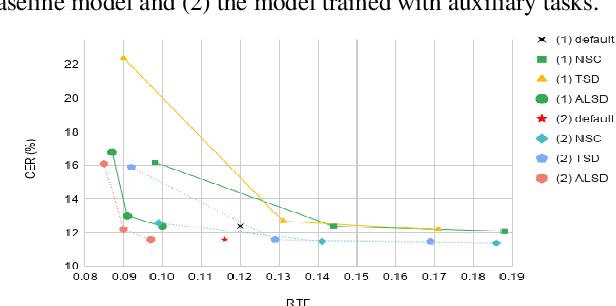
In this study, we present recent developments of models trained with the RNN-T loss in ESPnet. It involves the use of various architectures such as recently proposed Conformer, multi-task learning with different auxiliary criteria and multiple decoding strategies, including our own proposition. Through experiments and benchmarks, we show that our proposed systems can be competitive against other state-of-art systems on well-known datasets such as LibriSpeech and AISHELL-1. Additionally, we demonstrate that these models are promising against other already implemented systems in ESPnet in regards to both performance and decoding speed, enabling the possibility to have powerful systems for a streaming task. With these additions, we hope to expand the usefulness of the ESPnet toolkit for the research community and also give tools for the ASR industry to deploy our systems in realistic and production environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge