Fengyi Wang
Object Classification Utilizing Neuromorphic Proprioceptive Signals in Active Exploration: Validated on a Soft Anthropomorphic Hand
May 23, 2025Abstract:Proprioception, a key sensory modality in haptic perception, plays a vital role in perceiving the 3D structure of objects by providing feedback on the position and movement of body parts. The restoration of proprioceptive sensation is crucial for enabling in-hand manipulation and natural control in the prosthetic hand. Despite its importance, proprioceptive sensation is relatively unexplored in an artificial system. In this work, we introduce a novel platform that integrates a soft anthropomorphic robot hand (QB SoftHand) with flexible proprioceptive sensors and a classifier that utilizes a hybrid spiking neural network with different types of spiking neurons to interpret neuromorphic proprioceptive signals encoded by a biological muscle spindle model. The encoding scheme and the classifier are implemented and tested on the datasets we collected in the active exploration of ten objects from the YCB benchmark. Our results indicate that the classifier achieves more accurate inferences than existing learning approaches, especially in the early stage of the exploration. This system holds the potential for development in the areas of haptic feedback and neural prosthetics.
A Bio-mimetic Neuromorphic Model for Heat-evoked Nociceptive Withdrawal Reflex in Upper Limb
May 23, 2025Abstract:The nociceptive withdrawal reflex (NWR) is a mechanism to mediate interactions and protect the body from damage in a potentially dangerous environment. To better convey warning signals to users of prosthetic arms or autonomous robots and protect them by triggering a proper NWR, it is useful to use a biological representation of temperature information for fast and effective processing. In this work, we present a neuromorphic spiking network for heat-evoked NWR by mimicking the structure and encoding scheme of the reflex arc. The network is trained with the bio-plausible reward modulated spike timing-dependent plasticity learning algorithm. We evaluated the proposed model and three other methods in recent studies that trigger NWR in an experiment with radiant heat. We found that only the neuromorphic model exhibits the spatial summation (SS) effect and temporal summation (TS) effect similar to humans and can encode the reflex strength matching the intensity of the stimulus in the relative spike latency online. The improved bio-plausibility of this neuromorphic model could improve sensory feedback in neural prostheses.
SMPLOlympics: Sports Environments for Physically Simulated Humanoids
Jun 28, 2024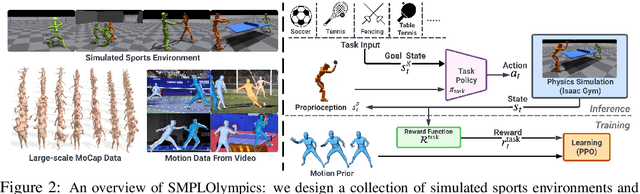
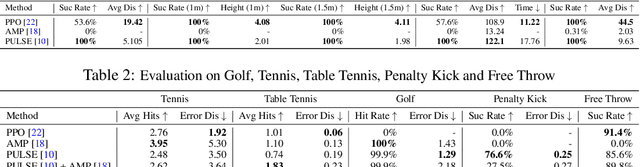

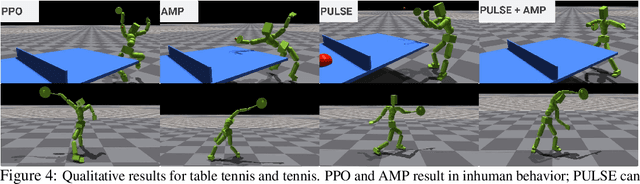
Abstract:We present SMPLOlympics, a collection of physically simulated environments that allow humanoids to compete in a variety of Olympic sports. Sports simulation offers a rich and standardized testing ground for evaluating and improving the capabilities of learning algorithms due to the diversity and physically demanding nature of athletic activities. As humans have been competing in these sports for many years, there is also a plethora of existing knowledge on the preferred strategy to achieve better performance. To leverage these existing human demonstrations from videos and motion capture, we design our humanoid to be compatible with the widely-used SMPL and SMPL-X human models from the vision and graphics community. We provide a suite of individual sports environments, including golf, javelin throw, high jump, long jump, and hurdling, as well as competitive sports, including both 1v1 and 2v2 games such as table tennis, tennis, fencing, boxing, soccer, and basketball. Our analysis shows that combining strong motion priors with simple rewards can result in human-like behavior in various sports. By providing a unified sports benchmark and baseline implementation of state and reward designs, we hope that SMPLOlympics can help the control and animation communities achieve human-like and performant behaviors.
ALYMPICS: Language Agents Meet Game Theory
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces Alympics, a platform that leverages Large Language Model (LLM) agents to facilitate investigations in game theory. By employing LLMs and autonomous agents to simulate human behavior and enable multi-agent collaborations, we can construct realistic and dynamic models of human interactions for game theory hypothesis formulating and testing. To demonstrate this, we present and implement a survival game involving unequal competition for limited resources. Through manipulation of resource availability and agent personalities, we observe how different agents engage in the competition and adapt their strategies. The use of LLM agents in game theory research offers significant advantages, including simulating realistic behavior, providing a controlled, scalable, and reproducible environment. Our work highlights the potential of LLM agents in enhancing the understanding of strategic decision-making within complex socioeconomic contexts. All codes are available at https://github.com/microsoft/Alympics
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge