Eva-Maria Messner
The MuSe 2021 Multimodal Sentiment Analysis Challenge: Sentiment, Emotion, Physiological-Emotion, and Stress
Apr 14, 2021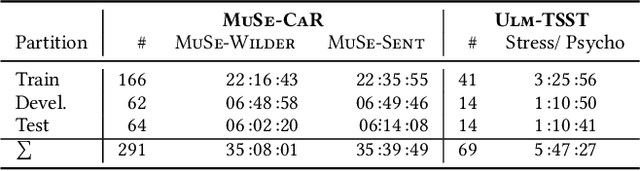
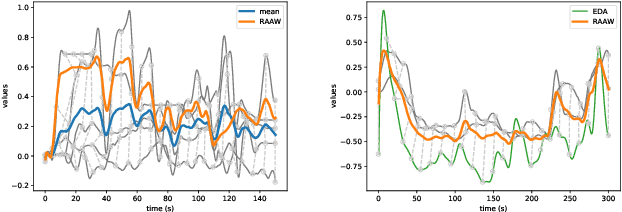
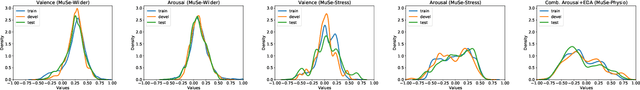
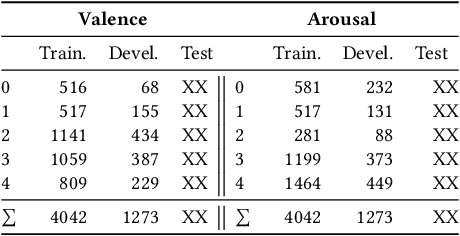
Abstract:Multimodal Sentiment Analysis (MuSe) 2021 is a challenge focusing on the tasks of sentiment and emotion, as well as physiological-emotion and emotion-based stress recognition through more comprehensively integrating the audio-visual, language, and biological signal modalities. The purpose of MuSe 2021 is to bring together communities from different disciplines; mainly, the audio-visual emotion recognition community (signal-based), the sentiment analysis community (symbol-based), and the health informatics community. We present four distinct sub-challenges: MuSe-Wilder and MuSe-Stress which focus on continuous emotion (valence and arousal) prediction; MuSe-Sent, in which participants recognise five classes each for valence and arousal; and MuSe-Physio, in which the novel aspect of `physiological-emotion' is to be predicted. For this years' challenge, we utilise the MuSe-CaR dataset focusing on user-generated reviews and introduce the Ulm-TSST dataset, which displays people in stressful depositions. This paper also provides detail on the state-of-the-art feature sets extracted from these datasets for utilisation by our baseline model, a Long Short-Term Memory-Recurrent Neural Network. For each sub-challenge, a competitive baseline for participants is set; namely, on test, we report a Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC) of .4616 CCC for MuSe-Wilder; .4717 CCC for MuSe-Stress, and .4606 CCC for MuSe-Physio. For MuSe-Sent an F1 score of 32.82 % is obtained.
Annotation of Emotion Carriers in Personal Narratives
Feb 28, 2020
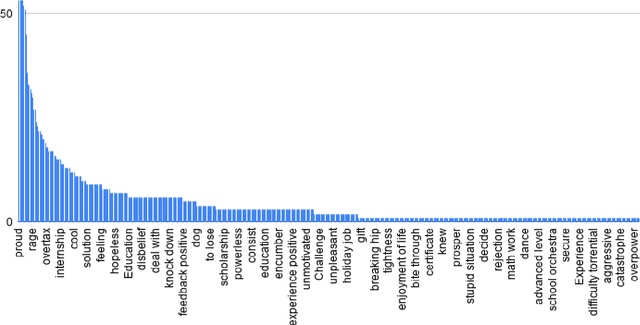
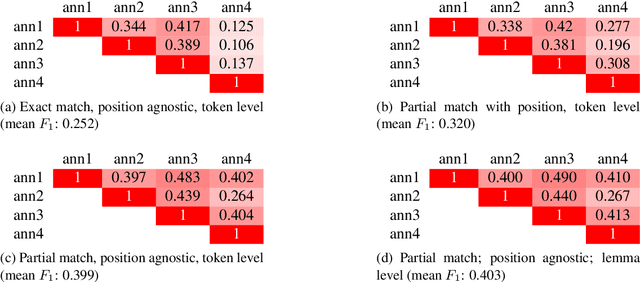
Abstract:We are interested in the problem of understanding personal narratives (PN) - spoken or written - recollections of facts, events, and thoughts. In PN, emotion carriers are the speech or text segments that best explain the emotional state of the user. Such segments may include entities, verb or noun phrases. Advanced automatic understanding of PNs requires not only the prediction of the user emotional state but also to identify which events (e.g. "the loss of relative" or "the visit of grandpa") or people ( e.g. "the old group of high school mates") carry the emotion manifested during the personal recollection. This work proposes and evaluates an annotation model for identifying emotion carriers in spoken personal narratives. Compared to other text genres such as news and microblogs, spoken PNs are particularly challenging because a narrative is usually unstructured, involving multiple sub-events and characters as well as thoughts and associated emotions perceived by the narrator. In this work, we experiment with annotating emotion carriers from speech transcriptions in the Ulm State-of-Mind in Speech (USoMS) corpus, a dataset of German PNs. We believe this resource could be used for experiments in the automatic extraction of emotion carriers from PN, a task that could provide further advancements in narrative understanding.
AVEC 2019 Workshop and Challenge: State-of-Mind, Detecting Depression with AI, and Cross-Cultural Affect Recognition
Jul 10, 2019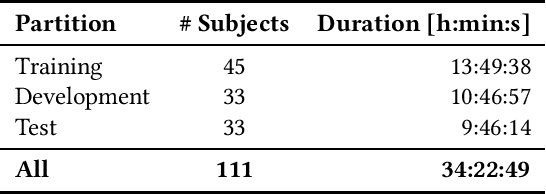
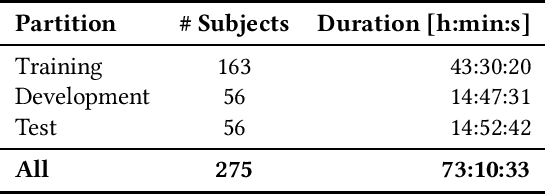
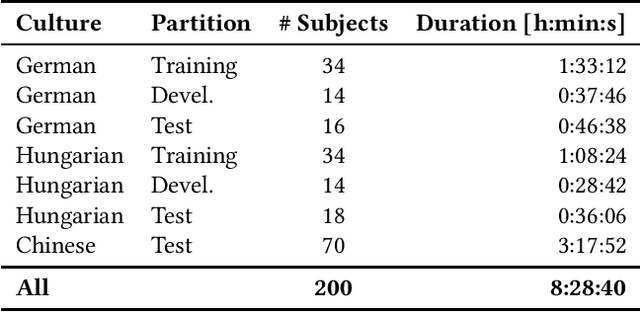
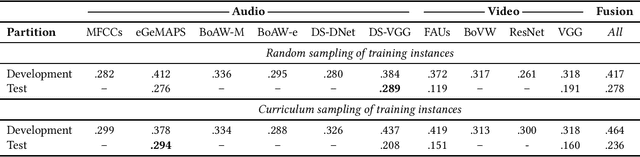
Abstract:The Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge and Workshop (AVEC 2019) "State-of-Mind, Detecting Depression with AI, and Cross-cultural Affect Recognition" is the ninth competition event aimed at the comparison of multimedia processing and machine learning methods for automatic audiovisual health and emotion analysis, with all participants competing strictly under the same conditions. The goal of the Challenge is to provide a common benchmark test set for multimodal information processing and to bring together the health and emotion recognition communities, as well as the audiovisual processing communities, to compare the relative merits of various approaches to health and emotion recognition from real-life data. This paper presents the major novelties introduced this year, the challenge guidelines, the data used, and the performance of the baseline systems on the three proposed tasks: state-of-mind recognition, depression assessment with AI, and cross-cultural affect sensing, respectively.
Modeling user context for valence prediction from narratives
May 09, 2019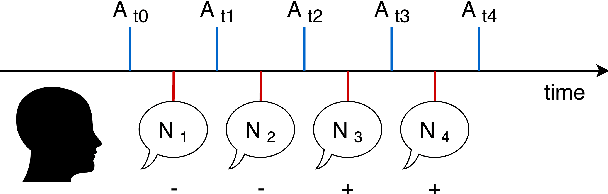
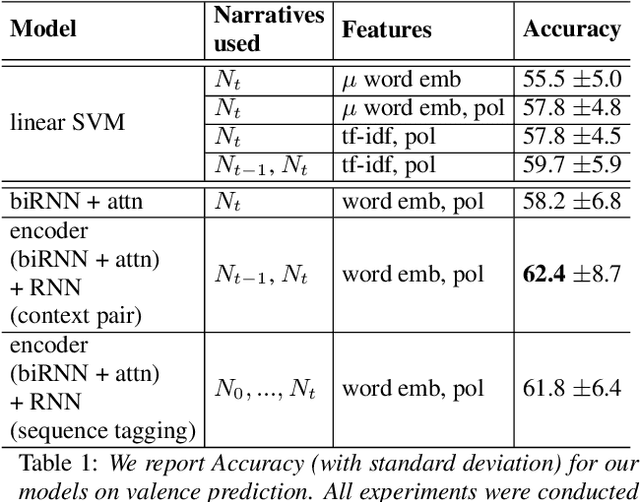

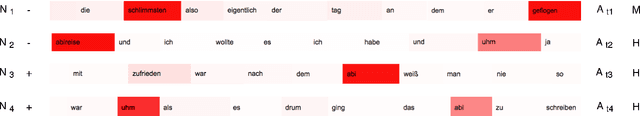
Abstract:Automated prediction of valence, one key feature of a person's emotional state, from individuals' personal narratives may provide crucial information for mental healthcare (e.g. early diagnosis of mental diseases, supervision of disease course, etc.). In the Interspeech 2018 ComParE Self-Assessed Affect challenge, the task of valence prediction was framed as a three-class classification problem using 8 seconds fragments from individuals' narratives. As such, the task did not allow for exploring contextual information of the narratives. In this work, we investigate the intrinsic information from multiple narratives recounted by the same individual in order to predict their current state-of-mind. Furthermore, with generalizability in mind, we decided to focus our experiments exclusively on textual information as the public availability of audio narratives is limited compared to text. Our hypothesis is, that context modeling might provide insights about emotion triggering concepts (e.g. events, people, places) mentioned in the narratives that are linked to an individual's state of mind. We explore multiple machine learning techniques to model narratives. We find that the models are able to capture inter-individual differences, leading to more accurate predictions of an individual's emotional state, as compared to single narratives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge