Eun Kyung Lee
Towards Efficient Key-Value Cache Management for Prefix Prefilling in LLM Inference
May 28, 2025Abstract:The increasing adoption of large language models (LLMs) with extended context windows necessitates efficient Key-Value Cache (KVC) management to optimize inference performance. Inference workloads like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and agents exhibit high cache reusability, making efficient caching critical to reducing redundancy and improving speed. We analyze real-world KVC access patterns using publicly available traces and evaluate commercial key-value stores like Redis and state-of-the-art RDMA-based systems (CHIME [1] and Sherman [2]) for KVC metadata management. Our work demonstrates the lack of tailored storage solution for KVC prefilling, underscores the need for an efficient distributed caching system with optimized metadata management for LLM workloads, and provides insights into designing improved KVC management systems for scalable, low-latency inference.
Mind the Memory Gap: Unveiling GPU Bottlenecks in Large-Batch LLM Inference
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Large language models have been widely adopted across different tasks, but their auto-regressive generation nature often leads to inefficient resource utilization during inference. While batching is commonly used to increase throughput, performance gains plateau beyond a certain batch size, especially with smaller models, a phenomenon that existing literature typically explains as a shift to the compute-bound regime. In this paper, through an in-depth GPU-level analysis, we reveal that large-batch inference remains memory-bound, with most GPU compute capabilities underutilized due to DRAM bandwidth saturation as the primary bottleneck. To address this, we propose a Batching Configuration Advisor (BCA) that optimizes memory allocation, reducing GPU memory requirements with minimal impact on throughput. The freed memory and underutilized GPU compute capabilities can then be leveraged by concurrent workloads. Specifically, we use model replication to improve serving throughput and GPU utilization. Our findings challenge conventional assumptions about LLM inference, offering new insights and practical strategies for improving resource utilization, particularly for smaller language models.
Towards Pareto Optimal Throughput in Small Language Model Serving
Apr 04, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized the state-of-the-art of many different natural language processing tasks. Although serving LLMs is computationally and memory demanding, the rise of Small Language Models (SLMs) offers new opportunities for resource-constrained users, who now are able to serve small models with cutting-edge performance. In this paper, we present a set of experiments designed to benchmark SLM inference at performance and energy levels. Our analysis provides a new perspective in serving, highlighting that the small memory footprint of SLMs allows for reaching the Pareto-optimal throughput within the resource capacity of a single accelerator. In this regard, we present an initial set of findings demonstrating how model replication can effectively improve resource utilization for serving SLMs.
FedCore: Straggler-Free Federated Learning with Distributed Coresets
Jan 31, 2024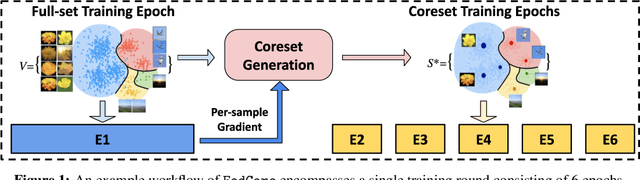
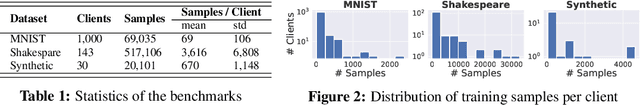
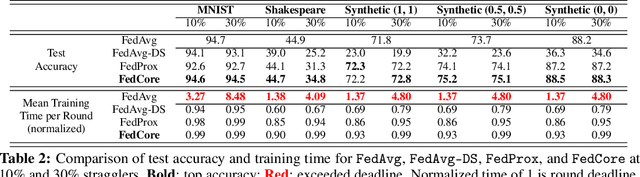
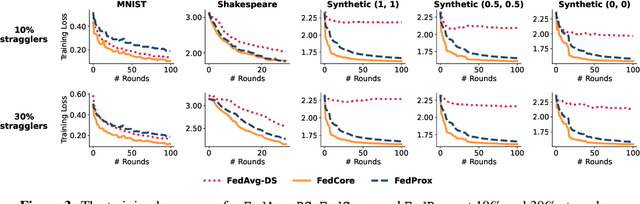
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) is a machine learning paradigm that allows multiple clients to collaboratively train a shared model while keeping their data on-premise. However, the straggler issue, due to slow clients, often hinders the efficiency and scalability of FL. This paper presents FedCore, an algorithm that innovatively tackles the straggler problem via the decentralized selection of coresets, representative subsets of a dataset. Contrary to existing centralized coreset methods, FedCore creates coresets directly on each client in a distributed manner, ensuring privacy preservation in FL. FedCore translates the coreset optimization problem into a more tractable k-medoids clustering problem and operates distributedly on each client. Theoretical analysis confirms FedCore's convergence, and practical evaluations demonstrate an 8x reduction in FL training time, without compromising model accuracy. Our extensive evaluations also show that FedCore generalizes well to existing FL frameworks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge