Eugen Hotaj
AutoML for Large Capacity Modeling of Meta's Ranking Systems
Nov 16, 2023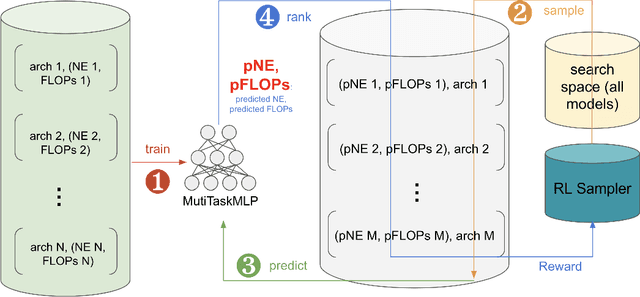
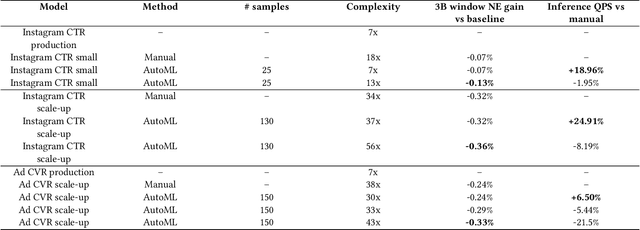
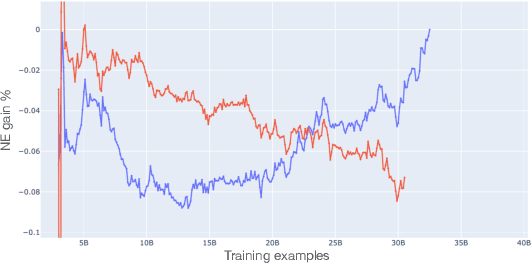

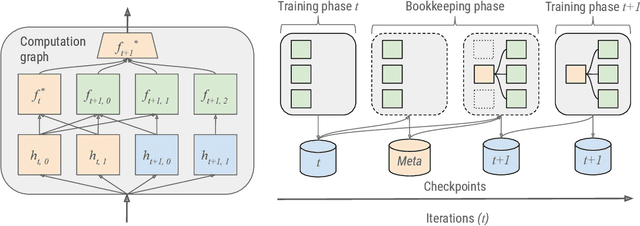
Abstract:Web-scale ranking systems at Meta serving billions of users is complex. Improving ranking models is essential but engineering heavy. Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) can release engineers from labor intensive work of tuning ranking models; however, it is unknown if AutoML is efficient enough to meet tight production timeline in real-world and, at the same time, bring additional improvements to the strong baselines. Moreover, to achieve higher ranking performance, there is an ever-increasing demand to scale up ranking models to even larger capacity, which imposes more challenges on the efficiency. The large scale of models and tight production schedule requires AutoML to outperform human baselines by only using a small number of model evaluation trials (around 100). We presents a sampling-based AutoML method, focusing on neural architecture search and hyperparameter optimization, addressing these challenges in Meta-scale production when building large capacity models. Our approach efficiently handles large-scale data demands. It leverages a lightweight predictor-based searcher and reinforcement learning to explore vast search spaces, significantly reducing the number of model evaluations. Through experiments in large capacity modeling for CTR and CVR applications, we show that our method achieves outstanding Return on Investment (ROI) versus human tuned baselines, with up to 0.09% Normalized Entropy (NE) loss reduction or $25\%$ Query per Second (QPS) increase by only sampling one hundred models on average from a curated search space. The proposed AutoML method has already made real-world impact where a discovered Instagram CTR model with up to -0.36% NE gain (over existing production baseline) was selected for large-scale online A/B test and show statistically significant gain. These production results proved AutoML efficacy and accelerated its adoption in ranking systems at Meta.
AdaNet: A Scalable and Flexible Framework for Automatically Learning Ensembles
Apr 30, 2019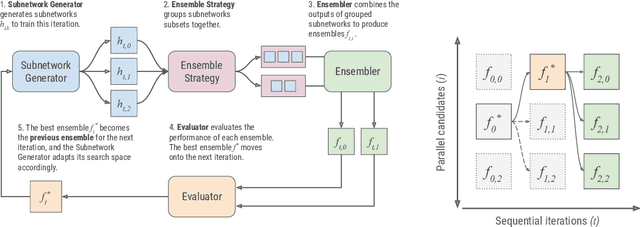
Abstract:AdaNet is a lightweight TensorFlow-based (Abadi et al., 2015) framework for automatically learning high-quality ensembles with minimal expert intervention. Our framework is inspired by the AdaNet algorithm (Cortes et al., 2017) which learns the structure of a neural network as an ensemble of subnetworks. We designed it to: (1) integrate with the existing TensorFlow ecosystem, (2) offer sensible default search spaces to perform well on novel datasets, (3) present a flexible API to utilize expert information when available, and (4) efficiently accelerate training with distributed CPU, GPU, and TPU hardware. The code is open-source and available at: https://github.com/tensorflow/adanet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge