Emily Zhou
Encoding Emotion Through Self-Supervised Eye Movement Reconstruction
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:The relationship between emotional expression and eye movement is well-documented, with literature establishing gaze patterns are reliable indicators of emotion. However, most studies utilize specialized, high-resolution eye-tracking equipment, limiting the potential reach of findings. We investigate how eye movement can be used to predict multimodal markers of emotional expression from naturalistic, low-resolution videos. We utilize a collection of video interviews from the USC Shoah Foundation's Visual History Archive with Holocaust survivors as they recount their experiences in the Auschwitz concentration camp. Inspired by pretraining methods on language models, we develop a novel gaze detection model that uses self-supervised eye movement reconstruction that can effectively leverage unlabeled video. We use this model's encoder embeddings to fine-tune models on two downstream tasks related to emotional expression. The first is aligning eye movement with directional emotion estimates from speech. The second task is using eye gaze as a predictor of three momentary manifestations of emotional behaviors: laughing, crying/sobbing, and sighing. We find our new model is predictive of emotion outcomes and observe a positive correlation between pretraining performance and emotion processing performance for both experiments. We conclude self-supervised eye movement reconstruction is an effective method for encoding the affective signal they carry.
Guiding Data Collection via Factored Scaling Curves
May 12, 2025Abstract:Generalist imitation learning policies trained on large datasets show great promise for solving diverse manipulation tasks. However, to ensure generalization to different conditions, policies need to be trained with data collected across a large set of environmental factor variations (e.g., camera pose, table height, distractors) $-$ a prohibitively expensive undertaking, if done exhaustively. We introduce a principled method for deciding what data to collect and how much to collect for each factor by constructing factored scaling curves (FSC), which quantify how policy performance varies as data scales along individual or paired factors. These curves enable targeted data acquisition for the most influential factor combinations within a given budget. We evaluate the proposed method through extensive simulated and real-world experiments, across both training-from-scratch and fine-tuning settings, and show that it boosts success rates in real-world tasks in new environments by up to 26% over existing data-collection strategies. We further demonstrate how factored scaling curves can effectively guide data collection using an offline metric, without requiring real-world evaluation at scale.
AffectEval: A Modular and Customizable Framework for Affective Computing
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:The field of affective computing focuses on recognizing, interpreting, and responding to human emotions, and has broad applications across education, child development, and human health and wellness. However, developing affective computing pipelines remains labor-intensive due to the lack of software frameworks that support multimodal, multi-domain emotion recognition applications. This often results in redundant effort when building pipelines for different applications. While recent frameworks attempt to address these challenges, they remain limited in reducing manual effort and ensuring cross-domain generalizability. We introduce AffectEval, a modular and customizable framework to facilitate the development of affective computing pipelines while reducing the manual effort and duplicate work involved in developing such pipelines. We validate AffectEval by replicating prior affective computing experiments, and we demonstrate that our framework reduces programming effort by up to 90%, as measured by the reduction in raw lines of code.
CAREForMe: Contextual Multi-Armed Bandit Recommendation Framework for Mental Health
Jan 26, 2024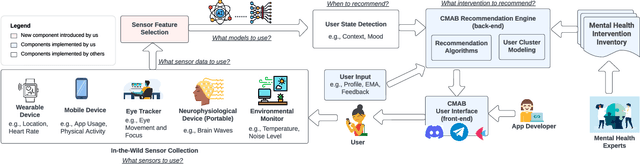
Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic has intensified the urgency for effective and accessible mental health interventions in people's daily lives. Mobile Health (mHealth) solutions, such as AI Chatbots and Mindfulness Apps, have gained traction as they expand beyond traditional clinical settings to support daily life. However, the effectiveness of current mHealth solutions is impeded by the lack of context-awareness, personalization, and modularity to foster their reusability. This paper introduces CAREForMe, a contextual multi-armed bandit (CMAB) recommendation framework for mental health. Designed with context-awareness, personalization, and modularity at its core, CAREForMe harnesses mobile sensing and integrates online learning algorithms with user clustering capability to deliver timely, personalized recommendations. With its modular design, CAREForMe serves as both a customizable recommendation framework to guide future research, and a collaborative platform to facilitate interdisciplinary contributions in mHealth research. We showcase CAREForMe's versatility through its implementation across various platforms (e.g., Discord, Telegram) and its customization to diverse recommendation features.
Designing a Socially Assistive Robot to Support Older Adults with Low Vision
Jan 06, 2024Abstract:Socially assistive robots (SARs) have shown great promise in supplementing and augmenting interventions to support the physical and mental well-being of older adults. However, past work has not yet explored the potential of applying SAR to lower the barriers of long-term low vision rehabilitation (LVR) interventions for older adults. In this work, we present a user-informed design process to validate the motivation and identify major design principles for developing SAR for long-term LVR. To evaluate user-perceived usefulness and acceptance of SAR in this novel domain, we performed a two-phase study through user surveys. First, a group (n=38) of older adults with LV completed a mailed-in survey. Next, a new group (n=13) of older adults with LV saw an in-clinic SAR demo and then completed the survey. The study participants reported that SARs would be useful, trustworthy, easy to use, and enjoyable while providing socio-emotional support to augment LVR interventions. The in-clinic demo group reported significantly more positive opinions of the SAR's capabilities than did the baseline survey group that used mailed-in forms without the SAR demo.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge