Emad Shihab
Will It Survive? Deciphering the Fate of AI-Generated Code in Open Source
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:The integration of AI agents as coding assistants into software development has raised questions about the long-term viability of AI agent-generated code. A prevailing hypothesis within the software engineering community suggests this code is "disposable", meaning it is merged quickly but discarded shortly thereafter. If true, organizations risk shifting maintenance burden from generation to post-deployment remediation. We investigate this hypothesis through survival analysis of 201 open-source projects, tracking over 200,000 code units authored by AI agents versus humans. Contrary to the disposable code narrative, agent-authored code survives significantly longer: at the line level, it exhibits a 15.8 percentage-point lower modification rate and 16% lower hazard of modification (HR = 0.842, p < 0.001). However, modification profiles differ. Agent-authored code shows modestly elevated corrective rates (26.3% vs. 23.0%), while human code shows higher adaptive rates. However, the effect sizes are small (Cramér's V = 0.116), and per-agent variation exceeds the agent-human gap. Turning to prediction, textual features can identify modification-prone code (AUC-ROC = 0.671), but predicting when modifications occur remains challenging (Macro F1 = 0.285), suggesting timing depends on external organizational dynamics. The bottleneck for agent-generated code may not be generation quality, but the organizational practices that govern its long-term evolution.
Tokenomics: Quantifying Where Tokens Are Used in Agentic Software Engineering
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:LLM-based Multi-Agent (LLM-MA) systems are increasingly applied to automate complex software engineering tasks such as requirements engineering, code generation, and testing. However, their operational efficiency and resource consumption remain poorly understood, hindering practical adoption due to unpredictable costs and environmental impact. To address this, we conduct an analysis of token consumption patterns in an LLM-MA system within the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), aiming to understand where tokens are consumed across distinct software engineering activities. We analyze execution traces from 30 software development tasks performed by the ChatDev framework using a GPT-5 reasoning model, mapping its internal phases to distinct development stages (Design, Coding, Code Completion, Code Review, Testing, and Documentation) to create a standardized evaluation framework. We then quantify and compare token distribution (input, output, reasoning) across these stages. Our preliminary findings show that the iterative Code Review stage accounts for the majority of token consumption for an average of 59.4% of tokens. Furthermore, we observe that input tokens consistently constitute the largest share of consumption for an average of 53.9%, providing empirical evidence for potentially significant inefficiencies in agentic collaboration. Our results suggest that the primary cost of agentic software engineering lies not in initial code generation but in automated refinement and verification. Our novel methodology can help practitioners predict expenses and optimize workflows, and it directs future research toward developing more token-efficient agent collaboration protocols.
Beyond Synthetic Benchmarks: Evaluating LLM Performance on Real-World Class-Level Code Generation
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have advanced code generation at the function level, yet their ability to produce correct class-level implementations in authentic software projects remains poorly understood. This work introduces a novel benchmark derived from open-source repositories, comprising real-world classes divided into seen and unseen partitions to evaluate generalization under practical conditions. The evaluation examines multiple LLMs under varied input specifications, retrieval-augmented configurations, and documentation completeness levels. Results reveal a stark performance disparity: LLMs achieve 84% to 89% correctness on established synthetic benchmarks but only 25% to 34% on real-world class tasks, with negligible differences between familiar and novel codebases. Comprehensive docstrings yield modest gains of 1% to 3% in functional accuracy, though statistical significance is rare. Retrieval-augmented generation proves most effective with partial documentation, improving correctness by 4% to 7% by supplying concrete implementation patterns absent from specifications. Error profiling identifies AttributeError, TypeError, and AssertionError as dominant failure modes (84% of cases), with synthetic tests overemphasizing assertion issues and real-world scenarios highlighting type and attribute mismatches. Retrieval augmentation reduces logical flaws but can introduce dependency conflicts. The benchmark and analysis expose critical limitations in current LLM capabilities for class-level engineering, offering actionable insights for enhancing context modelling, documentation strategies, and retrieval integration in production code assistance tools.
Automated File-Level Logging Generation for Machine Learning Applications using LLMs: A Case Study using GPT-4o Mini
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Logging is essential in software development, helping developers monitor system behavior and aiding in debugging applications. Given the ability of large language models (LLMs) to generate natural language and code, researchers are exploring their potential to generate log statements. However, prior work focuses on evaluating logs introduced in code functions, leaving file-level log generation underexplored -- especially in machine learning (ML) applications, where comprehensive logging can enhance reliability. In this study, we evaluate the capacity of GPT-4o mini as a case study to generate log statements for ML projects at file level. We gathered a set of 171 ML repositories containing 4,073 Python files with at least one log statement. We identified and removed the original logs from the files, prompted the LLM to generate logs for them, and evaluated both the position of the logs and log level, variables, and text quality of the generated logs compared to human-written logs. In addition, we manually analyzed a representative sample of generated logs to identify common patterns and challenges. We find that the LLM introduces logs in the same place as humans in 63.91% of cases, but at the cost of a high overlogging rate of 82.66%. Furthermore, our manual analysis reveals challenges for file-level logging, which shows overlogging at the beginning or end of a function, difficulty logging within large code blocks, and misalignment with project-specific logging conventions. While the LLM shows promise for generating logs for complete files, these limitations remain to be addressed for practical implementation.
A Large-scale Class-level Benchmark Dataset for Code Generation with LLMs
Apr 22, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated promising capabilities in code generation tasks. However, most existing benchmarks focus on isolated functions and fail to capture the complexity of real-world, class-level software structures. To address this gap, we introduce a large-scale, Python class-level dataset curated from $13{,}174$ real-world open-source projects. The dataset contains over 842,000 class skeletons, each including class and method signatures, along with associated docstrings when available. We preserve structural and contextual dependencies critical to realistic software development scenarios and enrich the dataset with static code metrics to support downstream analysis. To evaluate the usefulness of this dataset, we use extracted class skeletons as prompts for GPT-4 to generate full class implementations. Results show that the LLM-generated classes exhibit strong lexical and structural similarity to human-written counterparts, with average ROUGE@L, BLEU, and TSED scores of 0.80, 0.59, and 0.73, respectively. These findings confirm that well-structured prompts derived from real-world class skeletons significantly enhance LLM performance in class-level code generation. This dataset offers a valuable resource for benchmarking, training, and improving LLMs in realistic software engineering contexts.
Synergizing LLMs and Knowledge Graphs: A Novel Approach to Software Repository-Related Question Answering
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Software repositories contain valuable information for gaining insights into their development process. However, extracting insights from these repository data is time-consuming and requires technical expertise. While software engineering chatbots have been developed to facilitate natural language interactions with repositories, they struggle with understanding natural language and accurately retrieving relevant data. This study aims to improve the accuracy of LLM-based chatbots in answering repository-related questions by augmenting them with knowledge graphs. We achieve this in a two-step approach; (1) constructing a knowledge graph from the repository data and (2) synergizing the knowledge graph with LLM to allow for the natural language questions and answers. We curated a set of 20 questions with different complexities and evaluated our approach on five popular open-source projects. Our approach achieved an accuracy of 65%. We further investigated the limitations and identified six key issues, with the majority relating to the reasoning capability of the LLM. We experimented with a few-shot chain-of-thought prompting to determine if it could enhance our approach. This technique improved the overall accuracy to 84%. Our findings demonstrate the synergy between LLMs and knowledge graphs as a viable solution for making repository data accessible to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
An Approach for Auto Generation of Labeling Functions for Software Engineering Chatbots
Oct 09, 2024

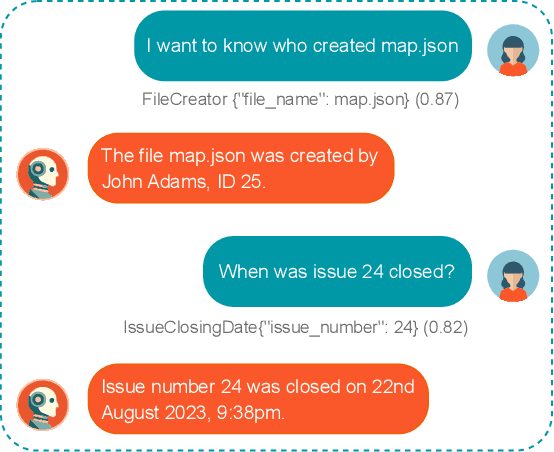
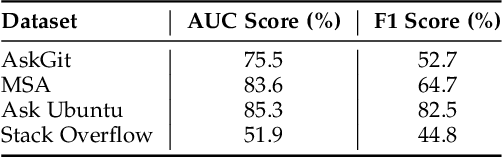
Abstract:Software engineering (SE) chatbots are increasingly gaining attention for their role in enhancing development processes. At the core of chatbots are the Natural Language Understanding platforms (NLUs), which enable them to comprehend and respond to user queries. Before deploying NLUs, there is a need to train them with labeled data. However, acquiring such labeled data for SE chatbots is challenging due to the scarcity of high-quality datasets. This challenge arises because training SE chatbots requires specialized vocabulary and phrases not found in typical language datasets. Consequently, chatbot developers often resort to manually annotating user queries to gather the data necessary for training effective chatbots, a process that is both time-consuming and resource-intensive. Previous studies propose approaches to support chatbot practitioners in annotating users' posed queries. However, these approaches require human intervention to generate rules, called labeling functions (LFs), that identify and categorize user queries based on specific patterns in the data. To address this issue, we propose an approach to automatically generate LFs by extracting patterns from labeled user queries. We evaluate the effectiveness of our approach by applying it to the queries of four diverse SE datasets (namely AskGit, MSA, Ask Ubuntu, and Stack Overflow) and measure the performance improvement gained from training the NLU on the queries labeled by the generated LFs. We find that the generated LFs effectively label data with AUC scores of up to 85.3%, and NLU's performance improvement of up to 27.2% across the studied datasets. Furthermore, our results show that the number of LFs used to generate LFs affects the labeling performance. We believe that our approach can save time and resources in labeling users' queries, allowing practitioners to focus on core chatbot functionalities.
Automatic Detection of LLM-generated Code: A Case Study of Claude 3 Haiku
Sep 02, 2024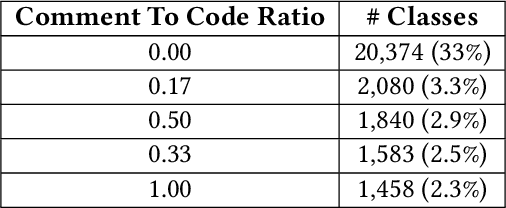
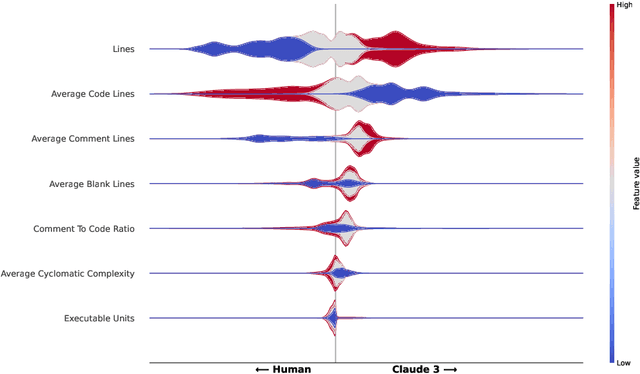
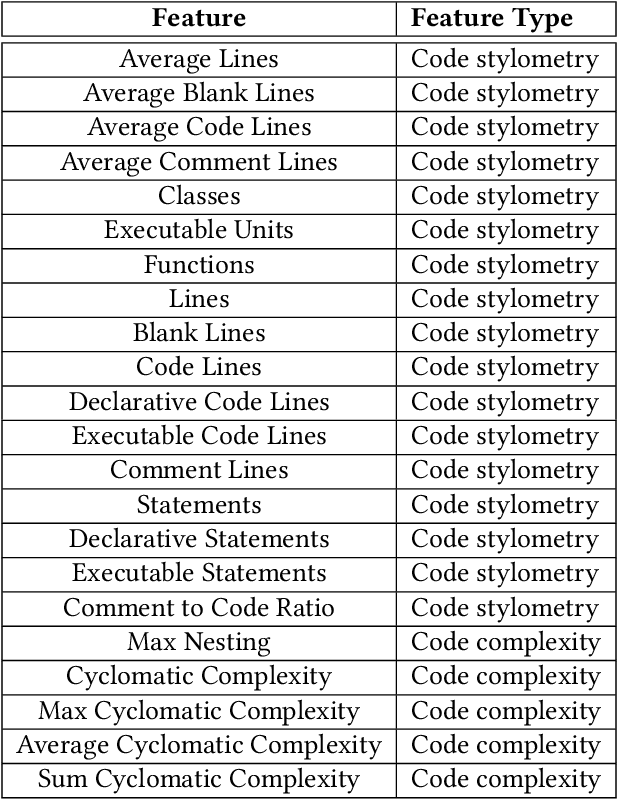
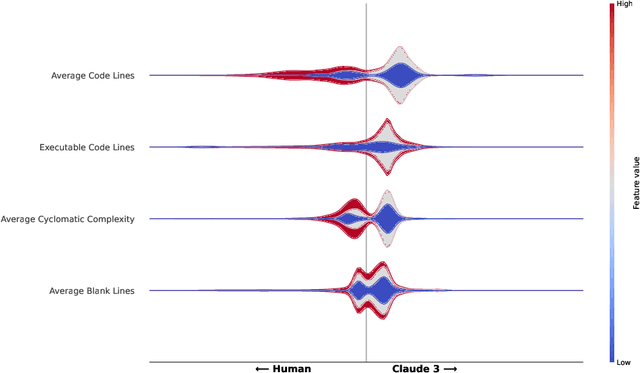
Abstract:Using Large Language Models (LLMs) has gained popularity among software developers for generating source code. However, the use of LLM-generated code can introduce risks of adding suboptimal, defective, and vulnerable code. This makes it necessary to devise methods for the accurate detection of LLM-generated code. Toward this goal, we perform a case study of Claude 3 Haiku (or Claude 3 for brevity) on CodeSearchNet dataset. We divide our analyses into two parts: function-level and class-level. We extract 22 software metric features, such as Code Lines and Cyclomatic Complexity, for each level of granularity. We then analyze code snippets generated by Claude 3 and their human-authored counterparts using the extracted features to understand how unique the code generated by Claude 3 is. In the following step, we use the unique characteristics of Claude 3-generated code to build Machine Learning (ML) models and identify which features of the code snippets make them more detectable by ML models. Our results indicate that Claude 3 tends to generate longer functions, but shorter classes than humans, and this characteristic can be used to detect Claude 3-generated code with ML models with 82% and 66% accuracies for function-level and class-level snippets, respectively.
Is ChatGPT a Good Software Librarian? An Exploratory Study on the Use of ChatGPT for Software Library Recommendations
Aug 09, 2024Abstract:Software libraries play a critical role in the functionality, efficiency, and maintainability of software systems. As developers increasingly rely on Large Language Models (LLMs) to streamline their coding processes, the effectiveness of these models in recommending appropriate libraries becomes crucial yet remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we assess the effectiveness of ChatGPT as a software librarian and identify areas for improvement. We conducted an empirical study using GPT-3.5 Turbo to generate Python code for 10,000 Stack Overflow questions. Our findings show that ChatGPT uses third-party libraries nearly 10% more often than human developers, favoring widely adopted and well-established options. However, 14.2% of the recommended libraries had restrictive copyleft licenses, which were not explicitly communicated by ChatGPT. Additionally, 6.5% of the libraries did not work out of the box, leading to potential developer confusion and wasted time. While ChatGPT can be an effective software librarian, it should be improved by providing more explicit information on maintainability metrics and licensing. We recommend that developers implement rigorous dependency management practices and double-check library licenses before integrating LLM-generated code into their projects.
On the Variability of AI-based Software Systems Due to Environment Configurations
Aug 05, 2024



Abstract:[Context] Nowadays, many software systems include Artificial Intelligence (AI) components and changes in the development environment have been known to induce variability in an AI-based system. [Objective] However, how an environment configuration impacts the variability of these systems is yet to be explored. Understanding and quantifying the degree of variability due to such configurations can help practitioners decide the best environment configuration for the most stable AI products. [Method] To achieve this goal, we performed experiments with eight different combinations of three key environment variables (operating system, Python version, and CPU architecture) on 30 open-source AI-based systems using the Travis CI platform. We evaluate variability using three metrics: the output of an AI component like an ML model (performance), the time required to build and run a system (processing time), and the cost associated with building and running a system (expense). [Results] Our results indicate that variability exists in all three metrics; however, it is observed more frequently with respect to processing time and expense than performance. For example, between Linux and MacOS, variabilities are observed in 23%, 96.67%, and 100% of the studied projects in performance, processing time, and expense, respectively. [Conclusion] Our findings underscore the importance of identifying the optimal combination of configuration settings to mitigate performance drops and reduce retraining time and cost before deploying an AI-based system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge