Eleonora Gualdoni
Analyze the Neurons, not the Embeddings: Understanding When and Where LLM Representations Align with Humans
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Modern large language models (LLMs) achieve impressive performance on some tasks, while exhibiting distinctly non-human-like behaviors on others. This raises the question of how well the LLM's learned representations align with human representations. In this work, we introduce a novel approach to the study of representation alignment: we adopt a method from research on activation steering to identify neurons responsible for specific concepts (e.g., 'cat') and then analyze the corresponding activation patterns. Our findings reveal that LLM representations closely align with human representations inferred from behavioral data. Notably, this alignment surpasses that of word embeddings, which have been center stage in prior work on human and model alignment. Additionally, our approach enables a more granular view of how LLMs represent concepts. Specifically, we show that LLMs organize concepts in a way that reflects hierarchical relationships interpretable to humans (e.g., 'animal'-'dog').
Scaling Laws for Forgetting during Finetuning with Pretraining Data Injection
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:A widespread strategy to obtain a language model that performs well on a target domain is to finetune a pretrained model to perform unsupervised next-token prediction on data from that target domain. Finetuning presents two challenges: (i) if the amount of target data is limited, as in most practical applications, the model will quickly overfit, and (ii) the model will drift away from the original model, forgetting the pretraining data and the generic knowledge that comes with it. We aim to derive scaling laws that quantify these two phenomena for various target domains, amounts of available target data, and model scales. We measure the efficiency of injecting pretraining data into the finetuning data mixture to avoid forgetting and mitigate overfitting. A key practical takeaway from our study is that injecting as little as 1% of pretraining data in the finetuning data mixture prevents the model from forgetting the pretraining set.
Why do objects have many names? A study on word informativeness in language use and lexical systems
Oct 10, 2024
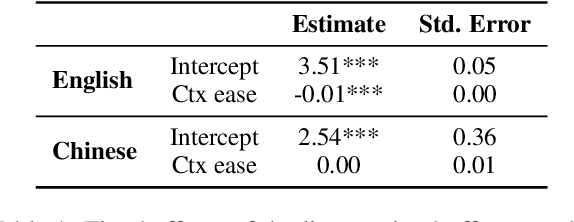
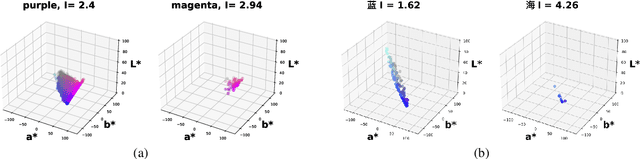
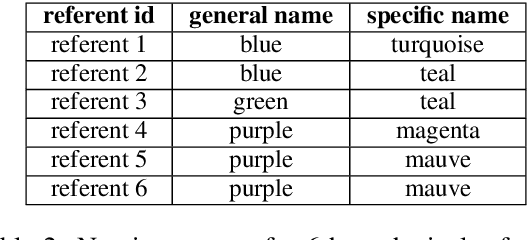
Abstract:Human lexicons contain many different words that speakers can use to refer to the same object, e.g., "purple" or "magenta" for the same shade of color. On the one hand, studies on language use have explored how speakers adapt their referring expressions to successfully communicate in context, without focusing on properties of the lexical system. On the other hand, studies in language evolution have discussed how competing pressures for informativeness and simplicity shape lexical systems, without tackling in-context communication. We aim at bridging the gap between these traditions, and explore why a soft mapping between referents and words is a good solution for communication, by taking into account both in-context communication and the structure of the lexicon. We propose a simple measure of informativeness for words and lexical systems, grounded in a visual space, and analyze color naming data for English and Mandarin Chinese. We conclude that optimal lexical systems are those where multiple words can apply to the same referent, conveying different amounts of information. Such systems allow speakers to maximize communication accuracy and minimize the amount of information they convey when communicating about referents in contexts.
Run Like a Girl! Sports-Related Gender Bias in Language and Vision
May 23, 2023
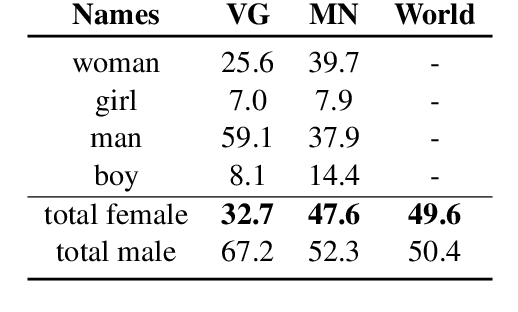
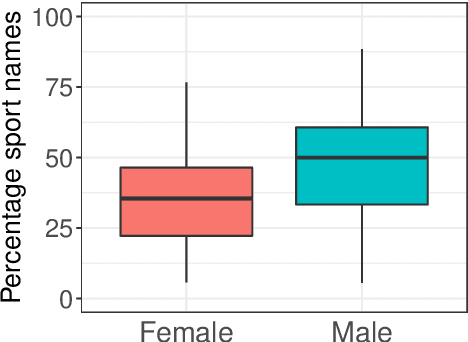
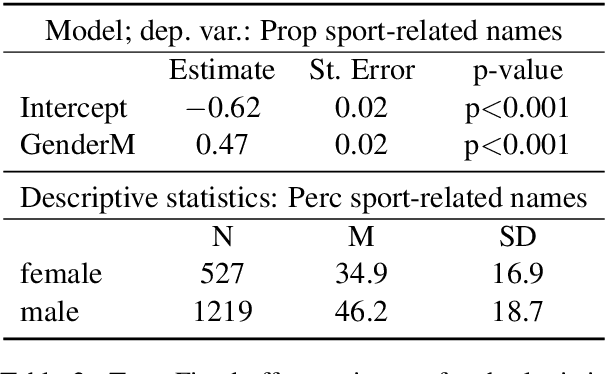
Abstract:Gender bias in Language and Vision datasets and models has the potential to perpetuate harmful stereotypes and discrimination. We analyze gender bias in two Language and Vision datasets. Consistent with prior work, we find that both datasets underrepresent women, which promotes their invisibilization. Moreover, we hypothesize and find that a bias affects human naming choices for people playing sports: speakers produce names indicating the sport (e.g. 'tennis player' or 'surfer') more often when it is a man or a boy participating in the sport than when it is a woman or a girl, with an average of 46% vs. 35% of sports-related names for each gender. A computational model trained on these naming data reproduces the bias. We argue that both the data and the model result in representational harm against women.
Cross-Domain Image Captioning with Discriminative Finetuning
Apr 04, 2023Abstract:Neural captioners are typically trained to mimic human-generated references without optimizing for any specific communication goal, leading to problems such as the generation of vague captions. In this paper, we show that fine-tuning an out-of-the-box neural captioner with a self-supervised discriminative communication objective helps to recover a plain, visually descriptive language that is more informative about image contents. Given a target image, the system must learn to produce a description that enables an out-of-the-box text-conditioned image retriever to identify such image among a set of candidates. We experiment with the popular ClipCap captioner, also replicating the main results with BLIP. In terms of similarity to ground-truth human descriptions, the captions emerging from discriminative finetuning lag slightly behind those generated by the non-finetuned model, when the latter is trained and tested on the same caption dataset. However, when the model is used without further tuning to generate captions for out-of-domain datasets, our discriminatively-finetuned captioner generates descriptions that resemble human references more than those produced by the same captioner without finetuning. We further show that, on the Conceptual Captions dataset, discriminatively finetuned captions are more helpful than either vanilla ClipCap captions or ground-truth captions for human annotators tasked with an image discrimination task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge