Why do objects have many names? A study on word informativeness in language use and lexical systems
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2024
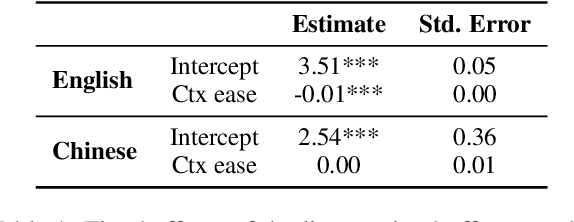
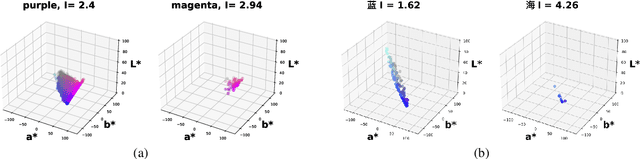
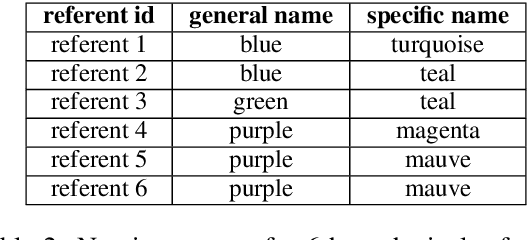
Human lexicons contain many different words that speakers can use to refer to the same object, e.g., "purple" or "magenta" for the same shade of color. On the one hand, studies on language use have explored how speakers adapt their referring expressions to successfully communicate in context, without focusing on properties of the lexical system. On the other hand, studies in language evolution have discussed how competing pressures for informativeness and simplicity shape lexical systems, without tackling in-context communication. We aim at bridging the gap between these traditions, and explore why a soft mapping between referents and words is a good solution for communication, by taking into account both in-context communication and the structure of the lexicon. We propose a simple measure of informativeness for words and lexical systems, grounded in a visual space, and analyze color naming data for English and Mandarin Chinese. We conclude that optimal lexical systems are those where multiple words can apply to the same referent, conveying different amounts of information. Such systems allow speakers to maximize communication accuracy and minimize the amount of information they convey when communicating about referents in contexts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge