Elahe Rahimian
DynaShare: Task and Instance Conditioned Parameter Sharing for Multi-Task Learning
May 26, 2023Abstract:Multi-task networks rely on effective parameter sharing to achieve robust generalization across tasks. In this paper, we present a novel parameter sharing method for multi-task learning that conditions parameter sharing on both the task and the intermediate feature representations at inference time. In contrast to traditional parameter sharing approaches, which fix or learn a deterministic sharing pattern during training and apply the same pattern to all examples during inference, we propose to dynamically decide which parts of the network to activate based on both the task and the input instance. Our approach learns a hierarchical gating policy consisting of a task-specific policy for coarse layer selection and gating units for individual input instances, which work together to determine the execution path at inference time. Experiments on the NYU v2, Cityscapes and MIMIC-III datasets demonstrate the potential of the proposed approach and its applicability across problem domains.
Transformer-based Hand Gesture Recognition via High-Density EMG Signals: From Instantaneous Recognition to Fusion of Motor Unit Spike Trains
Dec 07, 2022Abstract:Designing efficient and labor-saving prosthetic hands requires powerful hand gesture recognition algorithms that can achieve high accuracy with limited complexity and latency. In this context, the paper proposes a compact deep learning framework referred to as the CT-HGR, which employs a vision transformer network to conduct hand gesture recognition using highdensity sEMG (HD-sEMG) signals. The attention mechanism in the proposed model identifies similarities among different data segments with a greater capacity for parallel computations and addresses the memory limitation problems while dealing with inputs of large sequence lengths. CT-HGR can be trained from scratch without any need for transfer learning and can simultaneously extract both temporal and spatial features of HD-sEMG data. Additionally, the CT-HGR framework can perform instantaneous recognition using sEMG image spatially composed from HD-sEMG signals. A variant of the CT-HGR is also designed to incorporate microscopic neural drive information in the form of Motor Unit Spike Trains (MUSTs) extracted from HD-sEMG signals using Blind Source Separation (BSS). This variant is combined with its baseline version via a hybrid architecture to evaluate potentials of fusing macroscopic and microscopic neural drive information. The utilized HD-sEMG dataset involves 128 electrodes that collect the signals related to 65 isometric hand gestures of 20 subjects. The proposed CT-HGR framework is applied to 31.25, 62.5, 125, 250 ms window sizes of the above-mentioned dataset utilizing 32, 64, 128 electrode channels. The average accuracy over all the participants using 32 electrodes and a window size of 31.25 ms is 86.23%, which gradually increases till reaching 91.98% for 128 electrodes and a window size of 250 ms. The CT-HGR achieves accuracy of 89.13% for instantaneous recognition based on a single frame of HD-sEMG image.
Light-weighted CNN-Attention based architecture for Hand Gesture Recognition via ElectroMyography
Oct 27, 2022Abstract:Advancements in Biological Signal Processing (BSP) and Machine-Learning (ML) models have paved the path for development of novel immersive Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI). In this context, there has been a surge of significant interest in Hand Gesture Recognition (HGR) utilizing Surface-Electromyogram (sEMG) signals. This is due to its unique potential for decoding wearable data to interpret human intent for immersion in Mixed Reality (MR) environments. To achieve the highest possible accuracy, complicated and heavy-weighted Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are typically developed, which restricts their practical application in low-power and resource-constrained wearable systems. In this work, we propose a light-weighted hybrid architecture (HDCAM) based on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and attention mechanism to effectively extract local and global representations of the input. The proposed HDCAM model with 58,441 parameters reached a new state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance with 82.91% and 81.28% accuracy on window sizes of 300 ms and 200 ms for classifying 17 hand gestures. The number of parameters to train the proposed HDCAM architecture is 18.87 times less than its previous SOTA counterpart.
HYDRA-HGR: A Hybrid Transformer-based Architecture for Fusion of Macroscopic and Microscopic Neural Drive Information
Oct 27, 2022Abstract:Development of advance surface Electromyogram (sEMG)-based Human-Machine Interface (HMI) systems is of paramount importance to pave the way towards emergence of futuristic Cyber-Physical-Human (CPH) worlds. In this context, the main focus of recent literature was on development of different Deep Neural Network (DNN)-based architectures that perform Hand Gesture Recognition (HGR) at a macroscopic level (i.e., directly from sEMG signals). At the same time, advancements in acquisition of High-Density sEMG signals (HD-sEMG) have resulted in a surge of significant interest on sEMG decomposition techniques to extract microscopic neural drive information. However, due to complexities of sEMG decomposition and added computational overhead, HGR at microscopic level is less explored than its aforementioned DNN-based counterparts. In this regard, we propose the HYDRA-HGR framework, which is a hybrid model that simultaneously extracts a set of temporal and spatial features through its two independent Vision Transformer (ViT)-based parallel architectures (the so called Macro and Micro paths). The Macro Path is trained directly on the pre-processed HD-sEMG signals, while the Micro path is fed with the p-to-p values of the extracted Motor Unit Action Potentials (MUAPs) of each source. Extracted features at macroscopic and microscopic levels are then coupled via a Fully Connected (FC) fusion layer. We evaluate the proposed hybrid HYDRA-HGR framework through a recently released HD-sEMG dataset, and show that it significantly outperforms its stand-alone counterparts. The proposed HYDRA-HGR framework achieves average accuracy of 94.86% for the 250 ms window size, which is 5.52% and 8.22% higher than that of the Macro and Micro paths, respectively.
Multi-Content Time-Series Popularity Prediction with Multiple-Model Transformers in MEC Networks
Oct 12, 2022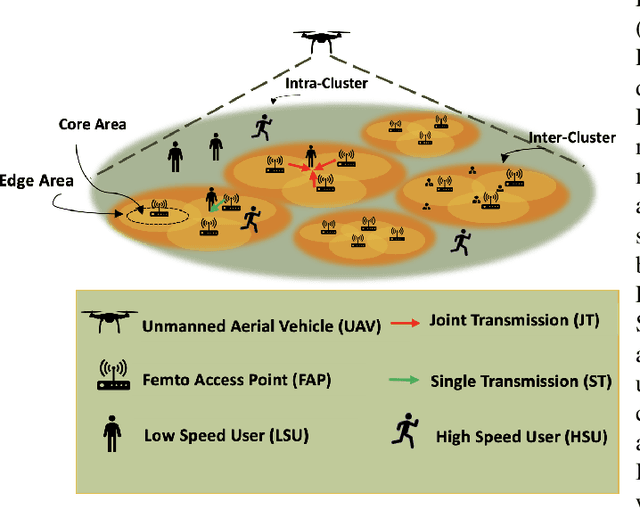
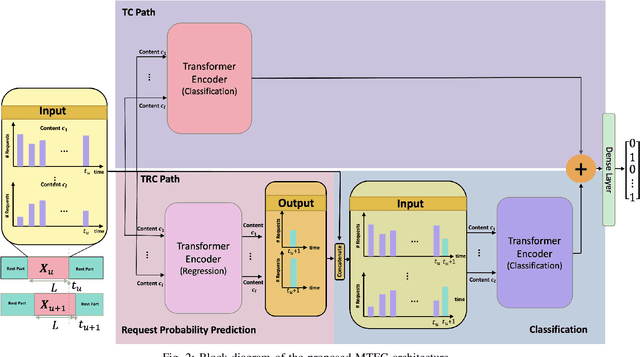
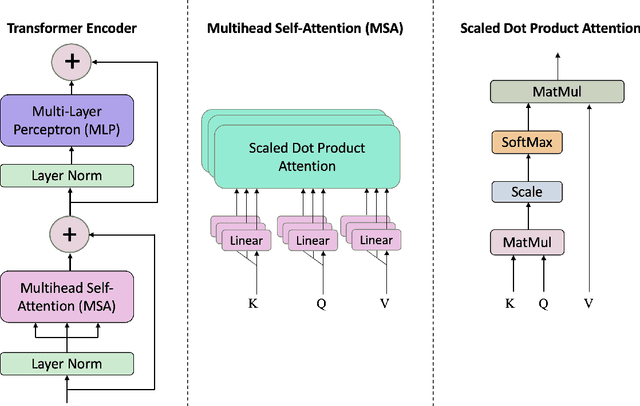
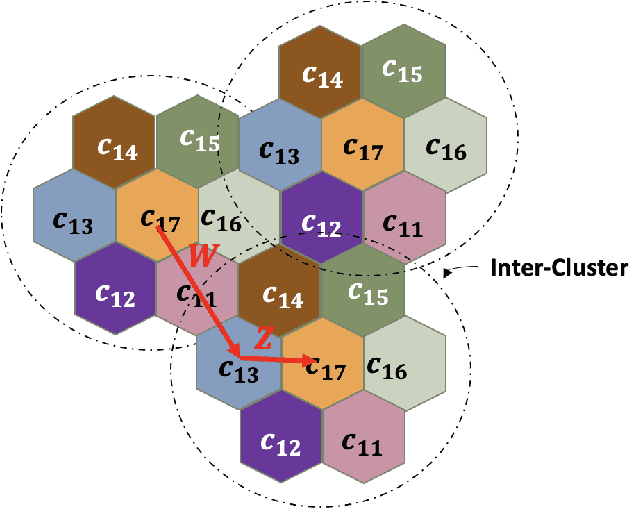
Abstract:Coded/uncoded content placement in Mobile Edge Caching (MEC) has evolved as an efficient solution to meet the significant growth of global mobile data traffic by boosting the content diversity in the storage of caching nodes. To meet the dynamic nature of the historical request pattern of multimedia contents, the main focus of recent researches has been shifted to develop data-driven and real-time caching schemes. In this regard and with the assumption that users' preferences remain unchanged over a short horizon, the Top-K popular contents are identified as the output of the learning model. Most existing datadriven popularity prediction models, however, are not suitable for the coded/uncoded content placement frameworks. On the one hand, in coded/uncoded content placement, in addition to classifying contents into two groups, i.e., popular and nonpopular, the probability of content request is required to identify which content should be stored partially/completely, where this information is not provided by existing data-driven popularity prediction models. On the other hand, the assumption that users' preferences remain unchanged over a short horizon only works for content with a smooth request pattern. To tackle these challenges, we develop a Multiple-model (hybrid) Transformer-based Edge Caching (MTEC) framework with higher generalization ability, suitable for various types of content with different time-varying behavior, that can be adapted with coded/uncoded content placement frameworks. Simulation results corroborate the effectiveness of the proposed MTEC caching framework in comparison to its counterparts in terms of the cache-hit ratio, classification accuracy, and the transferred byte volume.
TraHGR: Transformer for Hand Gesture Recognition via ElectroMyography
Mar 31, 2022



Abstract:Deep learning-based Hand Gesture Recognition (HGR) via surface Electromyogram (sEMG) signals has recently shown significant potential for development of advanced myoelectric-controlled prosthesis. Existing deep learning approaches, typically, include only one model as such can hardly maintain acceptable generalization performance in changing scenarios. In this paper, we aim to address this challenge by capitalizing on the recent advances of hybrid models and transformers. In other words, we propose a hybrid framework based on the transformer architecture, which is a relatively new and revolutionizing deep learning model. The proposed hybrid architecture, referred to as the Transformer for Hand Gesture Recognition (TraHGR), consists of two parallel paths followed by a linear layer that acts as a fusion center to integrate the advantage of each module and provide robustness over different scenarios. We evaluated the proposed architecture TraHGR based on the commonly used second Ninapro dataset, referred to as the DB2. The sEMG signals in the DB2 dataset are measured in the real-life conditions from 40 healthy users, each performing 49 gestures. We have conducted extensive set of experiments to test and validate the proposed TraHGR architecture, and have compared its achievable accuracy with more than five recently proposed HGR classification algorithms over the same dataset. We have also compared the results of the proposed TraHGR architecture with each individual path and demonstrated the distinguishing power of the proposed hybrid architecture. The recognition accuracies of the proposed TraHGR architecture are 86.18%, 88.91%, 81.44%, and 93.84%, which are 2.48%, 5.12%, 8.82%, and 4.30% higher than the state-ofthe-art performance for DB2 (49 gestures), DB2-B (17 gestures), DB2-C (23 gestures), and DB2-D (9 gestures), respectively.
ViT-HGR: Vision Transformer-based Hand Gesture Recognition from High Density Surface EMG Signals
Jan 25, 2022



Abstract:Recently, there has been a surge of significant interest on application of Deep Learning (DL) models to autonomously perform hand gesture recognition using surface Electromyogram (sEMG) signals. DL models are, however, mainly designed to be applied on sparse sEMG signals. Furthermore, due to their complex structure, typically, we are faced with memory constraints; require large training times and a large number of training samples, and; there is the need to resort to data augmentation and/or transfer learning. In this paper, for the first time (to the best of our knowledge), we investigate and design a Vision Transformer (ViT) based architecture to perform hand gesture recognition from High Density (HD-sEMG) signals. Intuitively speaking, we capitalize on the recent breakthrough role of the transformer architecture in tackling different complex problems together with its potential for employing more input parallelization via its attention mechanism. The proposed Vision Transformer-based Hand Gesture Recognition (ViT-HGR) framework can overcome the aforementioned training time problems and can accurately classify a large number of hand gestures from scratch without any need for data augmentation and/or transfer learning. The efficiency of the proposed ViT-HGR framework is evaluated using a recently-released HD-sEMG dataset consisting of 65 isometric hand gestures. Our experiments with 64-sample (31.25 ms) window size yield average test accuracy of 84.62 +/- 3.07%, where only 78, 210 number of parameters is utilized. The compact structure of the proposed ViT-based ViT-HGR framework (i.e., having significantly reduced number of trainable parameters) shows great potentials for its practical application for prosthetic control.
BP-Net: Cuff-less, Calibration-free, and Non-invasive Blood Pressure Estimation via a Generic Deep Convolutional Architecture
Dec 31, 2021



Abstract:Objective: The paper focuses on development of robust and accurate processing solutions for continuous and cuff-less blood pressure (BP) monitoring. In this regard, a robust deep learning-based framework is proposed for computation of low latency, continuous, and calibration-free upper and lower bounds on the systolic and diastolic BP. Method: Referred to as the BP-Net, the proposed framework is a novel convolutional architecture that provides longer effective memory while achieving superior performance due to incorporation of casual dialated convolutions and residual connections. To utilize the real potential of deep learning in extraction of intrinsic features (deep features) and enhance the long-term robustness, the BP-Net uses raw Electrocardiograph (ECG) and Photoplethysmograph (PPG) signals without extraction of any form of hand-crafted features as it is common in existing solutions. Results: By capitalizing on the fact that datasets used in recent literature are not unified and properly defined, a benchmark dataset is constructed from the MIMIC-I and MIMIC-III databases obtained from PhysioNet. The proposed BP-Net is evaluated based on this benchmark dataset demonstrating promising performance and shows superior generalizable capacity. Conclusion: The proposed BP-Net architecture is more accurate than canonical recurrent networks and enhances the long-term robustness of the BP estimation task. Significance: The proposed BP-Net architecture addresses key drawbacks of existing BP estimation solutions, i.e., relying heavily on extraction of hand-crafted features, such as pulse arrival time (PAT), and; Lack of robustness. Finally, the constructed BP-Net dataset provides a unified base for evaluation and comparison of deep learning-based BP estimation algorithms.
TEDGE-Caching: Transformer-based Edge Caching Towards 6G Networks
Dec 01, 2021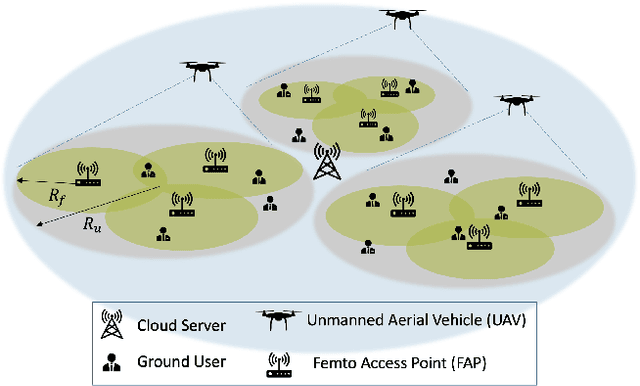

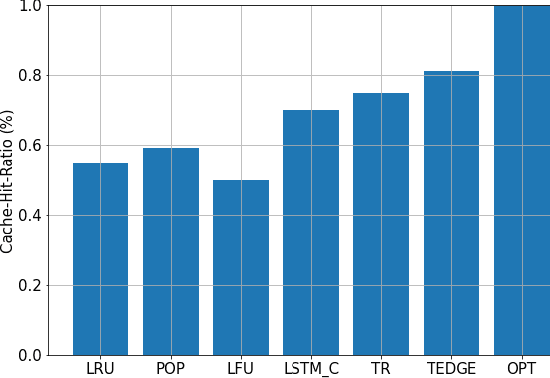
Abstract:As a consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic, the demand for telecommunication for remote learning/working and telemedicine has significantly increased. Mobile Edge Caching (MEC) in the 6G networks has been evolved as an efficient solution to meet the phenomenal growth of the global mobile data traffic by bringing multimedia content closer to the users. Although massive connectivity enabled by MEC networks will significantly increase the quality of communications, there are several key challenges ahead. The limited storage of edge nodes, the large size of multimedia content, and the time-variant users' preferences make it critical to efficiently and dynamically predict the popularity of content to store the most upcoming requested ones before being requested. Recent advancements in Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have drawn much research attention to predict the content popularity in proactive caching schemes. Existing DNN models in this context, however, suffer from longterm dependencies, computational complexity, and unsuitability for parallel computing. To tackle these challenges, we propose an edge caching framework incorporated with the attention-based Vision Transformer (ViT) neural network, referred to as the Transformer-based Edge (TEDGE) caching, which to the best of our knowledge, is being studied for the first time. Moreover, the TEDGE caching framework requires no data pre-processing and additional contextual information. Simulation results corroborate the effectiveness of the proposed TEDGE caching framework in comparison to its counterparts.
Hand Gesture Recognition Using Temporal Convolutions and Attention Mechanism
Oct 17, 2021



Abstract:Advances in biosignal signal processing and machine learning, in particular Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), have paved the way for the development of innovative Human-Machine Interfaces for decoding the human intent and controlling artificial limbs. DNN models have shown promising results with respect to other algorithms for decoding muscle electrical activity, especially for recognition of hand gestures. Such data-driven models, however, have been challenged by their need for a large number of trainable parameters and their structural complexity. Here we propose the novel Temporal Convolutions-based Hand Gesture Recognition architecture (TC-HGR) to reduce this computational burden. With this approach, we classified 17 hand gestures via surface Electromyogram (sEMG) signals by the adoption of attention mechanisms and temporal convolutions. The proposed method led to 81.65% and 80.72% classification accuracy for window sizes of 300ms and 200ms, respectively. The number of parameters to train the proposed TC-HGR architecture is 11.9 times less than that of its state-of-the-art counterpart.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge