Dongdong Hou
Semantic-Transferable Weakly-Supervised Endoscopic Lesions Segmentation
Aug 22, 2019



Abstract:Weakly-supervised learning under image-level labels supervision has been widely applied to semantic segmentation of medical lesions regions. However, 1) most existing models rely on effective constraints to explore the internal representation of lesions, which only produces inaccurate and coarse lesions regions; 2) they ignore the strong probabilistic dependencies between target lesions dataset (e.g., enteroscopy images) and well-to-annotated source diseases dataset (e.g., gastroscope images). To better utilize these dependencies, we present a new semantic lesions representation transfer model for weakly-supervised endoscopic lesions segmentation, which can exploit useful knowledge from relevant fully-labeled diseases segmentation task to enhance the performance of target weakly-labeled lesions segmentation task. More specifically, a pseudo label generator is proposed to leverage seed information to generate highly-confident pseudo pixel labels by incorporating class balance and super-pixel spatial prior. It can iteratively include more hard-to-transfer samples from weakly-labeled target dataset into training set. Afterwards, dynamically searched feature centroids for same class among different datasets are aligned by accumulating previously-learned features. Meanwhile, adversarial learning is also employed in this paper, to narrow the gap between the lesions among different datasets in output space. Finally, we build a new medical endoscopic dataset with 3659 images collected from more than 1100 volunteers. Extensive experiments on our collected dataset and several benchmark datasets validate the effectiveness of our model.
Gated Context Aggregation Network for Image Dehazing and Deraining
Nov 21, 2018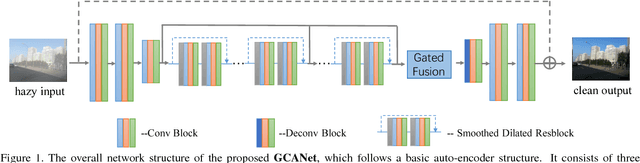
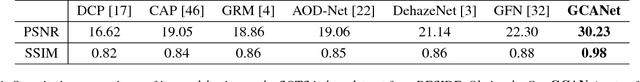
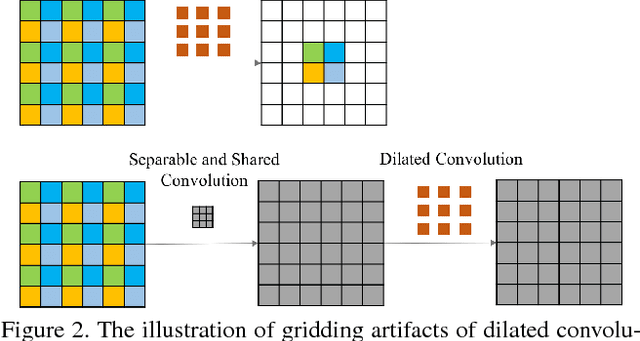

Abstract:Image dehazing aims to recover the uncorrupted content from a hazy image. Instead of leveraging traditional low-level or handcrafted image priors as the restoration constraints, e.g., dark channels and increased contrast, we propose an end-to-end gated context aggregation network to directly restore the final haze-free image. In this network, we adopt the latest smoothed dilation technique to help remove the gridding artifacts caused by the widely-used dilated convolution with negligible extra parameters, and leverage a gated sub-network to fuse the features from different levels. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method can surpass previous state-of-the-art methods by a large margin both quantitatively and qualitatively. In addition, to demonstrate the generality of the proposed method, we further apply it to the image deraining task, which also achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
Emerging Applications of Reversible Data Hiding
Nov 07, 2018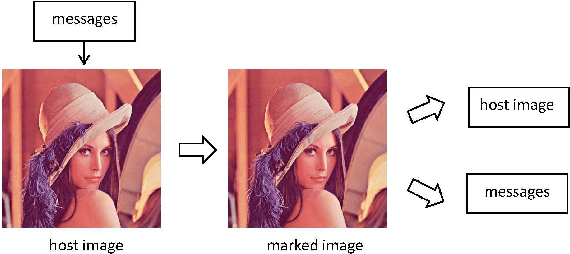
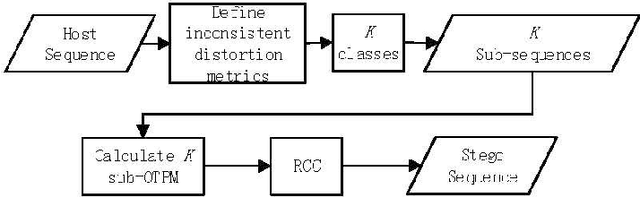
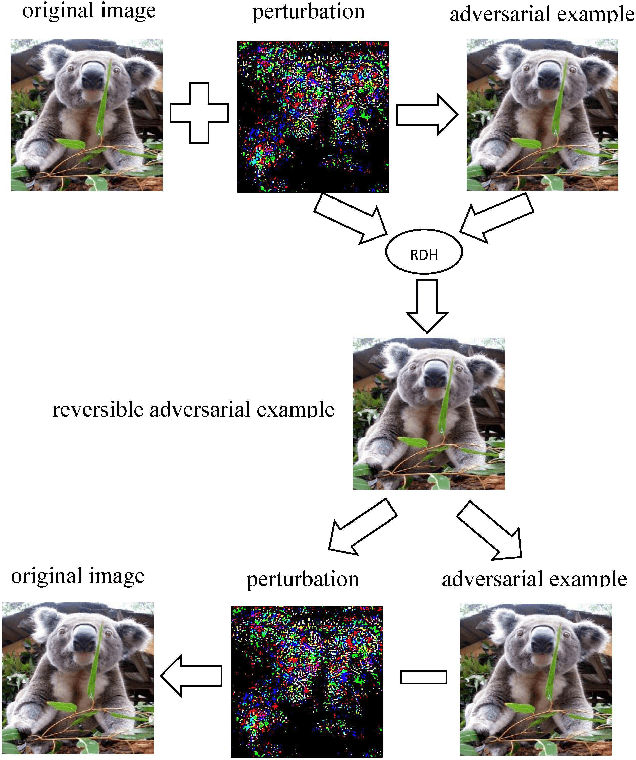
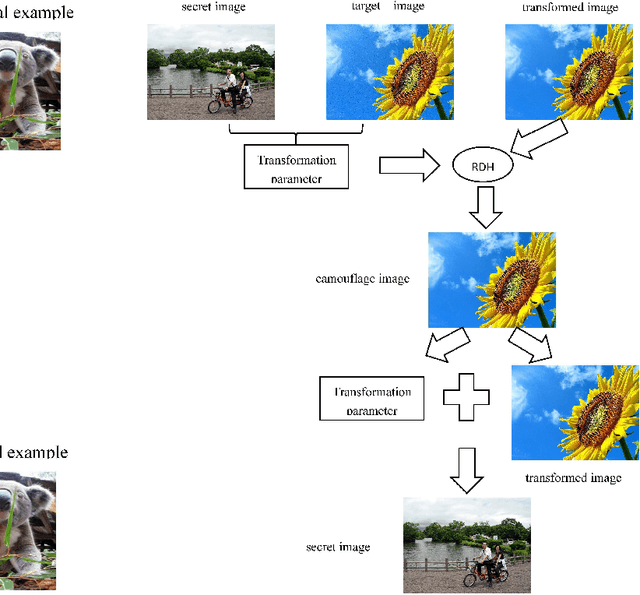
Abstract:Reversible data hiding (RDH) is one special type of information hiding, by which the host sequence as well as the embedded data can be both restored from the marked sequence without loss. Beside media annotation and integrity authentication, recently some scholars begin to apply RDH in many other fields innovatively. In this paper, we summarize these emerging applications, including steganography, adversarial example, visual transformation, image processing, and give out the general frameworks to make these operations reversible. As far as we are concerned, this is the first paper to summarize the extended applications of RDH.
Reversible Adversarial Examples
Nov 01, 2018


Abstract:Deep Neural Networks have recently led to significant improvement in many fields such as image classification and speech recognition. However, these machine learning models are vulnerable to adversarial examples which can mislead machine learning classifiers to give incorrect classifications. In this paper, we take advantage of reversible data hiding to construct reversible adversarial examples which are still misclassified by Deep Neural Networks. Furthermore, the proposed method can recover original images from reversible adversarial examples with no distortion.
Detection based Defense against Adversarial Examples from the Steganalysis Point ot View
Sep 07, 2018



Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have recently led to significant improvements in many fields. However, DNNs are vulnerable to adversarial examples which are samples with imperceptible perturbations while dramatically misleading the DNNs. Moreover, adversarial examples can be used to perform an attack on various kinds of DNN based systems, even if the adversary has no access to the underlying model. Many defense methods have been proposed, such as obfuscating gradients of the networks or detecting adversarial examples. However it is proved out that these defense methods are not effective or cannot resist secondary adversarial attacks. In this paper, we point out that steganalysis can be applied to adversarial examples detection, and propose a method to enhance steganalysis features by estimating the probability of modifications caused by adversarial attacks. Experimental results show that the proposed method can accurately detect adversarial examples. Moreover, secondary adversarial attacks cannot be directly performed to our method because our method is not based on a neural network but based on high-dimensional artificial features and FLD (Fisher Linear Discriminant) ensemble.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge