Desheng Wang
School of Electrical Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, Chengdu, P. R. China
AMoPO: Adaptive Multi-objective Preference Optimization without Reward Models and Reference Models
Jun 08, 2025



Abstract:Existing multi-objective preference alignment methods for large language models (LLMs) face limitations: (1) the inability to effectively balance various preference dimensions, and (2) reliance on auxiliary reward/reference models introduces computational complexity. To address these challenges, we propose Adaptive Multi-objective Preference Optimization (AMoPO), a novel framework that achieves dynamic balance across preference dimensions. By introducing the multi-objective optimization paradigm to use the dimension-aware generation metrics as implicit rewards, AMoPO aligns LLMs with diverse preferences without additional reward models or reference models. We introduce an adaptive weight assignment mechanism that models the generation space as a Gaussian distribution, allowing dynamic prioritization of preference dimensions. Empirical results demonstrate that AMoPO outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by 28.5%, and the experiments on 7B, 14B, and 32B models reveal the scaling ability of AMoPO. Moreover, additional analysis of multiple dimensions verifies its adaptability and effectiveness. These findings validate AMoPO's capability to achieve dimension-aware preference alignment, highlighting its superiority. Our codes and datasets are available at https://github.com/Javkonline/AMoPO.
Transfer Learning-Enhanced Instantaneous Multi-Person Indoor Localization by CSI
Mar 02, 2024


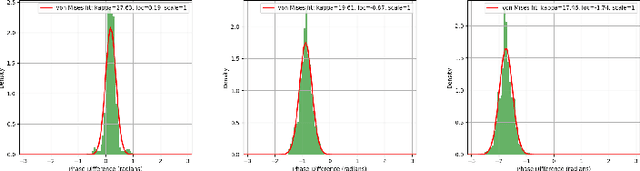
Abstract:Passive indoor localization, integral to smart buildings, emergency response, and indoor navigation, has traditionally been limited by a focus on single-target localization and reliance on multi-packet CSI. We introduce a novel Multi-target loss, notably enhancing multi-person localization. Utilizing this loss function, our instantaneous CSI-ResNet achieves an impressive 99.21% accuracy at 0.6m precision with single-timestamp CSI. A preprocessing algorithm is implemented to counteract WiFi-induced variability, thereby augmenting robustness. Furthermore, we incorporate Nuclear Norm-Based Transfer Pre-Training, ensuring adaptability in diverse environments, which provides a new paradigm for indoor multi-person localization. Additionally, we have developed an extensive dataset, surpassing existing ones in scope and diversity, to underscore the efficacy of our method and facilitate future fingerprint-based localization research.
CLLD: Contrastive Learning with Label Distance for Text Classificatioin
Oct 28, 2021



Abstract:Existed pre-trained models have achieved state-of-the-art performance on various text classification tasks. These models have proven to be useful in learning universal language representations. However, the semantic discrepancy between similar texts cannot be effectively distinguished by advanced pre-trained models, which have a great influence on the performance of hard-to-distinguish classes. To address this problem, we propose a novel Contrastive Learning with Label Distance (CLLD) in this work. Inspired by recent advances in contrastive learning, we specifically design a classification method with label distance for learning contrastive classes. CLLD ensures the flexibility within the subtle differences that lead to different label assignments, and generates the distinct representations for each class having similarity simultaneously. Extensive experiments on public benchmarks and internal datasets demonstrate that our method improves the performance of pre-trained models on classification tasks. Importantly, our experiments suggest that the learned label distance relieve the adversarial nature of interclasses.
Improving Global Adversarial Robustness Generalization With Adversarially Trained GAN
Mar 08, 2021



Abstract:Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have achieved beyond human-level accuracy in the image classification task and are widely deployed in real-world environments. However, CNNs show vulnerability to adversarial perturbations that are well-designed noises aiming to mislead the classification models. In order to defend against the adversarial perturbations, adversarially trained GAN (ATGAN) is proposed to improve the adversarial robustness generalization of the state-of-the-art CNNs trained by adversarial training. ATGAN incorporates adversarial training into standard GAN training procedure to remove obfuscated gradients which can lead to a false sense in defending against the adversarial perturbations and are commonly observed in existing GANs-based adversarial defense methods. Moreover, ATGAN adopts the image-to-image generator as data augmentation to increase the sample complexity needed for adversarial robustness generalization in adversarial training. Experimental results in MNIST SVHN and CIFAR-10 datasets show that the proposed method doesn't rely on obfuscated gradients and achieves better global adversarial robustness generalization performance than the adversarially trained state-of-the-art CNNs.
Revisiting Regex Generation for Modeling Industrial Applications by Incorporating Byte Pair Encoder
May 06, 2020

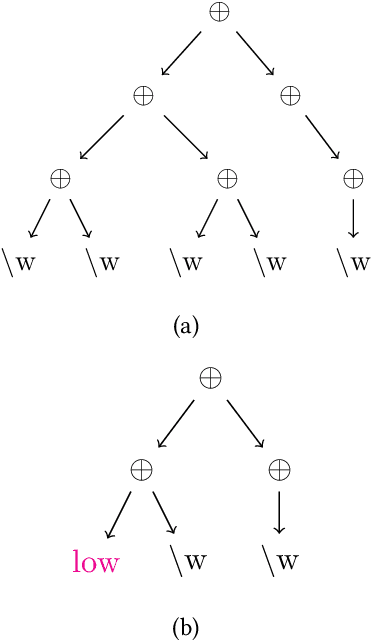

Abstract:Regular expression is important for many natural language processing tasks especially when used to deal with unstructured and semi-structured data. This work focuses on automatically generating regular expressions and proposes a novel genetic algorithm to deal with this problem. Different from the methods which generate regular expressions from character level, we first utilize byte pair encoder (BPE) to extract some frequent items, which are then used to construct regular expressions. The fitness function of our genetic algorithm contains multi objectives and is solved based on evolutionary procedure including crossover and mutation operation. In the fitness function, we take the length of generated regular expression, the maximum matching characters and samples for positive training samples, and the minimum matching characters and samples for negative training samples into consideration. In addition, to accelerate the training process, we do exponential decay on the population size of the genetic algorithm. Our method together with a strong baseline is tested on 13 kinds of challenging datasets. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, which outperforms the baseline on 10 kinds of data and achieves nearly 50 percent improvement on average. By doing exponential decay, the training speed is approximately 100 times faster than the methods without using exponential decay. In summary, our method possesses both effectiveness and efficiency, and can be implemented for the industry application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge