Dehui Kong
SYENet: A Simple Yet Effective Network for Multiple Low-Level Vision Tasks with Real-time Performance on Mobile Device
Aug 16, 2023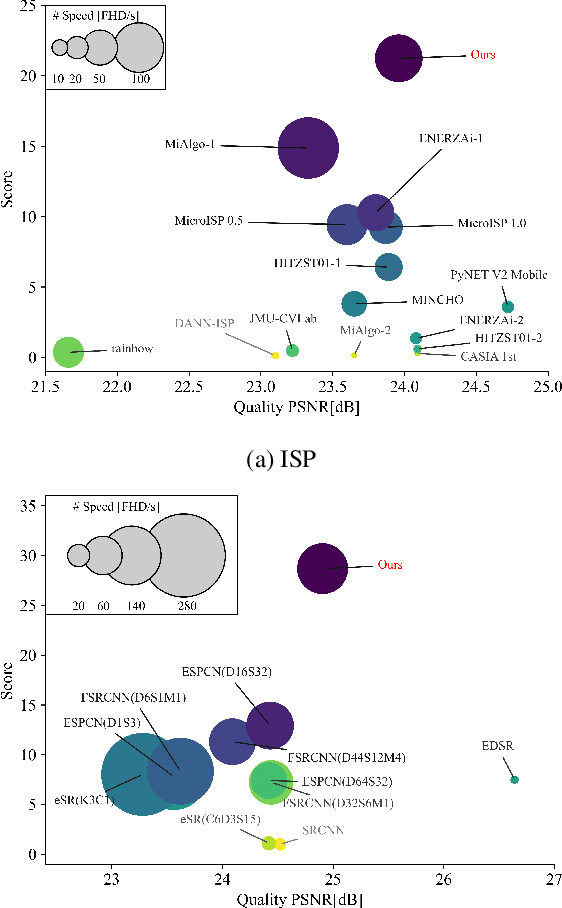



Abstract:With the rapid development of AI hardware accelerators, applying deep learning-based algorithms to solve various low-level vision tasks on mobile devices has gradually become possible. However, two main problems still need to be solved: task-specific algorithms make it difficult to integrate them into a single neural network architecture, and large amounts of parameters make it difficult to achieve real-time inference. To tackle these problems, we propose a novel network, SYENet, with only $~$6K parameters, to handle multiple low-level vision tasks on mobile devices in a real-time manner. The SYENet consists of two asymmetrical branches with simple building blocks. To effectively connect the results by asymmetrical branches, a Quadratic Connection Unit(QCU) is proposed. Furthermore, to improve performance, a new Outlier-Aware Loss is proposed to process the image. The proposed method proves its superior performance with the best PSNR as compared with other networks in real-time applications such as Image Signal Processing(ISP), Low-Light Enhancement(LLE), and Super-Resolution(SR) with 2K60FPS throughput on Qualcomm 8 Gen 1 mobile SoC(System-on-Chip). Particularly, for ISP task, SYENet got the highest score in MAI 2022 Learned Smartphone ISP challenge.
Learned Smartphone ISP on Mobile GPUs with Deep Learning, Mobile AI & AIM 2022 Challenge: Report
Nov 07, 2022
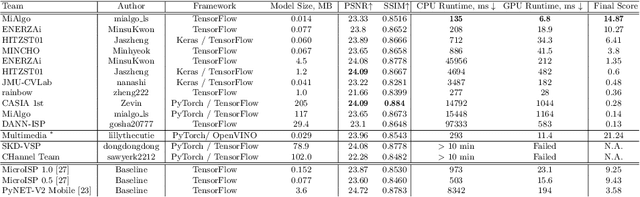
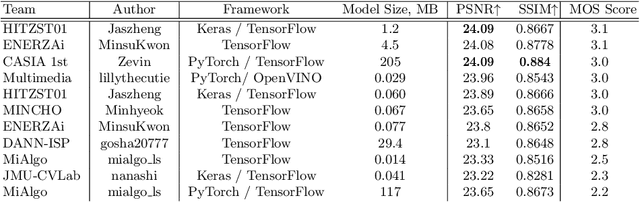
Abstract:The role of mobile cameras increased dramatically over the past few years, leading to more and more research in automatic image quality enhancement and RAW photo processing. In this Mobile AI challenge, the target was to develop an efficient end-to-end AI-based image signal processing (ISP) pipeline replacing the standard mobile ISPs that can run on modern smartphone GPUs using TensorFlow Lite. The participants were provided with a large-scale Fujifilm UltraISP dataset consisting of thousands of paired photos captured with a normal mobile camera sensor and a professional 102MP medium-format FujiFilm GFX100 camera. The runtime of the resulting models was evaluated on the Snapdragon's 8 Gen 1 GPU that provides excellent acceleration results for the majority of common deep learning ops. The proposed solutions are compatible with all recent mobile GPUs, being able to process Full HD photos in less than 20-50 milliseconds while achieving high fidelity results. A detailed description of all models developed in this challenge is provided in this paper.
Grassmannian Graph-attentional Landmark Selection for Domain Adaptation
Sep 07, 2021
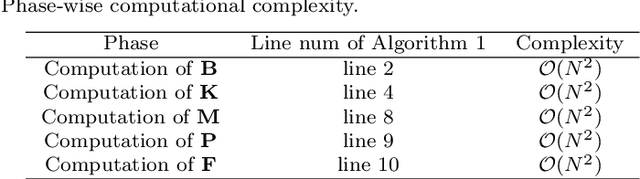

Abstract:Domain adaptation aims to leverage information from the source domain to improve the classification performance in the target domain. It mainly utilizes two schemes: sample reweighting and feature matching. While the first scheme allocates different weights to individual samples, the second scheme matches the feature of two domains using global structural statistics. The two schemes are complementary with each other, which are expected to jointly work for robust domain adaptation. Several methods combine the two schemes, but the underlying relationship of samples is insufficiently analyzed due to the neglect of the hierarchy of samples and the geometric properties between samples. To better combine the advantages of the two schemes, we propose a Grassmannian graph-attentional landmark selection (GGLS) framework for domain adaptation. GGLS presents a landmark selection scheme using attention-induced neighbors of the graphical structure of samples and performs distribution adaptation and knowledge adaptation over Grassmann manifold. the former treats the landmarks of each sample differently, and the latter avoids feature distortion and achieves better geometric properties. Experimental results on different real-world cross-domain visual recognition tasks demonstrate that GGLS provides better classification accuracies compared with state-of-the-art domain adaptation methods.
GAN for Vision, KG for Relation: a Two-stage Deep Network for Zero-shot Action Recognition
May 25, 2021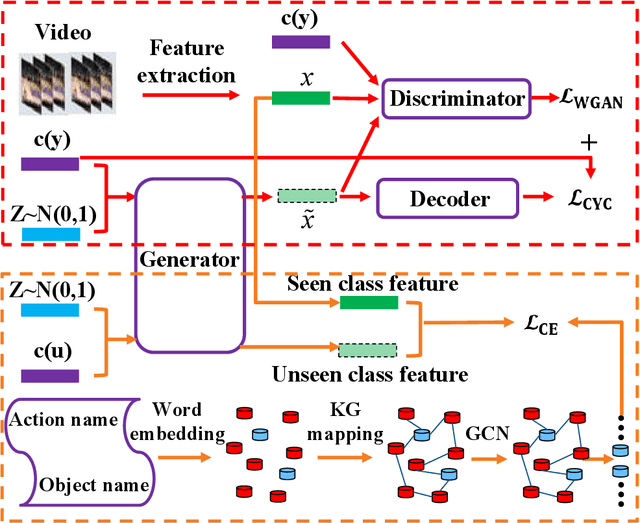
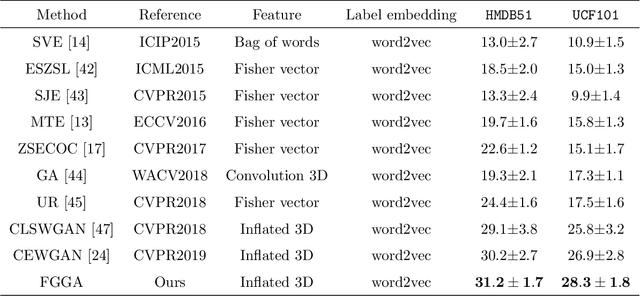

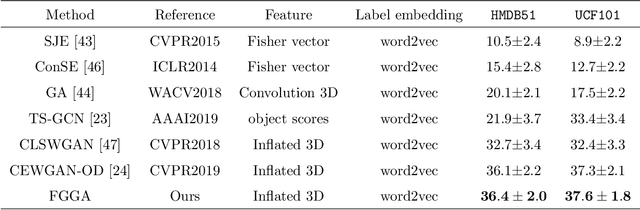
Abstract:Zero-shot action recognition can recognize samples of unseen classes that are unavailable in training by exploring common latent semantic representation in samples. However, most methods neglected the connotative relation and extensional relation between the action classes, which leads to the poor generalization ability of the zero-shot learning. Furthermore, the learned classifier incline to predict the samples of seen class, which leads to poor classification performance. To solve the above problems, we propose a two-stage deep neural network for zero-shot action recognition, which consists of a feature generation sub-network serving as the sampling stage and a graph attention sub-network serving as the classification stage. In the sampling stage, we utilize a generative adversarial networks (GAN) trained by action features and word vectors of seen classes to synthesize the action features of unseen classes, which can balance the training sample data of seen classes and unseen classes. In the classification stage, we construct a knowledge graph (KG) based on the relationship between word vectors of action classes and related objects, and propose a graph convolution network (GCN) based on attention mechanism, which dynamically updates the relationship between action classes and objects, and enhances the generalization ability of zero-shot learning. In both stages, we all use word vectors as bridges for feature generation and classifier generalization from seen classes to unseen classes. We compare our method with state-of-the-art methods on UCF101 and HMDB51 datasets. Experimental results show that our proposed method improves the classification performance of the trained classifier and achieves higher accuracy.
Real-time Human Action Recognition Using Locally Aggregated Kinematic-Guided Skeletonlet and Supervised Hashing-by-Analysis Model
May 24, 2021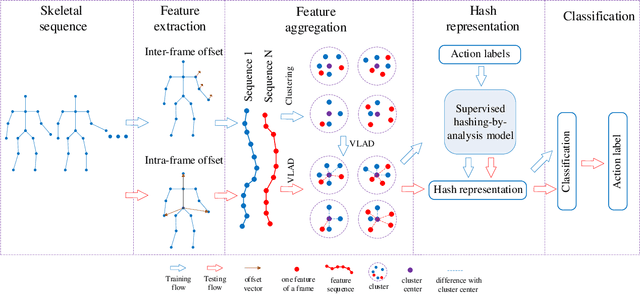
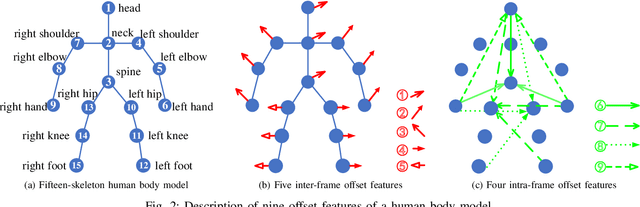
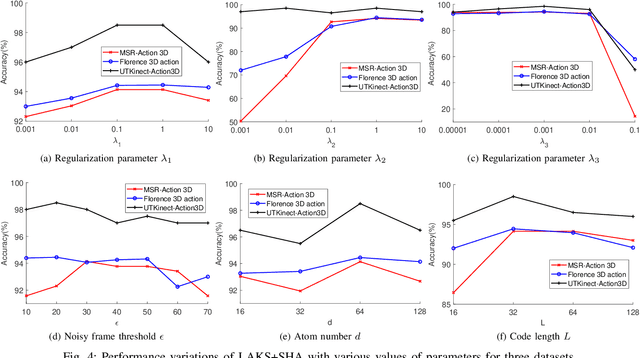
Abstract:3D action recognition is referred to as the classification of action sequences which consist of 3D skeleton joints. While many research work are devoted to 3D action recognition, it mainly suffers from three problems: highly complicated articulation, a great amount of noise, and a low implementation efficiency. To tackle all these problems, we propose a real-time 3D action recognition framework by integrating the locally aggregated kinematic-guided skeletonlet (LAKS) with a supervised hashing-by-analysis (SHA) model. We first define the skeletonlet as a few combinations of joint offsets grouped in terms of kinematic principle, and then represent an action sequence using LAKS, which consists of a denoising phase and a locally aggregating phase. The denoising phase detects the noisy action data and adjust it by replacing all the features within it with the features of the corresponding previous frame, while the locally aggregating phase sums the difference between an offset feature of the skeletonlet and its cluster center together over all the offset features of the sequence. Finally, the SHA model which combines sparse representation with a hashing model, aiming at promoting the recognition accuracy while maintaining a high efficiency. Experimental results on MSRAction3D, UTKinectAction3D and Florence3DAction datasets demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both recognition accuracy and implementation efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge