Decheng Liu
MGFFD-VLM: Multi-Granularity Prompt Learning for Face Forgery Detection with VLM
Jul 16, 2025



Abstract:Recent studies have utilized visual large language models (VLMs) to answer not only "Is this face a forgery?" but also "Why is the face a forgery?" These studies introduced forgery-related attributes, such as forgery location and type, to construct deepfake VQA datasets and train VLMs, achieving high accuracy while providing human-understandable explanatory text descriptions. However, these methods still have limitations. For example, they do not fully leverage face quality-related attributes, which are often abnormal in forged faces, and they lack effective training strategies for forgery-aware VLMs. In this paper, we extend the VQA dataset to create DD-VQA+, which features a richer set of attributes and a more diverse range of samples. Furthermore, we introduce a novel forgery detection framework, MGFFD-VLM, which integrates an Attribute-Driven Hybrid LoRA Strategy to enhance the capabilities of Visual Large Language Models (VLMs). Additionally, our framework incorporates Multi-Granularity Prompt Learning and a Forgery-Aware Training Strategy. By transforming classification and forgery segmentation results into prompts, our method not only improves forgery classification but also enhances interpretability. To further boost detection performance, we design multiple forgery-related auxiliary losses. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach surpasses existing methods in both text-based forgery judgment and analysis, achieving superior accuracy.
Towards Generalized Proactive Defense against Face Swappingwith Contour-Hybrid Watermark
May 25, 2025Abstract:Face swapping, recognized as a privacy and security concern, has prompted considerable defensive research. With the advancements in AI-generated content, the discrepancies between the real and swapped faces have become nuanced. Considering the difficulty of forged traces detection, we shift the focus to the face swapping purpose and proactively embed elaborate watermarks against unknown face swapping techniques. Given that the constant purpose is to swap the original face identity while preserving the background, we concentrate on the regions surrounding the face to ensure robust watermark generation, while embedding the contour texture and face identity information to achieve progressive image determination. The watermark is located in the facial contour and contains hybrid messages, dubbed the contour-hybrid watermark (CMark). Our approach generalizes face swapping detection without requiring any swapping techniques during training and the storage of large-scale messages in advance. Experiments conducted across 8 face swapping techniques demonstrate the superiority of our approach compared with state-of-the-art passive and proactive detectors while achieving a favorable balance between the image quality and watermark robustness.
A Knowledge-guided Adversarial Defense for Resisting Malicious Visual Manipulation
Apr 11, 2025



Abstract:Malicious applications of visual manipulation have raised serious threats to the security and reputation of users in many fields. To alleviate these issues, adversarial noise-based defenses have been enthusiastically studied in recent years. However, ``data-only" methods tend to distort fake samples in the low-level feature space rather than the high-level semantic space, leading to limitations in resisting malicious manipulation. Frontier research has shown that integrating knowledge in deep learning can produce reliable and generalizable solutions. Inspired by these, we propose a knowledge-guided adversarial defense (KGAD) to actively force malicious manipulation models to output semantically confusing samples. Specifically, in the process of generating adversarial noise, we focus on constructing significant semantic confusions at the domain-specific knowledge level, and exploit a metric closely related to visual perception to replace the general pixel-wise metrics. The generated adversarial noise can actively interfere with the malicious manipulation model by triggering knowledge-guided and perception-related disruptions in the fake samples. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we conduct qualitative and quantitative experiments on human perception and visual quality assessment. The results on two different tasks both show that our defense provides better protection compared to state-of-the-art methods and achieves great generalizability.
Improving Adversarial Robustness via Phase and Amplitude-aware Prompting
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:Deep neural networks are found to be vulnerable to adversarial noises. The prompt-based defense has been increasingly studied due to its high efficiency. However, existing prompt-based defenses mainly exploited mixed prompt patterns, where critical patterns closely related to object semantics lack sufficient focus. The phase and amplitude spectra have been proven to be highly related to specific semantic patterns and crucial for robustness. To this end, in this paper, we propose a Phase and Amplitude-aware Prompting (PAP) defense. Specifically, we construct phase-level and amplitude-level prompts for each class, and adjust weights for prompting according to the model's robust performance under these prompts during training. During testing, we select prompts for each image using its predicted label to obtain the prompted image, which is inputted to the model to get the final prediction. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Thinking Racial Bias in Fair Forgery Detection: Models, Datasets and Evaluations
Jul 19, 2024



Abstract:Due to the successful development of deep image generation technology, forgery detection plays a more important role in social and economic security. Racial bias has not been explored thoroughly in the deep forgery detection field. In the paper, we first contribute a dedicated dataset called the Fair Forgery Detection (FairFD) dataset, where we prove the racial bias of public state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. Different from existing forgery detection datasets, the self-construct FairFD dataset contains a balanced racial ratio and diverse forgery generation images with the largest-scale subjects. Additionally, we identify the problems with naive fairness metrics when benchmarking forgery detection models. To comprehensively evaluate fairness, we design novel metrics including Approach Averaged Metric and Utility Regularized Metric, which can avoid deceptive results. Extensive experiments conducted with nine representative forgery detection models demonstrate the value of the proposed dataset and the reasonability of the designed fairness metrics. We also conduct more in-depth analyses to offer more insights to inspire researchers in the community.
Federated Face Forgery Detection Learning with Personalized Representation
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Deep generator technology can produce high-quality fake videos that are indistinguishable, posing a serious social threat. Traditional forgery detection methods directly centralized training on data and lacked consideration of information sharing in non-public video data scenarios and data privacy. Naturally, the federated learning strategy can be applied for privacy protection, which aggregates model parameters of clients but not original data. However, simple federated learning can't achieve satisfactory performance because of poor generalization capabilities for the real hybrid-domain forgery dataset. To solve the problem, the paper proposes a novel federated face forgery detection learning with personalized representation. The designed Personalized Forgery Representation Learning aims to learn the personalized representation of each client to improve the detection performance of individual client models. In addition, a personalized federated learning training strategy is utilized to update the parameters of the distributed detection model. Here collaborative training is conducted on multiple distributed client devices, and shared representations of these client models are uploaded to the server side for aggregation. Experiments on several public face forgery detection datasets demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed algorithm compared with state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at \emph{https://github.com/GANG370/PFR-Forgery.}
Imperceptible Face Forgery Attack via Adversarial Semantic Mask
Jun 16, 2024



Abstract:With the great development of generative model techniques, face forgery detection draws more and more attention in the related field. Researchers find that existing face forgery models are still vulnerable to adversarial examples with generated pixel perturbations in the global image. These generated adversarial samples still can't achieve satisfactory performance because of the high detectability. To address these problems, we propose an Adversarial Semantic Mask Attack framework (ASMA) which can generate adversarial examples with good transferability and invisibility. Specifically, we propose a novel adversarial semantic mask generative model, which can constrain generated perturbations in local semantic regions for good stealthiness. The designed adaptive semantic mask selection strategy can effectively leverage the class activation values of different semantic regions, and further ensure better attack transferability and stealthiness. Extensive experiments on the public face forgery dataset prove the proposed method achieves superior performance compared with several representative adversarial attack methods. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/clawerO-O/ASMA.
Mitigating Feature Gap for Adversarial Robustness by Feature Disentanglement
Jan 26, 2024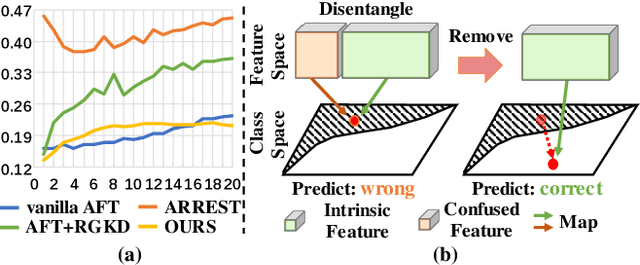
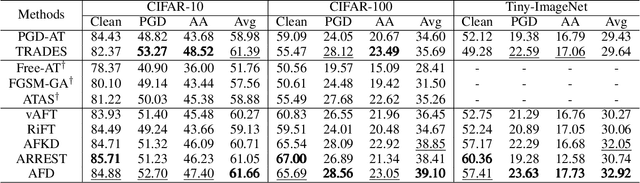
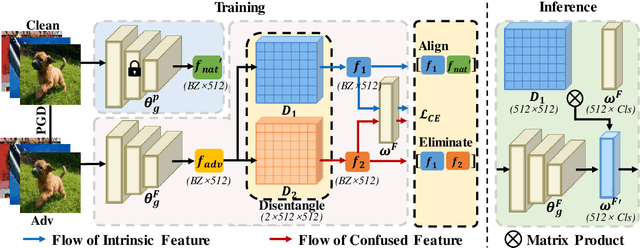
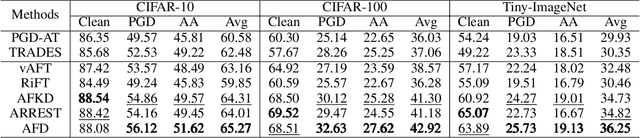
Abstract:Deep neural networks are vulnerable to adversarial samples. Adversarial fine-tuning methods aim to enhance adversarial robustness through fine-tuning the naturally pre-trained model in an adversarial training manner. However, we identify that some latent features of adversarial samples are confused by adversarial perturbation and lead to an unexpectedly increasing gap between features in the last hidden layer of natural and adversarial samples. To address this issue, we propose a disentanglement-based approach to explicitly model and further remove the latent features that cause the feature gap. Specifically, we introduce a feature disentangler to separate out the latent features from the features of the adversarial samples, thereby boosting robustness by eliminating the latent features. Besides, we align features in the pre-trained model with features of adversarial samples in the fine-tuned model, to further benefit from the features from natural samples without confusion. Empirical evaluations on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach surpasses existing adversarial fine-tuning methods and adversarial training baselines.
Masked Attribute Description Embedding for Cloth-Changing Person Re-identification
Jan 12, 2024Abstract:Cloth-changing person re-identification (CC-ReID) aims to match persons who change clothes over long periods. The key challenge in CC-ReID is to extract clothing-independent features, such as face, hairstyle, body shape, and gait. Current research mainly focuses on modeling body shape using multi-modal biological features (such as silhouettes and sketches). However, it does not fully leverage the personal description information hidden in the original RGB image. Considering that there are certain attribute descriptions which remain unchanged after the changing of cloth, we propose a Masked Attribute Description Embedding (MADE) method that unifies personal visual appearance and attribute description for CC-ReID. Specifically, handling variable clothing-sensitive information, such as color and type, is challenging for effective modeling. To address this, we mask the clothing and color information in the personal attribute description extracted through an attribute detection model. The masked attribute description is then connected and embedded into Transformer blocks at various levels, fusing it with the low-level to high-level features of the image. This approach compels the model to discard clothing information. Experiments are conducted on several CC-ReID benchmarks, including PRCC, LTCC, Celeb-reID-light, and LaST. Results demonstrate that MADE effectively utilizes attribute description, enhancing cloth-changing person re-identification performance, and compares favorably with state-of-the-art methods. The code is available at https://github.com/moon-wh/MADE.
Adv-Diffusion: Imperceptible Adversarial Face Identity Attack via Latent Diffusion Model
Dec 28, 2023Abstract:Adversarial attacks involve adding perturbations to the source image to cause misclassification by the target model, which demonstrates the potential of attacking face recognition models. Existing adversarial face image generation methods still can't achieve satisfactory performance because of low transferability and high detectability. In this paper, we propose a unified framework Adv-Diffusion that can generate imperceptible adversarial identity perturbations in the latent space but not the raw pixel space, which utilizes strong inpainting capabilities of the latent diffusion model to generate realistic adversarial images. Specifically, we propose the identity-sensitive conditioned diffusion generative model to generate semantic perturbations in the surroundings. The designed adaptive strength-based adversarial perturbation algorithm can ensure both attack transferability and stealthiness. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments on the public FFHQ and CelebA-HQ datasets prove the proposed method achieves superior performance compared with the state-of-the-art methods without an extra generative model training process. The source code is available at https://github.com/kopper-xdu/Adv-Diffusion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge