Davide Dalle Pezze
ProDER: A Continual Learning Approach for Fault Prediction in Evolving Smart Grids
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:As smart grids evolve to meet growing energy demands and modern operational challenges, the ability to accurately predict faults becomes increasingly critical. However, existing AI-based fault prediction models struggle to ensure reliability in evolving environments where they are required to adapt to new fault types and operational zones. In this paper, we propose a continual learning (CL) framework in the smart grid context to evolve the model together with the environment. We design four realistic evaluation scenarios grounded in class-incremental and domain-incremental learning to emulate evolving grid conditions. We further introduce Prototype-based Dark Experience Replay (ProDER), a unified replay-based approach that integrates prototype-based feature regularization, logit distillation, and a prototype-guided replay memory. ProDER achieves the best performance among tested CL techniques, with only a 0.045 accuracy drop for fault type prediction and 0.015 for fault zone prediction. These results demonstrate the practicality of CL for scalable, real-world fault prediction in smart grids.
Towards Continual Visual Anomaly Detection in the Medical Domain
Aug 25, 2025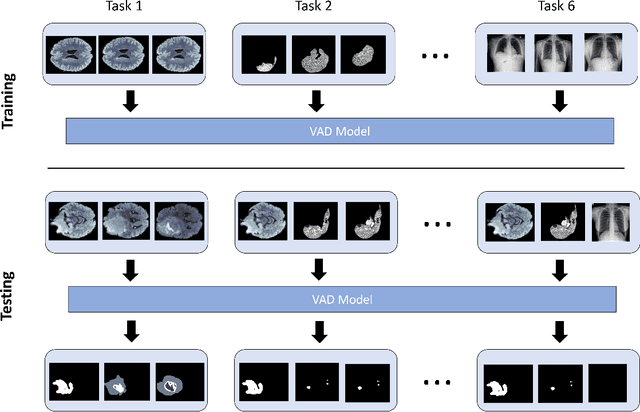
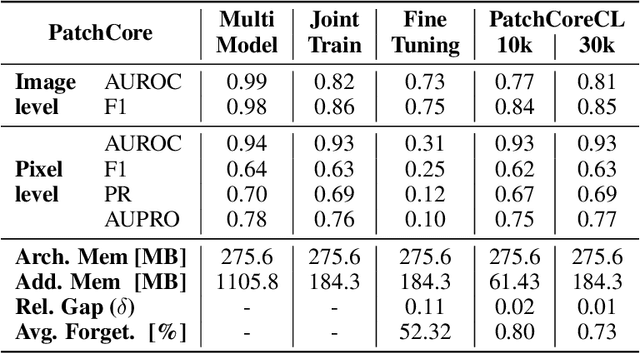
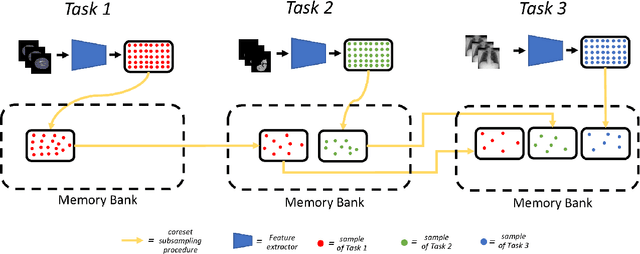
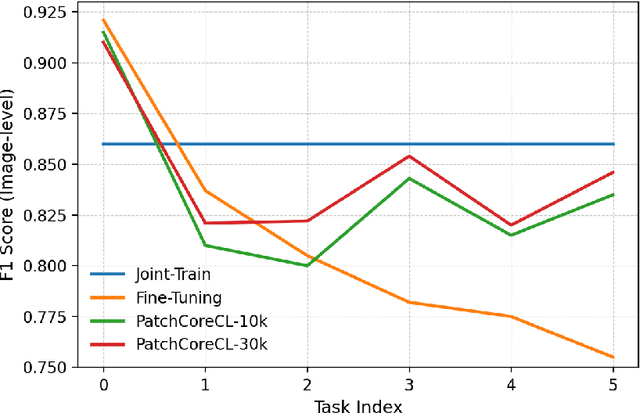
Abstract:Visual Anomaly Detection (VAD) seeks to identify abnormal images and precisely localize the corresponding anomalous regions, relying solely on normal data during training. This approach has proven essential in domains such as manufacturing and, more recently, in the medical field, where accurate and explainable detection is critical. Despite its importance, the impact of evolving input data distributions over time has received limited attention, even though such changes can significantly degrade model performance. In particular, given the dynamic and evolving nature of medical imaging data, Continual Learning (CL) provides a natural and effective framework to incrementally adapt models while preserving previously acquired knowledge. This study explores for the first time the application of VAD models in a CL scenario for the medical field. In this work, we utilize a CL version of the well-established PatchCore model, called PatchCoreCL, and evaluate its performance using BMAD, a real-world medical imaging dataset with both image-level and pixel-level annotations. Our results demonstrate that PatchCoreCL is an effective solution, achieving performance comparable to the task-specific models, with a forgetting value less than a 1%, highlighting the feasibility and potential of CL for adaptive VAD in medical imaging.
MoViAD: Modular Visual Anomaly Detection
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:VAD is a critical field in machine learning focused on identifying deviations from normal patterns in images, often challenged by the scarcity of anomalous data and the need for unsupervised training. To accelerate research and deployment in this domain, we introduce MoViAD, a comprehensive and highly modular library designed to provide fast and easy access to state-of-the-art VAD models, trainers, datasets, and VAD utilities. MoViAD supports a wide array of scenarios, including continual, semi-supervised, few-shots, noisy, and many more. In addition, it addresses practical deployment challenges through dedicated Edge and IoT settings, offering optimized models and backbones, along with quantization and compression utilities for efficient on-device execution and distributed inference. MoViAD integrates a selection of backbones, robust evaluation VAD metrics (pixel-level and image-level) and useful profiling tools for efficiency analysis. The library is designed for fast, effortless deployment, enabling machine learning engineers to easily use it for their specific setup with custom models, datasets, and backbones. At the same time, it offers the flexibility and extensibility researchers need to develop and experiment with new methods.
Domain Adaptation for Image Classification of Defects in Semiconductor Manufacturing
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:In the semiconductor sector, due to high demand but also strong and increasing competition, time to market and quality are key factors in securing significant market share in various application areas. Thanks to the success of deep learning methods in recent years in the computer vision domain, Industry 4.0 and 5.0 applications, such as defect classification, have achieved remarkable success. In particular, Domain Adaptation (DA) has proven highly effective since it focuses on using the knowledge learned on a (source) domain to adapt and perform effectively on a different but related (target) domain. By improving robustness and scalability, DA minimizes the need for extensive manual re-labeling or re-training of models. This not only reduces computational and resource costs but also allows human experts to focus on high-value tasks. Therefore, we tested the efficacy of DA techniques in semi-supervised and unsupervised settings within the context of the semiconductor field. Moreover, we propose the DBACS approach, a CycleGAN-inspired model enhanced with additional loss terms to improve performance. All the approaches are studied and validated on real-world Electron Microscope images considering the unsupervised and semi-supervised settings, proving the usefulness of our method in advancing DA techniques for the semiconductor field.
Towards Scalable IoT Deployment for Visual Anomaly Detection via Efficient Compression
May 15, 2025Abstract:Visual Anomaly Detection (VAD) is a key task in industrial settings, where minimizing operational costs is essential. Deploying deep learning models within Internet of Things (IoT) environments introduces specific challenges due to limited computational power and bandwidth of edge devices. This study investigates how to perform VAD effectively under such constraints by leveraging compact, efficient processing strategies. We evaluate several data compression techniques, examining the tradeoff between system latency and detection accuracy. Experiments on the MVTec AD benchmark demonstrate that significant compression can be achieved with minimal loss in anomaly detection performance compared to uncompressed data. Current results show up to 80% reduction in end-to-end inference time, including edge processing, transmission, and server computation.
Evaluating Modern Visual Anomaly Detection Approaches in Semiconductor Manufacturing: A Comparative Study
May 12, 2025Abstract:Semiconductor manufacturing is a complex, multistage process. Automated visual inspection of Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) images is indispensable for minimizing equipment downtime and containing costs. Most previous research considers supervised approaches, assuming a sufficient number of anomalously labeled samples. On the contrary, Visual Anomaly Detection (VAD), an emerging research domain, focuses on unsupervised learning, avoiding the costly defect collection phase while providing explanations of the predictions. We introduce a benchmark for VAD in the semiconductor domain by leveraging the MIIC dataset. Our results demonstrate the efficacy of modern VAD approaches in this field.
Teach YOLO to Remember: A Self-Distillation Approach for Continual Object Detection
Mar 06, 2025
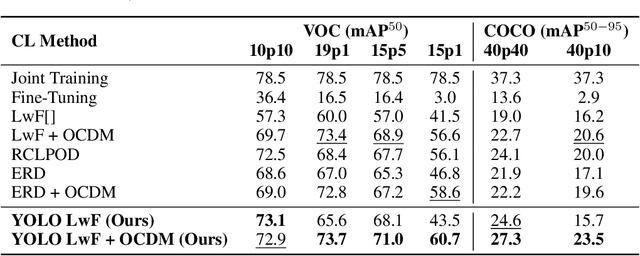
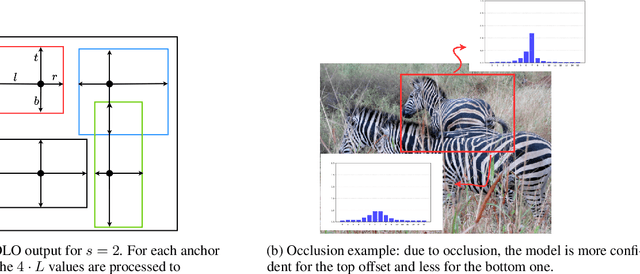
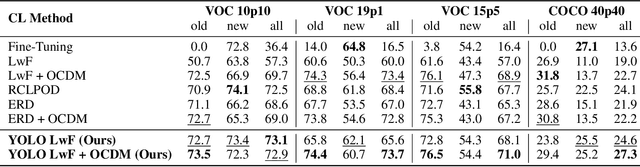
Abstract:Real-time object detectors like YOLO achieve exceptional performance when trained on large datasets for multiple epochs. However, in real-world scenarios where data arrives incrementally, neural networks suffer from catastrophic forgetting, leading to a loss of previously learned knowledge. To address this, prior research has explored strategies for Class Incremental Learning (CIL) in Continual Learning for Object Detection (CLOD), with most approaches focusing on two-stage object detectors. However, existing work suggests that Learning without Forgetting (LwF) may be ineffective for one-stage anchor-free detectors like YOLO due to noisy regression outputs, which risk transferring corrupted knowledge. In this work, we introduce YOLO LwF, a self-distillation approach tailored for YOLO-based continual object detection. We demonstrate that when coupled with a replay memory, YOLO LwF significantly mitigates forgetting. Compared to previous approaches, it achieves state-of-the-art performance, improving mAP by +2.1% and +2.9% on the VOC and COCO benchmarks, respectively.
Memory Efficient Continual Learning for Edge-Based Visual Anomaly Detection
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Visual Anomaly Detection (VAD) is a critical task in computer vision with numerous real-world applications. However, deploying these models on edge devices presents significant challenges, such as constrained computational and memory resources. Additionally, dynamic data distributions in real-world settings necessitate continuous model adaptation, further complicating deployment under limited resources. To address these challenges, we present a novel investigation into the problem of Continual Learning for Visual Anomaly Detection (CLAD) on edge devices. We evaluate the STFPM approach, given its low memory footprint on edge devices, which demonstrates good performance when combined with the Replay approach. Furthermore, we propose to study the behavior of a recently proposed approach, PaSTe, specifically designed for the edge but not yet explored in the Continual Learning context. Our results show that PaSTe is not only a lighter version of STPFM, but it also achieves superior anomaly detection performance, improving the f1 pixel performance by 10% with the Replay technique. In particular, the structure of PaSTe allows us to test it using a series of Compressed Replay techniques, reducing memory overhead by a maximum of 91.5% compared to the traditional Replay for STFPM. Our study proves the feasibility of deploying VAD models that adapt and learn incrementally on CLAD scenarios on resource-constrained edge devices.
From Vision to Sound: Advancing Audio Anomaly Detection with Vision-Based Algorithms
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in Visual Anomaly Detection (VAD) have introduced sophisticated algorithms leveraging embeddings generated by pre-trained feature extractors. Inspired by these developments, we investigate the adaptation of such algorithms to the audio domain to address the problem of Audio Anomaly Detection (AAD). Unlike most existing AAD methods, which primarily classify anomalous samples, our approach introduces fine-grained temporal-frequency localization of anomalies within the spectrogram, significantly improving explainability. This capability enables a more precise understanding of where and when anomalies occur, making the results more actionable for end users. We evaluate our approach on industrial and environmental benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of VAD techniques in detecting anomalies in audio signals. Moreover, they improve explainability by enabling localized anomaly identification, making audio anomaly detection systems more interpretable and practical.
Continual Learning for Behavior-based Driver Identification
Dec 14, 2024



Abstract:Behavior-based Driver Identification is an emerging technology that recognizes drivers based on their unique driving behaviors, offering important applications such as vehicle theft prevention and personalized driving experiences. However, most studies fail to account for the real-world challenges of deploying Deep Learning models within vehicles. These challenges include operating under limited computational resources, adapting to new drivers, and changes in driving behavior over time. The objective of this study is to evaluate if Continual Learning (CL) is well-suited to address these challenges, as it enables models to retain previously learned knowledge while continually adapting with minimal computational overhead and resource requirements. We tested several CL techniques across three scenarios of increasing complexity based on the well-known OCSLab dataset. This work provides an important step forward in scalable driver identification solutions, demonstrating that CL approaches, such as DER, can obtain strong performance, with only an 11% reduction in accuracy compared to the static scenario. Furthermore, to enhance the performance, we propose two new methods, SmooER and SmooDER, that leverage the temporal continuity of driver identity over time to enhance classification accuracy. Our novel method, SmooDER, achieves optimal results with only a 2% reduction compared to the 11\% of the DER approach. In conclusion, this study proves the feasibility of CL approaches to address the challenges of Driver Identification in dynamic environments, making them suitable for deployment on cloud infrastructure or directly within vehicles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge