Riccardo De Monte
Teach YOLO to Remember: A Self-Distillation Approach for Continual Object Detection
Mar 06, 2025
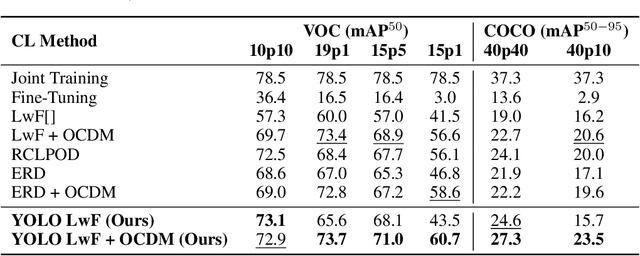
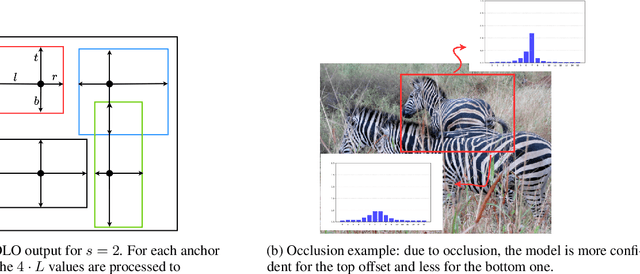
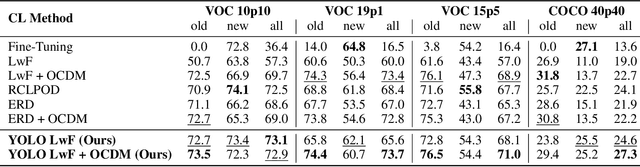
Abstract:Real-time object detectors like YOLO achieve exceptional performance when trained on large datasets for multiple epochs. However, in real-world scenarios where data arrives incrementally, neural networks suffer from catastrophic forgetting, leading to a loss of previously learned knowledge. To address this, prior research has explored strategies for Class Incremental Learning (CIL) in Continual Learning for Object Detection (CLOD), with most approaches focusing on two-stage object detectors. However, existing work suggests that Learning without Forgetting (LwF) may be ineffective for one-stage anchor-free detectors like YOLO due to noisy regression outputs, which risk transferring corrupted knowledge. In this work, we introduce YOLO LwF, a self-distillation approach tailored for YOLO-based continual object detection. We demonstrate that when coupled with a replay memory, YOLO LwF significantly mitigates forgetting. Compared to previous approaches, it achieves state-of-the-art performance, improving mAP by +2.1% and +2.9% on the VOC and COCO benchmarks, respectively.
Tiny Robotics Dataset and Benchmark for Continual Object Detection
Sep 24, 2024



Abstract:Detecting objects in mobile robotics is crucial for numerous applications, from autonomous navigation to inspection. However, robots are often required to perform tasks in different domains with respect to the training one and need to adapt to these changes. Tiny mobile robots, subject to size, power, and computational constraints, encounter even more difficulties in running and adapting these algorithms. Such adaptability, though, is crucial for real-world deployment, where robots must operate effectively in dynamic and unpredictable settings. In this work, we introduce a novel benchmark to evaluate the continual learning capabilities of object detection systems in tiny robotic platforms. Our contributions include: (i) Tiny Robotics Object Detection (TiROD), a comprehensive dataset collected using a small mobile robot, designed to test the adaptability of object detectors across various domains and classes; (ii) an evaluation of state-of-the-art real-time object detectors combined with different continual learning strategies on this dataset, providing detailed insights into their performance and limitations; and (iii) we publish the data and the code to replicate the results to foster continuous advancements in this field. Our benchmark results indicate key challenges that must be addressed to advance the development of robust and efficient object detection systems for tiny robotics.
Replay Consolidation with Label Propagation for Continual Object Detection
Sep 09, 2024


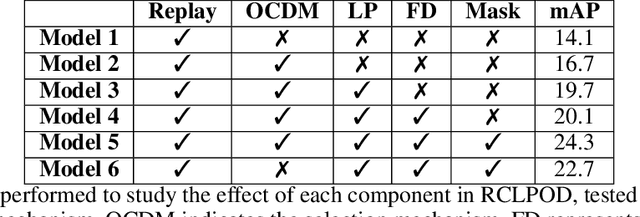
Abstract:Object Detection is a highly relevant computer vision problem with many applications such as robotics and autonomous driving. Continual Learning~(CL) considers a setting where a model incrementally learns new information while retaining previously acquired knowledge. This is particularly challenging since Deep Learning models tend to catastrophically forget old knowledge while training on new data. In particular, Continual Learning for Object Detection~(CLOD) poses additional difficulties compared to CL for Classification. In CLOD, images from previous tasks may contain unknown classes that could reappear labeled in future tasks. These missing annotations cause task interference issues for replay-based approaches. As a result, most works in the literature have focused on distillation-based approaches. However, these approaches are effective only when there is a strong overlap of classes across tasks. To address the issues of current methodologies, we propose a novel technique to solve CLOD called Replay Consolidation with Label Propagation for Object Detection (RCLPOD). Based on the replay method, our solution avoids task interference issues by enhancing the buffer memory samples. Our method is evaluated against existing techniques in CLOD literature, demonstrating its superior performance on established benchmarks like VOC and COCO.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge