David Lane
Multi-Task Reinforcement Learning based Mobile Manipulation Control for Dynamic Object Tracking and Grasping
Jun 07, 2020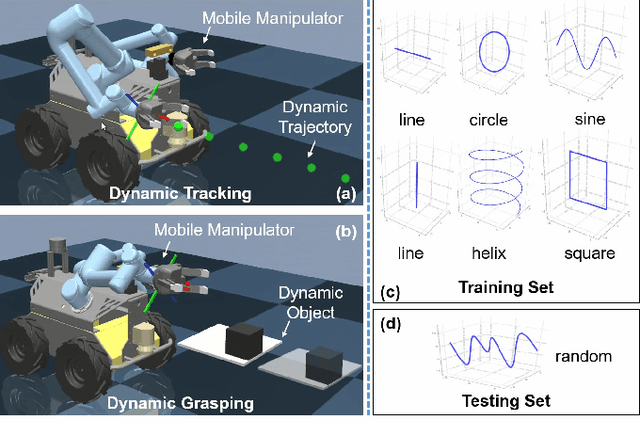
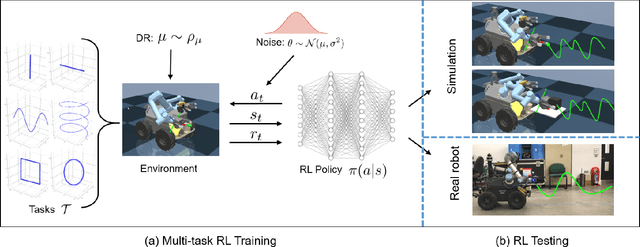
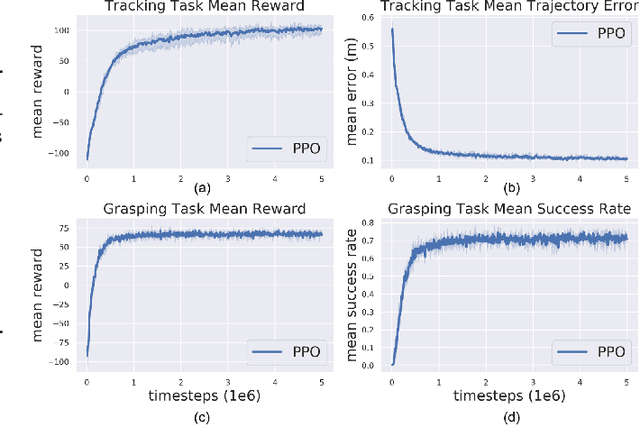
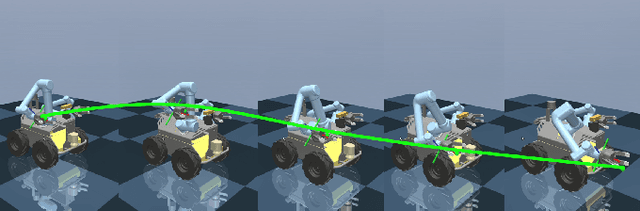
Abstract:Agile control of mobile manipulator is challenging because of the high complexity coupled by the robotic system and the unstructured working environment. Tracking and grasping a dynamic object with a random trajectory is even harder. In this paper, a multi-task reinforcement learning-based mobile manipulation control framework is proposed to achieve general dynamic object tracking and grasping. Several basic types of dynamic trajectories are chosen as the task training set. To improve the policy generalization in practice, random noise and dynamics randomization are introduced during the training process. Extensive experiments show that our policy trained can adapt to unseen random dynamic trajectories with about 0.1m tracking error and 75\% grasping success rate of dynamic objects. The trained policy can also be successfully deployed on a real mobile manipulator.
Robots in the Danger Zone: Exploring Public Perception through Engagement
Apr 01, 2020
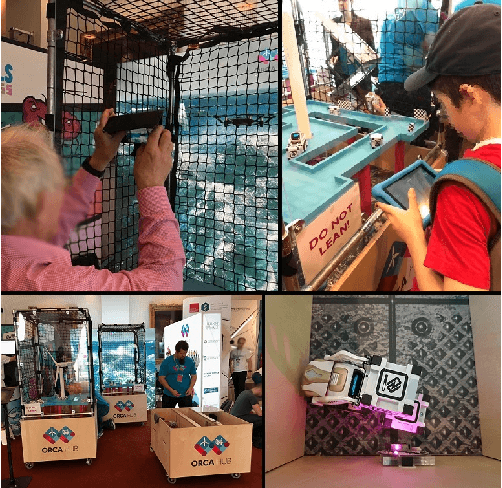
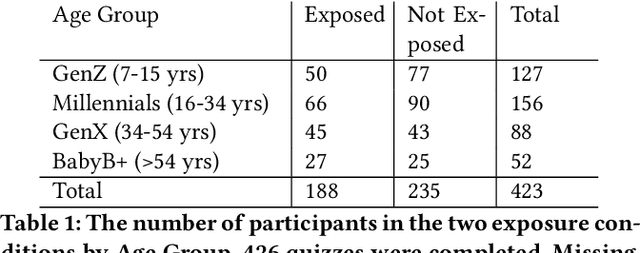

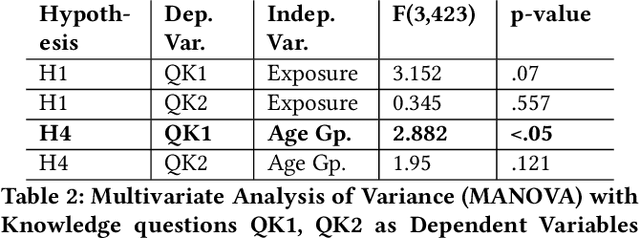
Abstract:Public perceptions of Robotics and Artificial Intelligence (RAI) are important in the acceptance, uptake, government regulation and research funding of this technology. Recent research has shown that the public's understanding of RAI can be negative or inaccurate. We believe effective public engagement can help ensure that public opinion is better informed. In this paper, we describe our first iteration of a high throughput in-person public engagement activity. We describe the use of a light touch quiz-format survey instrument to integrate in-the-wild research participation into the engagement, allowing us to probe both the effectiveness of our engagement strategy, and public perceptions of the future roles of robots and humans working in dangerous settings, such as in the off-shore energy sector. We critique our methods and share interesting results into generational differences within the public's view of the future of Robotics and AI in hazardous environments. These findings include that older peoples' views about the future of robots in hazardous environments were not swayed by exposure to our exhibit, while the views of younger people were affected by our exhibit, leading us to consider carefully in future how to more effectively engage with and inform older people.
* Accepted in HRI 2020, Keywords: Human robot interaction, robotics, artificial intelligence, public engagement, public perceptions of robots, robotics and society
The ORCA Hub: Explainable Offshore Robotics through Intelligent Interfaces
Mar 06, 2018
Abstract:We present the UK Robotics and Artificial Intelligence Hub for Offshore Robotics for Certification of Assets (ORCA Hub), a 3.5 year EPSRC funded, multi-site project. The ORCA Hub vision is to use teams of robots and autonomous intelligent systems (AIS) to work on offshore energy platforms to enable cheaper, safer and more efficient working practices. The ORCA Hub will research, integrate, validate and deploy remote AIS solutions that can operate with existing and future offshore energy assets and sensors, interacting safely in autonomous or semi-autonomous modes in complex and cluttered environments, co-operating with remote operators. The goal is that through the use of such robotic systems offshore, the need for personnel will decrease. To enable this to happen, the remote operator will need a high level of situation awareness and key to this is the transparency of what the autonomous systems are doing and why. This increased transparency will facilitate a trusting relationship, which is particularly key in high-stakes, hazardous situations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge