Dapeng Shi
Step-Audio 2 Technical Report
Jul 24, 2025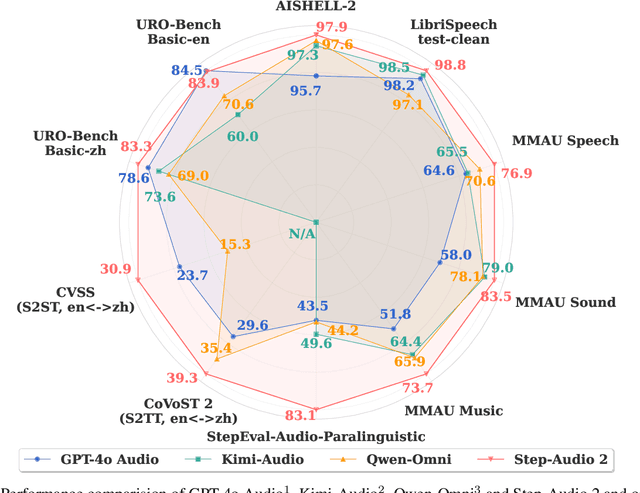

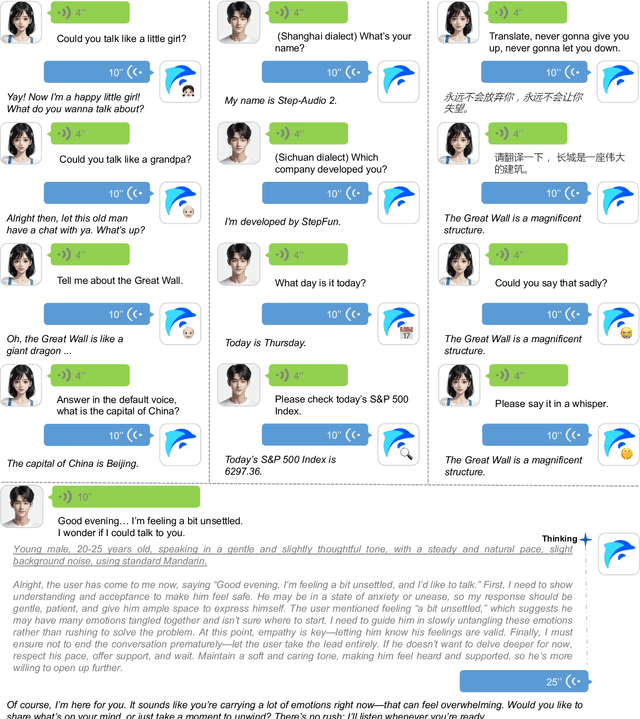

Abstract:This paper presents Step-Audio 2, an end-to-end multi-modal large language model designed for industry-strength audio understanding and speech conversation. By integrating a latent audio encoder and reasoning-centric reinforcement learning (RL), Step-Audio 2 achieves promising performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and audio understanding. To facilitate genuine end-to-end speech conversation, Step-Audio 2 incorporates the generation of discrete audio tokens into language modeling, significantly enhancing its responsiveness to paralinguistic information such as speaking styles and emotions. To effectively leverage the rich textual and acoustic knowledge in real-world data, Step-Audio 2 integrates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and is able to call external tools such as web search to mitigate hallucination and audio search to switch timbres. Trained on millions of hours of speech and audio data, Step-Audio 2 delivers intelligence and expressiveness across diverse conversational scenarios. Evaluation results demonstrate that Step-Audio 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on various audio understanding and conversational benchmarks compared to other open-source and commercial solutions. Please visit https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio2 for more information.
Step-Audio-AQAA: a Fully End-to-End Expressive Large Audio Language Model
Jun 10, 2025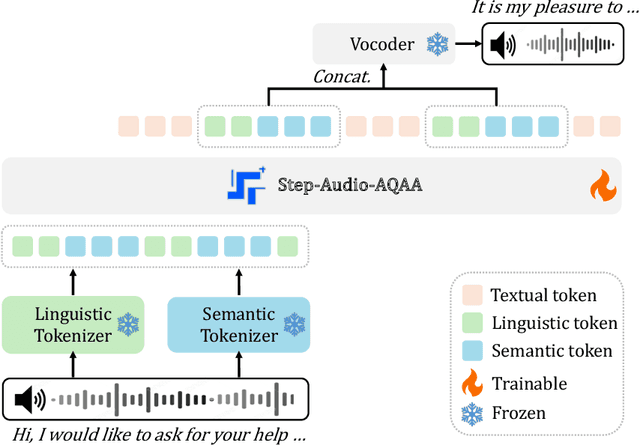
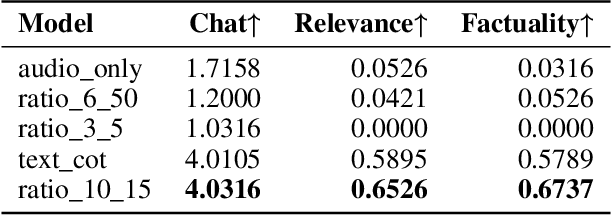
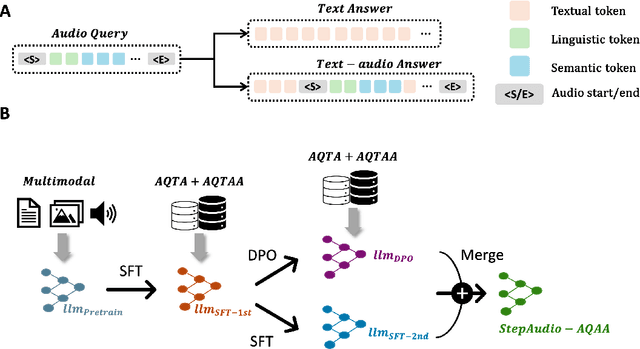
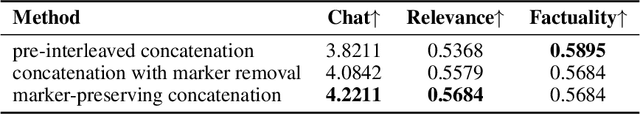
Abstract:Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) have significantly advanced intelligent human-computer interaction, yet their reliance on text-based outputs limits their ability to generate natural speech responses directly, hindering seamless audio interactions. To address this, we introduce Step-Audio-AQAA, a fully end-to-end LALM designed for Audio Query-Audio Answer (AQAA) tasks. The model integrates a dual-codebook audio tokenizer for linguistic and semantic feature extraction, a 130-billion-parameter backbone LLM and a neural vocoder for high-fidelity speech synthesis. Our post-training approach employs interleaved token-output of text and audio to enhance semantic coherence and combines Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with model merge to improve performance. Evaluations on the StepEval-Audio-360 benchmark demonstrate that Step-Audio-AQAA excels especially in speech control, outperforming the state-of-art LALMs in key areas. This work contributes a promising solution for end-to-end LALMs and highlights the critical role of token-based vocoder in enhancing overall performance for AQAA tasks.
Step-Audio: Unified Understanding and Generation in Intelligent Speech Interaction
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Real-time speech interaction, serving as a fundamental interface for human-machine collaboration, holds immense potential. However, current open-source models face limitations such as high costs in voice data collection, weakness in dynamic control, and limited intelligence. To address these challenges, this paper introduces Step-Audio, the first production-ready open-source solution. Key contributions include: 1) a 130B-parameter unified speech-text multi-modal model that achieves unified understanding and generation, with the Step-Audio-Chat version open-sourced; 2) a generative speech data engine that establishes an affordable voice cloning framework and produces the open-sourced lightweight Step-Audio-TTS-3B model through distillation; 3) an instruction-driven fine control system enabling dynamic adjustments across dialects, emotions, singing, and RAP; 4) an enhanced cognitive architecture augmented with tool calling and role-playing abilities to manage complex tasks effectively. Based on our new StepEval-Audio-360 evaluation benchmark, Step-Audio achieves state-of-the-art performance in human evaluations, especially in terms of instruction following. On open-source benchmarks like LLaMA Question, shows 9.3% average performance improvement, demonstrating our commitment to advancing the development of open-source multi-modal language technologies. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio.
Simultaneous Identification of Sparse Structures and Communities in Heterogeneous Graphical Models
May 16, 2024Abstract:Exploring and detecting community structures hold significant importance in genetics, social sciences, neuroscience, and finance. Especially in graphical models, community detection can encourage the exploration of sets of variables with group-like properties. In this paper, within the framework of Gaussian graphical models, we introduce a novel decomposition of the underlying graphical structure into a sparse part and low-rank diagonal blocks (non-overlapped communities). We illustrate the significance of this decomposition through two modeling perspectives and propose a three-stage estimation procedure with a fast and efficient algorithm for the identification of the sparse structure and communities. Also on the theoretical front, we establish conditions for local identifiability and extend the traditional irrepresentability condition to an adaptive form by constructing an effective norm, which ensures the consistency of model selection for the adaptive $\ell_1$ penalized estimator in the second stage. Moreover, we also provide the clustering error bound for the K-means procedure in the third stage. Extensive numerical experiments are conducted to demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over existing approaches in estimating graph structures. Furthermore, we apply our method to the stock return data, revealing its capability to accurately identify non-overlapped community structures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge