Danyang Liu
TrustScore: Reference-Free Evaluation of LLM Response Trustworthiness
Feb 19, 2024

Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities across various domains, prompting a surge in their practical applications. However, concerns have arisen regarding the trustworthiness of LLMs outputs, particularly in closed-book question-answering tasks, where non-experts may struggle to identify inaccuracies due to the absence of contextual or ground truth information. This paper introduces TrustScore, a framework based on the concept of Behavioral Consistency, which evaluates whether an LLMs response aligns with its intrinsic knowledge. Additionally, TrustScore can seamlessly integrate with fact-checking methods, which assesses alignment with external knowledge sources. The experimental results show that TrustScore achieves strong correlations with human judgments, surpassing existing reference-free metrics, and achieving results on par with reference-based metrics.
Visual Storytelling with Question-Answer Plans
Oct 17, 2023Abstract:Visual storytelling aims to generate compelling narratives from image sequences. Existing models often focus on enhancing the representation of the image sequence, e.g., with external knowledge sources or advanced graph structures. Despite recent progress, the stories are often repetitive, illogical, and lacking in detail. To mitigate these issues, we present a novel framework which integrates visual representations with pretrained language models and planning. Our model translates the image sequence into a visual prefix, a sequence of continuous embeddings which language models can interpret. It also leverages a sequence of question-answer pairs as a blueprint plan for selecting salient visual concepts and determining how they should be assembled into a narrative. Automatic and human evaluation on the VIST benchmark (Huang et al., 2016) demonstrates that blueprint-based models generate stories that are more coherent, interesting, and natural compared to competitive baselines and state-of-the-art systems.
Modeling Spatiotemporal Periodicity and Collaborative Signal for Local-Life Service Recommendation
Sep 22, 2023



Abstract:Online local-life service platforms provide services like nearby daily essentials and food delivery for hundreds of millions of users. Different from other types of recommender systems, local-life service recommendation has the following characteristics: (1) spatiotemporal periodicity, which means a user's preferences for items vary from different locations at different times. (2) spatiotemporal collaborative signal, which indicates similar users have similar preferences at specific locations and times. However, most existing methods either focus on merely the spatiotemporal contexts in sequences, or model the user-item interactions without spatiotemporal contexts in graphs. To address this issue, we design a new method named SPCS in this paper. Specifically, we propose a novel spatiotemporal graph transformer (SGT) layer, which explicitly encodes relative spatiotemporal contexts, and aggregates the information from multi-hop neighbors to unify spatiotemporal periodicity and collaborative signal. With extensive experiments on both public and industrial datasets, this paper validates the state-of-the-art performance of SPCS.
Detecting and Grounding Important Characters in Visual Stories
Mar 30, 2023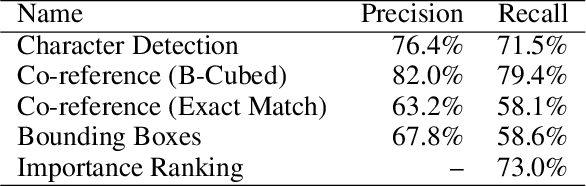


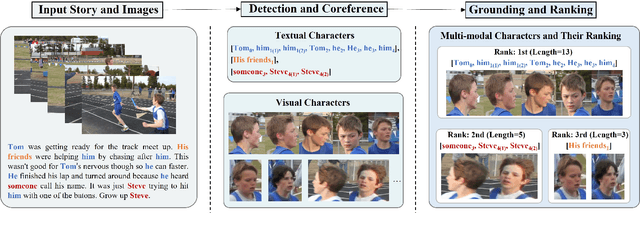
Abstract:Characters are essential to the plot of any story. Establishing the characters before writing a story can improve the clarity of the plot and the overall flow of the narrative. However, previous work on visual storytelling tends to focus on detecting objects in images and discovering relationships between them. In this approach, characters are not distinguished from other objects when they are fed into the generation pipeline. The result is a coherent sequence of events rather than a character-centric story. In order to address this limitation, we introduce the VIST-Character dataset, which provides rich character-centric annotations, including visual and textual co-reference chains and importance ratings for characters. Based on this dataset, we propose two new tasks: important character detection and character grounding in visual stories. For both tasks, we develop simple, unsupervised models based on distributional similarity and pre-trained vision-and-language models. Our new dataset, together with these models, can serve as the foundation for subsequent work on analysing and generating stories from a character-centric perspective.
Fast and Accurate Knowledge-Aware Document Representation Enhancement for News Recommendations
Oct 25, 2019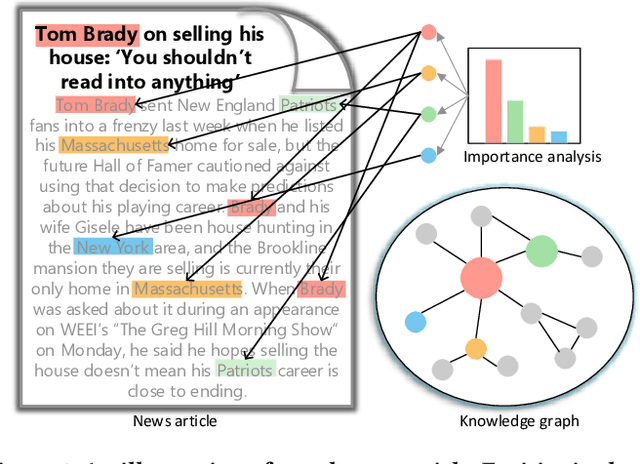



Abstract:Knowledge graph contains well-structured external information and has shown to be useful for recommender systems. Most existing knowledge-aware methods assume that the item from recommender systems can be linked to an entity in a knowledge graph, thus item embeddings can be better learned by jointly modeling of both recommender systems and a knowledge graph. However, this is not the situation for news recommendation, where items, namely news articles, are in fact related to a collection of knowledge entities. The importance score and semantic information of entities in one article differ from each other, which depend on the topic of the article and relations among co-occurred entities. How to fully utilize these entities for better news recommendation service is non-trivial. In this paper, we propose a fast and effective knowledge-aware representation enhancement model for improving news document understanding. The model, named \emph{KRED}, consists of three layers: (1) an entity representation layer; (2) a context embedding layer; and (3) an information distillation layer. An entity is represented by the embeddings of itself and its surrounding entities. The context embedding layer is designed to distinguish dynamic context of different entities such as frequency, category and position. The information distillation layer will aggregate the entity embeddings under the guidance of the original document vector, transforming the document vector into a new one. We have conduct extensive experiments on a real-world news reading dataset. The results demonstrate that our proposed model greatly benefits a variety of news recommendation tasks, including personalized news recommendation, article category classification, article popularity prediction and local news detection.
Collaborative Metric Learning with Memory Network for Multi-Relational Recommender Systems
Jun 24, 2019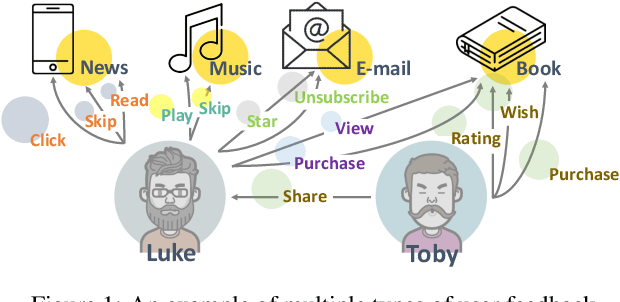
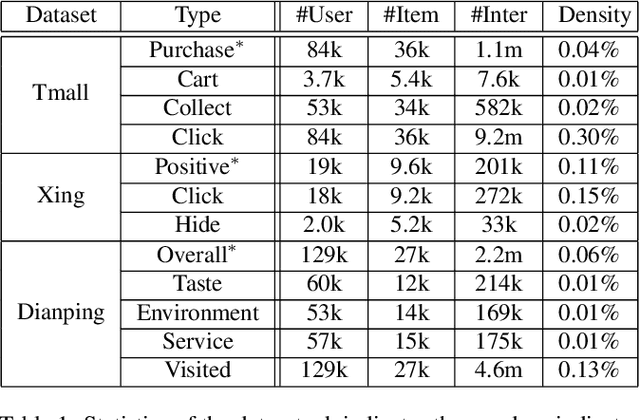
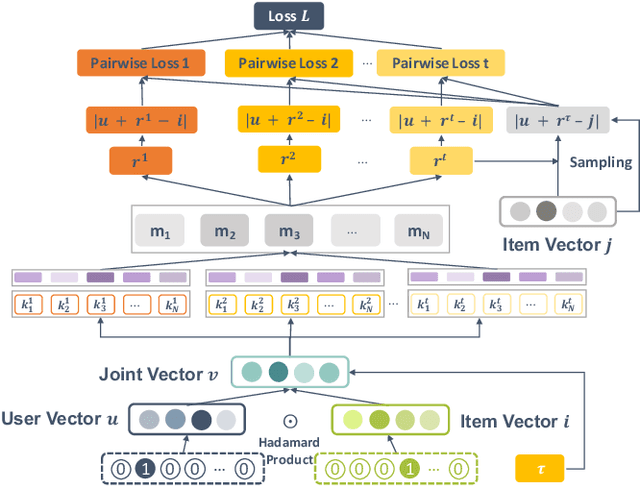

Abstract:The success of recommender systems in modern online platforms is inseparable from the accurate capture of users' personal tastes. In everyday life, large amounts of user feedback data are created along with user-item online interactions in a variety of ways, such as browsing, purchasing, and sharing. These multiple types of user feedback provide us with tremendous opportunities to detect individuals' fine-grained preferences. Different from most existing recommender systems that rely on a single type of feedback, we advocate incorporating multiple types of user-item interactions for better recommendations. Based on the observation that the underlying spectrum of user preferences is reflected in various types of interactions with items and can be uncovered by latent relational learning in metric space, we propose a unified neural learning framework, named Multi-Relational Memory Network (MRMN). It can not only model fine-grained user-item relations but also enable us to discriminate between feedback types in terms of the strength and diversity of user preferences. Extensive experiments show that the proposed MRMN model outperforms competitive state-of-the-art algorithms in a wide range of scenarios, including e-commerce, local services, and job recommendations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge