Daniel Scharstein
A Practical Stereo Depth System for Smart Glasses
Nov 19, 2022



Abstract:We present the design of a productionized end-to-end stereo depth sensing system that does pre-processing, online stereo rectification, and stereo depth estimation with a fallback to monocular depth estimation when rectification is unreliable. The output of our depth sensing system is then used in a novel view generation pipeline to create 3D computational photography effect using point-of-view images captured by smart glasses. All these steps are executed on-device on the stringent compute budget of a mobile phone, and because we expect the users can use a wide range of smartphones, our design needs to be general and cannot be dependent on a particular hardware or ML accelerator such as a smartphone GPU. Although each of these steps is well-studied, a description of a practical system is still lacking. For such a system, each of these steps need to work in tandem with one another and fallback gracefully on failures within the system or less than ideal input data. We show how we handle unforeseen changes to calibration, e.g. due to heat, robustly support depth estimation in the wild, and still abide by the memory and latency constraints required for a smooth user experience. We show that our trained models are fast, that run in less than 1s on a six-year-old Samsung Galaxy S8 phone's CPU. Our models generalize well to unseen data and achieve good results on Middlebury and in-the-wild images captured from the smart glasses.
Capturing and Inferring Dense Full-Body Human-Scene Contact
Jun 20, 2022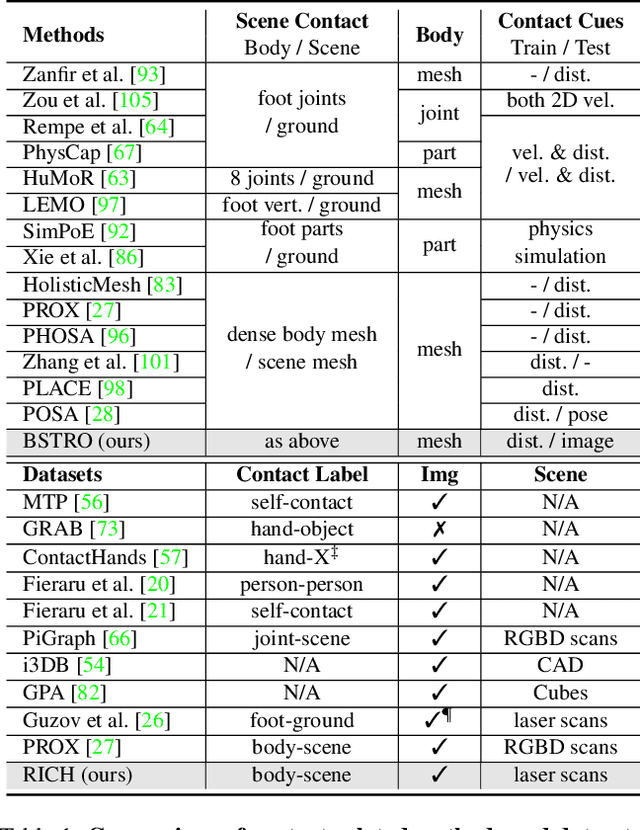
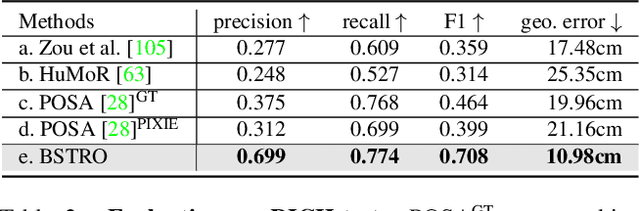
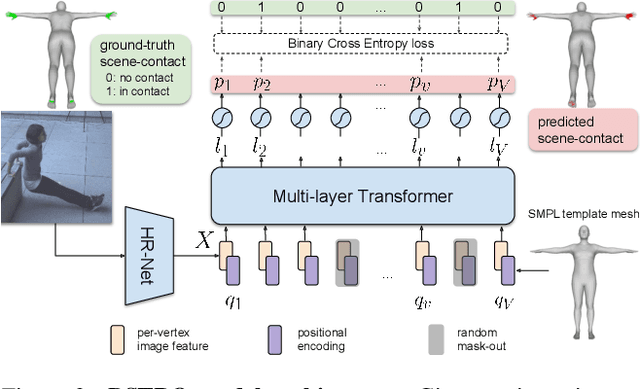
Abstract:Inferring human-scene contact (HSC) is the first step toward understanding how humans interact with their surroundings. While detecting 2D human-object interaction (HOI) and reconstructing 3D human pose and shape (HPS) have enjoyed significant progress, reasoning about 3D human-scene contact from a single image is still challenging. Existing HSC detection methods consider only a few types of predefined contact, often reduce body and scene to a small number of primitives, and even overlook image evidence. To predict human-scene contact from a single image, we address the limitations above from both data and algorithmic perspectives. We capture a new dataset called RICH for "Real scenes, Interaction, Contact and Humans." RICH contains multiview outdoor/indoor video sequences at 4K resolution, ground-truth 3D human bodies captured using markerless motion capture, 3D body scans, and high resolution 3D scene scans. A key feature of RICH is that it also contains accurate vertex-level contact labels on the body. Using RICH, we train a network that predicts dense body-scene contacts from a single RGB image. Our key insight is that regions in contact are always occluded so the network needs the ability to explore the whole image for evidence. We use a transformer to learn such non-local relationships and propose a new Body-Scene contact TRansfOrmer (BSTRO). Very few methods explore 3D contact; those that do focus on the feet only, detect foot contact as a post-processing step, or infer contact from body pose without looking at the scene. To our knowledge, BSTRO is the first method to directly estimate 3D body-scene contact from a single image. We demonstrate that BSTRO significantly outperforms the prior art. The code and dataset are available at https://rich.is.tue.mpg.de.
Semi-Global Stereo Matching with Surface Orientation Priors
Dec 03, 2017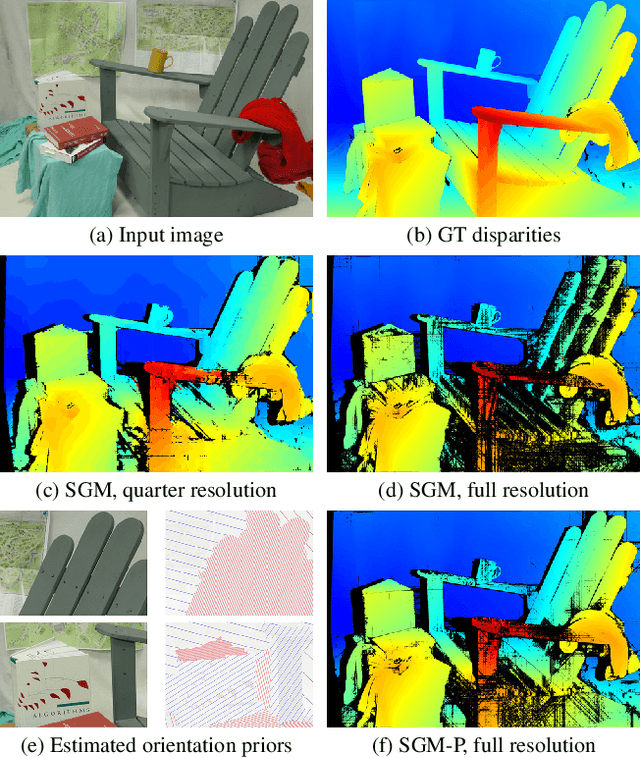
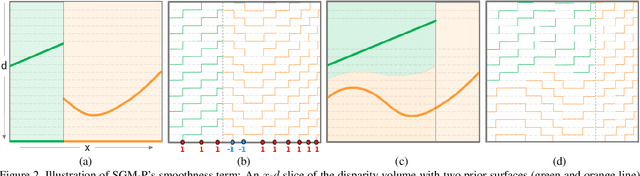
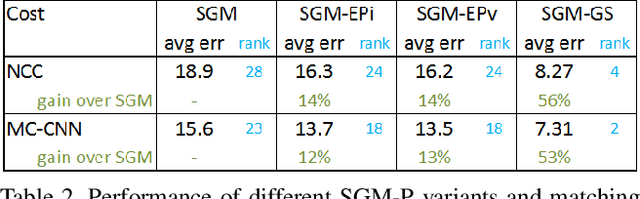
Abstract:Semi-Global Matching (SGM) is a widely-used efficient stereo matching technique. It works well for textured scenes, but fails on untextured slanted surfaces due to its fronto-parallel smoothness assumption. To remedy this problem, we propose a simple extension, termed SGM-P, to utilize precomputed surface orientation priors. Such priors favor different surface slants in different 2D image regions or 3D scene regions and can be derived in various ways. In this paper we evaluate plane orientation priors derived from stereo matching at a coarser resolution and show that such priors can yield significant performance gains for difficult weakly-textured scenes. We also explore surface normal priors derived from Manhattan-world assumptions, and we analyze the potential performance gains using oracle priors derived from ground-truth data. SGM-P only adds a minor computational overhead to SGM and is an attractive alternative to more complex methods employing higher-order smoothness terms.
Modeling Radiometric Uncertainty for Vision with Tone-mapped Color Images
Apr 09, 2014



Abstract:To produce images that are suitable for display, tone-mapping is widely used in digital cameras to map linear color measurements into narrow gamuts with limited dynamic range. This introduces non-linear distortion that must be undone, through a radiometric calibration process, before computer vision systems can analyze such photographs radiometrically. This paper considers the inherent uncertainty of undoing the effects of tone-mapping. We observe that this uncertainty varies substantially across color space, making some pixels more reliable than others. We introduce a model for this uncertainty and a method for fitting it to a given camera or imaging pipeline. Once fit, the model provides for each pixel in a tone-mapped digital photograph a probability distribution over linear scene colors that could have induced it. We demonstrate how these distributions can be useful for visual inference by incorporating them into estimation algorithms for a representative set of vision tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge