Daniel Bonilla Licea
Robust Planning and Control of Omnidirectional MRAVs for Aerial Communications in Wireless Networks
Apr 21, 2025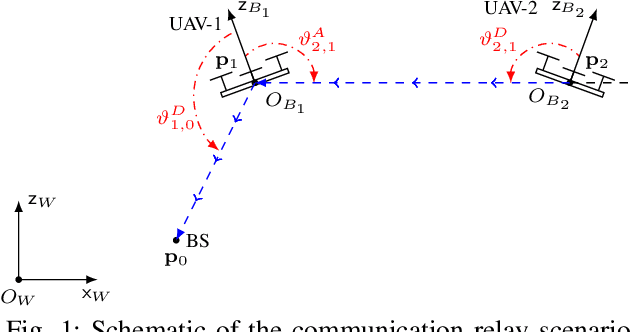
Abstract:A new class of Multi-Rotor Aerial Vehicles (MRAVs), known as omnidirectional MRAVs (o-MRAVs), has gained attention for their ability to independently control 3D position and orientation. This capability enhances robust planning and control in aerial communication networks, enabling more adaptive trajectory planning and precise antenna alignment without additional mechanical components. These features are particularly valuable in uncertain environments, where disturbances such as wind and interference affect communication stability. This paper examines o-MRAVs in the context of robust aerial network planning, comparing them with the more common under-actuated MRAVs (u-MRAVs). Key applications, including physical layer security, optical communications, and network densification, are highlighted, demonstrating the potential of o-MRAVs to improve reliability and efficiency in dynamic communication scenarios.
Towards Agile Swarming in Real World: Onboard Relative Localization with Fast Tracking of Active Blinking Markers
Feb 03, 2025Abstract:A novel onboard tracking approach enabling vision-based relative localization and communication using Active blinking Marker Tracking (AMT) is introduced in this article. Active blinking markers on multi-robot team members improve the robustness of relative localization for aerial vehicles in tightly coupled swarms during real-world deployments, while also serving as a resilient communication channel. Traditional tracking algorithms struggle to track fast moving blinking markers due to their intermittent appearance in the camera frames. AMT addresses this by using weighted polynomial regression to predict the future appearance of active blinking markers while accounting for uncertainty in the prediction. In outdoor experiments, the AMT approach outperformed state-of-the-art methods in tracking density, accuracy, and complexity. The experimental validation of this novel tracking approach for relative localization involved testing motion patterns motivated by our research on agile multi-robot deployment.
Reshaping UAV-Enabled Communications with Omnidirectional Multi-Rotor Aerial Vehicles
Nov 04, 2024



Abstract:A new class of Multi-Rotor Aerial Vehicles (MRAVs), known as omnidirectional MRAVs (o-MRAVs), has attracted significant interest in the robotics community. These MRAVs have the unique capability of independently controlling their 3D position and 3D orientation. In the context of aerial communication networks, this translates into the ability to control the position and orientation of the antenna mounted on the MRAV without any additional devices tasked for antenna orientation. This additional Degrees of Freedom (DoF) adds a new dimension to aerial communication systems, creating various research opportunities in communications-aware trajectory planning and positioning. This paper presents this new class of MRAVs and discusses use cases in areas such as physical layer security and optical communications. Furthermore, the benefits of these MRAVs are illustrated with realistic simulation scenarios. Finally, new research problems and opportunities introduced by this advanced robotics technology are discussed.
Harnessing the Potential of Omnidirectional Multi-Rotor Aerial Vehicles in Cooperative Jamming Against Eavesdropping
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:Recent research in communications-aware robotics has been propelled by advancements in 5G and emerging 6G technologies. This field now includes the integration of Multi-Rotor Aerial Vehicles (MRAVs) into cellular networks, with a specific focus on under-actuated MRAVs. These vehicles face challenges in independently controlling position and orientation due to their limited control inputs, which adversely affects communication metrics such as Signal-to-Noise Ratio. In response, a newer class of omnidirectional MRAVs has been developed, which can control both position and orientation simultaneously by tilting their propellers. However, exploiting this capability fully requires sophisticated motion planning techniques. This paper presents a novel application of omnidirectional MRAVs designed to enhance communication security and thwart eavesdropping. It proposes a strategy where one MRAV functions as an aerial Base Station, while another acts as a friendly jammer to secure communications. This study is the first to apply such a strategy to MRAVs in scenarios involving eavesdroppers.
PACNav: Enhancing Collective Navigation for UAV Swarms in Communication-Challenged Environments
Apr 20, 2024Abstract:This article presents Persistence Administered Collective Navigation (PACNav) as an approach for achieving decentralized collective navigation of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) swarms. The technique is inspired by the flocking and collective navigation behavior observed in natural swarms, such as cattle herds, bird flocks, and even large groups of humans. PACNav relies solely on local observations of relative positions of UAVs, making it suitable for large swarms deprived of communication capabilities and external localization systems. We introduce the novel concepts of path persistence and path similarity, which allow each swarm member to analyze the motion of others. PACNav is grounded on two main principles: (1) UAVs with little variation in motion direction exhibit high path persistence and are considered reliable leaders by other UAVs; (2) groups of UAVs that move in a similar direction demonstrate high path similarity, and such groups are assumed to contain a reliable leader. The proposed approach also incorporates a reactive collision avoidance mechanism to prevent collisions with swarm members and environmental obstacles. The method is validated through simulated and real-world experiments conducted in a natural forest.
Omnidirectional Multi-Rotor Aerial Vehicle Pose Optimization: A Novel Approach to Physical Layer Security
Jan 05, 2024

Abstract:The integration of Multi-Rotor Aerial Vehicles (MRAVs) into 5G and 6G networks enhances coverage, connectivity, and congestion management. This fosters communication-aware robotics, exploring the interplay between robotics and communications, but also makes the MRAVs susceptible to malicious attacks, such as jamming. One traditional approach to counter these attacks is the use of beamforming on the MRAVs to apply physical layer security techniques. In this paper, we explore pose optimization as an alternative approach to countering jamming attacks on MRAVs. This technique is intended for omnidirectional MRAVs, which are drones capable of independently controlling both their position and orientation, as opposed to the more common underactuated MRAVs whose orientation cannot be controlled independently of their position. In this paper, we consider an omnidirectional MRAV serving as a Base Station (BS) for legitimate ground nodes, under attack by a malicious jammer. We optimize the MRAV pose (i.e., position and orientation) to maximize the minimum Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio (SINR) over all legitimate nodes.
MRS Drone: A Modular Platform for Real-World Deployment of Aerial Multi-Robot Systems
Jun 12, 2023Abstract:This paper presents a modular autonomous Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) platform called the Multi-robot Systems (MRS) Drone that can be used in a large range of indoor and outdoor applications. The MRS Drone features unique modularity with respect to changes in actuators, frames, and sensory configuration. As the name suggests, the platform is specially tailored for deployment within a MRS group. The MRS Drone contributes to the state-of-the-art of UAV platforms by allowing smooth real-world deployment of multiple aerial robots, as well as by outperforming other platforms with its modularity. For real-world multi-robot deployment in various applications, the platform is easy to both assemble and modify. Moreover, it is accompanied by a realistic simulator to enable safe pre-flight testing and a smooth transition to complex real-world experiments. In this manuscript, we present mechanical and electrical designs, software architecture, and technical specifications to build a fully autonomous multi UAV system. Finally, we demonstrate the full capabilities and the unique modularity of the MRS Drone in various real-world applications that required a diverse range of platform configurations.
Communications-Aware Robotics: Challenges and Opportunities
Apr 13, 2023Abstract:The use of Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) has seen significant growth in the research community, industry, and society. Many of these agents are equipped with communication systems that are essential for completing certain tasks successfully. This has led to the emergence of a new interdisciplinary field at the intersection of robotics and communications, which has been further driven by the integration of UAVs into 5G and 6G communication networks. However, one of the main challenges in this research area is how many researchers tend to oversimplify either the robotics or the communications aspects, hindering the full potential of this new interdisciplinary field. In this paper, we present some of the necessary modeling tools for addressing these problems from both a robotics and communications perspective, using the UAV communications relay as an example.
Distributed formation-enforcing control for UAVs robust to observation noise in relative pose measurements
Apr 06, 2023



Abstract:A technique that allows a formation-enforcing control (FEC) derived from graph rigidity theory to interface with a realistic relative localization system is proposed in this paper. Recent research in sensor-based multi-robot control has given rise to multiple modalities of mutual relative localization systems. In particular, vision-based relative localization has reached the stage where it can be carried onboard lightweight UAVs in order to retrieve the relative positions and relative orientations of cooperating units. A separate stream of development spawned distributed formation-enforcing control which can lead individual robots into a desired formation using relative localization of their neighbors. These two fields naturally complement each other by achieving real-world flights of UAVs in formation without the need for absolute localization in the world. However, real relative localization systems are, without exception, burdened by non-negligible sensory noise, which is typically not fully taken into account in formation-enforcing control algorithms. Such noise can lead to rapid changes in velocity, which further interferes with visual localization. Our approach provides a solution to these challenges, enabling practical deployment of FEC under realistic conditions, as we demonstrated in real-world experiments.
PACNav: A collective navigation approach for UAV swarms deprived of communication and external localization
Feb 09, 2023Abstract:This article proposes Persistence Administered Collective Navigation (PACNav) as an approach for achieving decentralized collective navigation of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) swarms. The technique is based on the flocking and collective navigation behavior observed in natural swarms, such as cattle herds, bird flocks, and even large groups of humans. As global and concurrent information of all swarm members is not available in natural swarms, these systems use local observations to achieve the desired behavior. Similarly, PACNav relies only on local observations of relative positions of UAVs, making it suitable for large swarms deprived of communication capabilities and external localization systems. We introduce the novel concepts of path persistence and path similarity that allow each swarm member to analyze the motion of other members in order to determine its own future motion. PACNav is based on two main principles: (1) UAVs with little variation in motion direction have high path persistence, and are considered by other UAVs to be reliable leaders; (2) groups of UAVs that move in a similar direction have high path similarity, and such groups are assumed to contain a reliable leader. The proposed approach also embeds a reactive collision avoidance mechanism to avoid collisions with swarm members and environmental obstacles. This collision avoidance ensures safety while reducing deviations from the assigned path. Along with several simulated experiments, we present a real-world experiment in a natural forest, showcasing the validity and effectiveness of the proposed collective navigation approach in challenging environments. The source code is released as open-source, making it possible to replicate the obtained results and facilitate the continuation of research by the community.
* 17 pages, 16 figures, journal paper
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge