Dandan Tang
Reflections from the 2024 Large Language Model (LLM) Hackathon for Applications in Materials Science and Chemistry
Nov 20, 2024
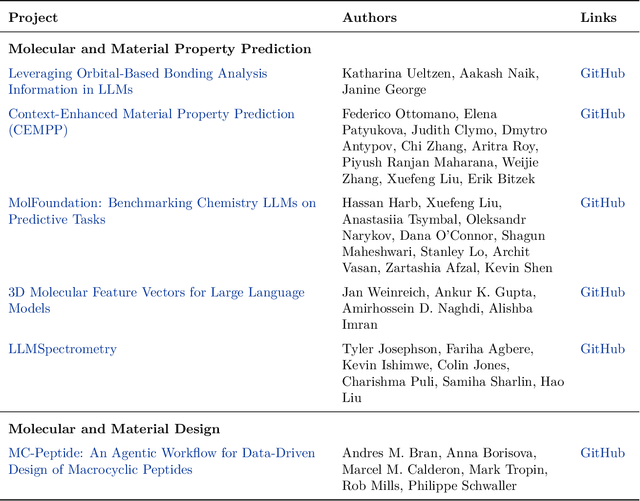
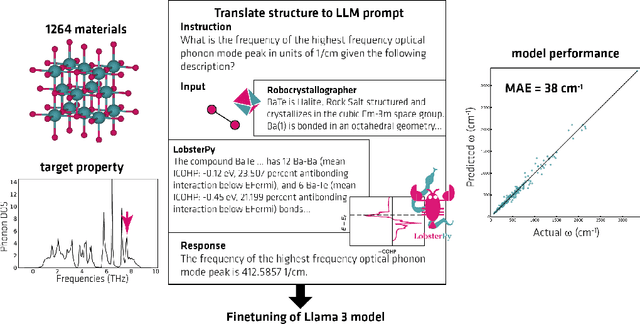
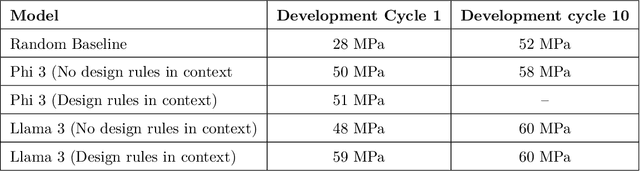
Abstract:Here, we present the outcomes from the second Large Language Model (LLM) Hackathon for Applications in Materials Science and Chemistry, which engaged participants across global hybrid locations, resulting in 34 team submissions. The submissions spanned seven key application areas and demonstrated the diverse utility of LLMs for applications in (1) molecular and material property prediction; (2) molecular and material design; (3) automation and novel interfaces; (4) scientific communication and education; (5) research data management and automation; (6) hypothesis generation and evaluation; and (7) knowledge extraction and reasoning from scientific literature. Each team submission is presented in a summary table with links to the code and as brief papers in the appendix. Beyond team results, we discuss the hackathon event and its hybrid format, which included physical hubs in Toronto, Montreal, San Francisco, Berlin, Lausanne, and Tokyo, alongside a global online hub to enable local and virtual collaboration. Overall, the event highlighted significant improvements in LLM capabilities since the previous year's hackathon, suggesting continued expansion of LLMs for applications in materials science and chemistry research. These outcomes demonstrate the dual utility of LLMs as both multipurpose models for diverse machine learning tasks and platforms for rapid prototyping custom applications in scientific research.
MIPD: A Multi-sensory Interactive Perception Dataset for Embodied Intelligent Driving
Nov 08, 2024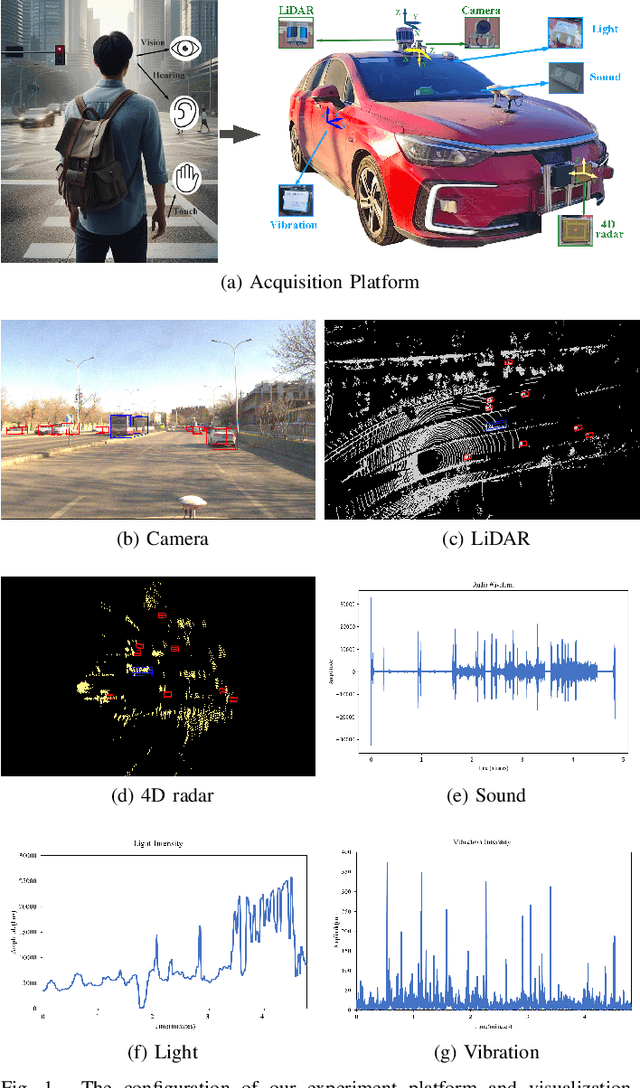
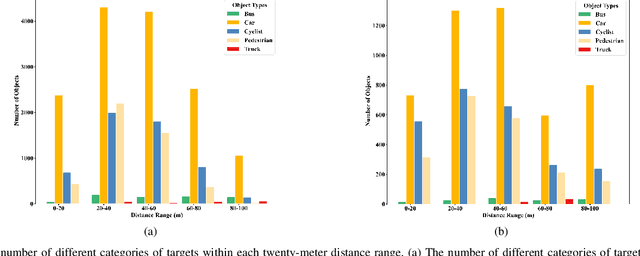
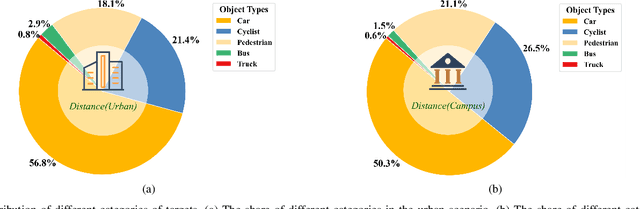
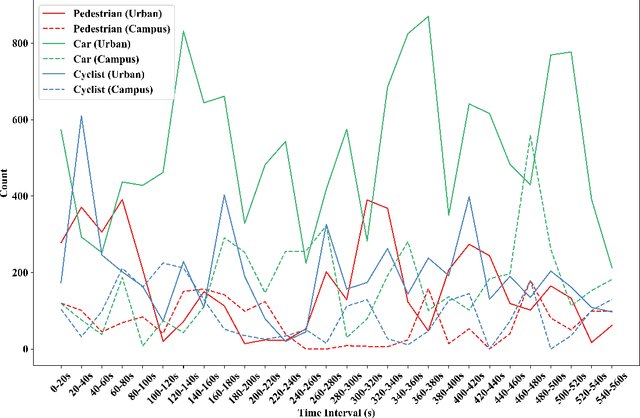
Abstract:During the process of driving, humans usually rely on multiple senses to gather information and make decisions. Analogously, in order to achieve embodied intelligence in autonomous driving, it is essential to integrate multidimensional sensory information in order to facilitate interaction with the environment. However, the current multi-modal fusion sensing schemes often neglect these additional sensory inputs, hindering the realization of fully autonomous driving. This paper considers multi-sensory information and proposes a multi-modal interactive perception dataset named MIPD, enabling expanding the current autonomous driving algorithm framework, for supporting the research on embodied intelligent driving. In addition to the conventional camera, lidar, and 4D radar data, our dataset incorporates multiple sensor inputs including sound, light intensity, vibration intensity and vehicle speed to enrich the dataset comprehensiveness. Comprising 126 consecutive sequences, many exceeding twenty seconds, MIPD features over 8,500 meticulously synchronized and annotated frames. Moreover, it encompasses many challenging scenarios, covering various road and lighting conditions. The dataset has undergone thorough experimental validation, producing valuable insights for the exploration of next-generation autonomous driving frameworks.
Evaluation of Missing Data Analytical Techniques in Longitudinal Research: Traditional and Machine Learning Approaches
Jun 19, 2024Abstract:Missing Not at Random (MNAR) and nonnormal data are challenging to handle. Traditional missing data analytical techniques such as full information maximum likelihood estimation (FIML) may fail with nonnormal data as they are built on normal distribution assumptions. Two-Stage Robust Estimation (TSRE) does manage nonnormal data, but both FIML and TSRE are less explored in longitudinal studies under MNAR conditions with nonnormal distributions. Unlike traditional statistical approaches, machine learning approaches do not require distributional assumptions about the data. More importantly, they have shown promise for MNAR data; however, their application in longitudinal studies, addressing both Missing at Random (MAR) and MNAR scenarios, is also underexplored. This study utilizes Monte Carlo simulations to assess and compare the effectiveness of six analytical techniques for missing data within the growth curve modeling framework. These techniques include traditional approaches like FIML and TSRE, machine learning approaches by single imputation (K-Nearest Neighbors and missForest), and machine learning approaches by multiple imputation (micecart and miceForest). We investigate the influence of sample size, missing data rate, missing data mechanism, and data distribution on the accuracy and efficiency of model estimation. Our findings indicate that FIML is most effective for MNAR data among the tested approaches. TSRE excels in handling MAR data, while missForest is only advantageous in limited conditions with a combination of very skewed distributions, very large sample sizes (e.g., n larger than 1000), and low missing data rates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge